Deck 15: Entities Overview
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/80
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Entities Overview
1
Corporations are legally better suited for taking a business public compared with LLCs and general partnerships.
True
2
S corporation shareholders are legally responsible for paying the S corporation's debts because S corporations are treated as flow-through entities for tax purposes.
False
3
Entities taxed as partnerships can use special allocations to reward owners based on their responsibilities, contributions, and individual needs.
True
4
Sole proprietors are subject to self-employment taxes on net income from their sole proprietorships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
In certain circumstances, C corporation shareholders can elect to change the entity to a flow-through entity for tax purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Unincorporated entities with only one individual owner are taxed as sole proprietorships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Both tax and nontax objectives should be considered when choosing the entity type for a new business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Sole proprietorships are not treated as legal entities separate from their individual owners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An unincorporated entity with more than one owner is, by default, taxed as a partnership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
For tax purposes, only unincorporated entities can be considered to be disregarded entities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Limited partnerships are legally formed by filing a certificate of limited partnership with the state in which the partnership will be organized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Tax rules require that entities be classified the same way for tax purposes as they are classified for legal purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Corporations are legally formed by filing articles of organization with the state in which the corporation will be created.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
C corporations and S corporations are separate taxpaying entities that pay tax on their own income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Unincorporated entities are typically treated as flow-through entities for tax purposes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Shareholders of C corporations receiving property distributions must recognize dividend income equal to the fair market value of the distributed property if the distributing corporation has sufficient earnings and profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
S corporations have more restrictive ownership requirements than other entities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
General partnerships are legally formed by filing a partnership agreement with the state in which the partnership will be formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
LLC members have more flexibility than corporate shareholders to alter their legal arrangements with respect to one another, the entity, and with outsiders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A single-member LLC is taxed as a partnership.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If a C corporation incurs a net operating loss in 2018, it may carry the loss back two years and forward 20 years to offset income in those years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which legal entity provides the least flexible legal arrangement for owners?
A) Corporation.
B) LLC.
C) Partnership.
D) Sole Proprietorship.
A) Corporation.
B) LLC.
C) Partnership.
D) Sole Proprietorship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If a C corporation incurs a net operating loss in 2017, it may carry the loss back two years and forward 20 years to offset income in those years. However, it may offset only 80% of the taxable income before the NOL deduction in those years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Business income allocations from an S corporation to its shareholders are potentially subject to the 3.8 percent net investment income tax if the shareholders are passive investors in the S corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What document must LLCs file with the state to organize their business?
A) Articles of incorporation.
B) Certificate of LLC.
C) Articles of organization.
D) Partnership agreement.
E) None of the choices are correct. LLCs do not have to file with the state to organize their business.
A) Articles of incorporation.
B) Certificate of LLC.
C) Articles of organization.
D) Partnership agreement.
E) None of the choices are correct. LLCs do not have to file with the state to organize their business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which legal entity is correctly paired with the party that bears the ultimate responsibility for paying the legal entity's liabilities?
A) LLC - LLC members.
B) Corporation - Corporation.
C) General Partnership - Partnership.
D) Limited Partnership - General partner.
E) Corporation - Corporation and Limited Partnership - General partner.
A) LLC - LLC members.
B) Corporation - Corporation.
C) General Partnership - Partnership.
D) Limited Partnership - General partner.
E) Corporation - Corporation and Limited Partnership - General partner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which legal entity is generally best suited for going public?
A) Corporation.
B) LLC.
C) Limited Liability Partnership.
D) General Partnership.
E) All of these entities are equally suited for going public.
A) Corporation.
B) LLC.
C) Limited Liability Partnership.
D) General Partnership.
E) All of these entities are equally suited for going public.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Losses from C corporations are never available to offset a shareholder's personal income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If an individual forms a sole proprietorship, which nontax factor will be of greatest benefit to the sole proprietor?
A) Liability protection.
B) Legal flexibility in defining rights and responsibilities of owners.
C) Facilitates initial public offerings.
D) Minimal time and cost to organize.
A) Liability protection.
B) Legal flexibility in defining rights and responsibilities of owners.
C) Facilitates initial public offerings.
D) Minimal time and cost to organize.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Business income allocations to owners from an LLC that is taxed as a partnership are subject to self-employment tax if the owners are significantly involved in the entity's business activities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The deduction for qualified business income applies to owners of C corporations but not to flow-through entity owners.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An S corporation shareholder who is not a passive investor is allowed to deduct a business loss allocation from the S corporation to the extent of the shareholder's basis in the stock no matter how large the loss.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following legal entities file documents with the state to be formally recognized by the state?
A) Limited Liability Company.
B) General Partnership.
C) Sole Proprietorship (non LLC).
D) None of the choices are correct.
A) Limited Liability Company.
B) General Partnership.
C) Sole Proprietorship (non LLC).
D) None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Owners who work for entities taxed as a partnership receive guaranteed payments as compensation. The guaranteed payments are not self-employment income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Beginning in 2018, C corporations are no longer subject to double taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If a C corporation incurs a net operating loss in 2018 and carries the loss forward to 2019, the NOL carryover is not allowed to offset 100% of the corporation's taxable income (before the net operating loss deduction).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The C corporation tax rate is significantly lower than the top individual marginal tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
For tax purposes, sole proprietorships pay sole proprietors guaranteed payments as compensation for their services.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
S corporation shareholders who work for the S corporation receive compensation in the form of a guaranteed payment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
S corporation shareholders are subject to self-employment tax on business income allocations from the S corporation if they are actively involved in the S corporation's business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The deduction for qualified business income applies to income of all but which of the following tax entity types?
A) Sole proprietorship.
B) Entity taxed as a partnership.
C) S corporation.
D) C corporation.
A) Sole proprietorship.
B) Entity taxed as a partnership.
C) S corporation.
D) C corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Roberto and Reagan are both 25 percent owner/managers for Bright Light Enterprises. Roberto runs the retail store in Sacramento, CA, and Reagan runs the retail store in San Francisco, CA. Bright Light generated a $125,000 profit companywide made up of a $75,000 profit from the Sacramento store, a ($25,000) loss from the San Francisco store, and a combined $75,000 profit from the remaining stores. If Bright Light is taxed as a partnership and decides that Roberto and Reagan will be allocated 70 percent of his own store's profit with the remaining profits allocated pro rata among all the owners, how much income will be allocated to Reagan?
A) ($25,000)
B) ($17,500)
C) $5,000
D) $20,000
A) ($25,000)
B) ($17,500)
C) $5,000
D) $20,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
On which tax form does a single member LLC with one individual owner report its income and losses?
A) Form 1120.
B) Form 1120S.
C) Form 1065.
D) Form 1040, Schedule C.
A) Form 1120.
B) Form 1120S.
C) Form 1065.
D) Form 1040, Schedule C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If individual taxpayers are the shareholders of PST Corporation and PST corporation is a shareholder of MNO Corporation, how many levels of tax is MNO's pre-tax income potentially exposed to?
A) No taxation.
B) Single taxation.
C) Double taxation.
D) Triple taxation.
A) No taxation.
B) Single taxation.
C) Double taxation.
D) Triple taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Logan, a 50 percent shareholder in Military Gear Inc. (MG), is comparing the tax consequences of losses from C corporations with losses from S corporations. Assume MG has a $100,000 tax loss for the year, Logan's tax basis in his MG stock was $150,000 at the beginning of the year, and he received $75,000 ordinary income from other sources during the year. Assuming Logan's marginal tax rate is 24%, how much more tax will Logan pay currently if MG is a C corporation compared to the tax he would pay if it were an S corporation?
A) $0
B) $6,000
C) $12,000
D) $18,000
A) $0
B) $6,000
C) $12,000
D) $18,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Robert is seeking additional capital to expand ABC Inc. In order to qualify ABC as an S corporation, which type of investor group could Robert obtain capital from?
A) 30 different partnerships.
B) 10 different C corporations.
C) 90 nonresident individuals.
D) 120 unrelated resident individuals.
E) None of the choices are correct.
A) 30 different partnerships.
B) 10 different C corporations.
C) 90 nonresident individuals.
D) 120 unrelated resident individuals.
E) None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following statements is true for a C corporation incurring a net operating loss (NOL) for a tax year that begins in 2018?
A) It may carry the NOL back two years and forward 20 years.
B) It may not carry the NOL back to prior years but it may carry it forward 20 years.
C) It may not carry the NOL back to prior years but it can carry the loss forward indefinitely.
D) It may carry the loss back two years and carry the loss forward indefinitely.
E) None of the choices are correct.
A) It may carry the NOL back two years and forward 20 years.
B) It may not carry the NOL back to prior years but it may carry it forward 20 years.
C) It may not carry the NOL back to prior years but it can carry the loss forward indefinitely.
D) It may carry the loss back two years and carry the loss forward indefinitely.
E) None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Roberto and Reagan are both 25 percent owner/managers for Bright Light Inc. Roberto runs the retail store in Sacramento, CA, and Reagan runs the retail store in San Francisco, CA. Bright Light Inc. generated a $125,000 profit companywide made up of a $75,000 profit from the Sacramento store, a ($25,000) loss from the San Francisco store, and a combined $75,000 profit from the remaining stores. If Bright Light Inc. is an S corporation, how much income will be allocated to Roberto?
A) $31,250
B) $62,500
C) $75,000
D) $125,000
A) $31,250
B) $62,500
C) $75,000
D) $125,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If C corporations retain their after-tax earnings, when will their shareholders who are individuals be taxed on the retained earnings?
A) Shareholders will be taxed when they sell their shares at a gain.
B) Shareholders will be taxed in the year they elect to be taxed on undistributed retained earnings.
C) Shareholders will be taxed on undistributed retained earnings in the year the corporation files its tax return.
D) None of the choices are correct.
A) Shareholders will be taxed when they sell their shares at a gain.
B) Shareholders will be taxed in the year they elect to be taxed on undistributed retained earnings.
C) Shareholders will be taxed on undistributed retained earnings in the year the corporation files its tax return.
D) None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What kind of deduction is the deduction for qualified business income?
A) A for AGI deduction.
B) A from AGI deduction that is not an itemized deduction.
C) A from AGI deduction that is an itemized deduction.
D) None of the choices are correct.
A) A for AGI deduction.
B) A from AGI deduction that is not an itemized deduction.
C) A from AGI deduction that is an itemized deduction.
D) None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which tax classifications can potentially apply to LLCs?
A) Partnership.
B) Partnership and sole proprietorship.
C) S corporation.
D) C corporation.
E) All of the choices are correct.
A) Partnership.
B) Partnership and sole proprietorship.
C) S corporation.
D) C corporation.
E) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following entity characteristics are generally key drivers for small business owners in deciding which entity to choose?
A) Rate at which income from entity will be taxed.
B) Required accounting period.
C) Liability protection.
D) Rate at which income from entity will be taxed and required accounting period.
E) Rate at which income from entity will be taxed and liability protection.
A) Rate at which income from entity will be taxed.
B) Required accounting period.
C) Liability protection.
D) Rate at which income from entity will be taxed and required accounting period.
E) Rate at which income from entity will be taxed and liability protection.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following statements is false for a C corporation that incurred a net operating loss for a tax year ending in 2017?
A) If it carries back the NOL and/or carries it forward, it may offset up to 80% of the taxable income (before the NOL deduction) in those years.
B) It may carry the NOL forward for up to 20 years and offset up to 100% of the taxable income (before the NOL deduction) in those years.
C) It may carry the NOL back two years and offset up to 100% of the taxable income (before the NOL deduction) in those years.
D) None of these (selecting this option means you believe all of these responses are true).
A) If it carries back the NOL and/or carries it forward, it may offset up to 80% of the taxable income (before the NOL deduction) in those years.
B) It may carry the NOL forward for up to 20 years and offset up to 100% of the taxable income (before the NOL deduction) in those years.
C) It may carry the NOL back two years and offset up to 100% of the taxable income (before the NOL deduction) in those years.
D) None of these (selecting this option means you believe all of these responses are true).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What tax year-end must an unincorporated entity with only one owner adopt?
A) The entity is free to adopt any tax year-end.
B) The entity must adopt the same year-end as its owner.
C) The entity must adopt a calendar year-end.
D) The entity may adopt any year-end except for a calendar year-end.
A) The entity is free to adopt any tax year-end.
B) The entity must adopt the same year-end as its owner.
C) The entity must adopt a calendar year-end.
D) The entity may adopt any year-end except for a calendar year-end.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Generally, which of the following flow-through entities can elect to be treated as a C corporation?
A) Limited partnership.
B) Limited Liability Company.
C) General partnership.
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) Limited partnership.
B) Limited Liability Company.
C) General partnership.
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
On which tax form do LLCs with more than one owner generally report their income and losses?
A) Form 1120.
B) Form 1120S.
C) Form 1065.
D) Form 1040, Schedule C.
A) Form 1120.
B) Form 1120S.
C) Form 1065.
D) Form 1040, Schedule C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Which of the following legal entities are generally classified as C corporations for tax purposes?
A) Limited liability companies.
B) S corporations.
C) Limited partnerships.
D) Sole proprietorships.
E) None of the choices are correct.
A) Limited liability companies.
B) S corporations.
C) Limited partnerships.
D) Sole proprietorships.
E) None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
On which form is income from a single member LLC with one corporate (C corporation) owner reported?
A) Form 1120 used by C corporations to report their income.
B) Form 1120S used by S corporations to report their income.
C) Form 1065 used by partnerships to report their income.
D) Form 1040, Schedule C used by sole proprietorships to report their income.
E) None of the choices are correct.
A) Form 1120 used by C corporations to report their income.
B) Form 1120S used by S corporations to report their income.
C) Form 1065 used by partnerships to report their income.
D) Form 1040, Schedule C used by sole proprietorships to report their income.
E) None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Crocker and Company (CC) is a C corporation. For the year, CC reported taxable income of $550,000. At the end of the year, CC distributed all its after-tax earnings to Jimmy, the company's sole shareholder. Jimmy's marginal ordinary tax rate is 37 percent and his marginal tax rate on dividends is 23.8 percent, including the net investment income tax. What is the overall tax rate on Crocker and Company's pre-tax income?
A) 18.8%
B) 23.8%
C) 21%
D) 39.8%
E) 44.8%
A) 18.8%
B) 23.8%
C) 21%
D) 39.8%
E) 44.8%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When an employee/shareholder receives a business income allocation from an S corporation, what taxes apply to the business income allocation?
A) FICA tax only.
B) Self-employment tax only.
C) FICA and self-employment tax.
D) Regular income tax.
E) None of the choices are correct.
A) FICA tax only.
B) Self-employment tax only.
C) FICA and self-employment tax.
D) Regular income tax.
E) None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Assume you plan to start a new enterprise; you know the probability of having losses for the first three years of operations is almost 90 percent, and you know you will report a substantial amount of income from other sources during those same three years. From a tax perspective, which of the following entity choices would not allow you to offset the entity losses against your income from other sources?
A) C corporation.
B) LLC.
C) General partnership.
D) S corporation.
A) C corporation.
B) LLC.
C) General partnership.
D) S corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
From a tax perspective, which entity choice is preferred when a liquidating distribution occurs and the entity has appreciated assets?
A) Partnership.
B) S corporation.
C) C corporation.
D) S corporation and C corporation.
A) Partnership.
B) S corporation.
C) C corporation.
D) S corporation and C corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In its first year of existence, BYC Corporation (a C corporation) reported a loss for tax purposes of ($40,000). How much tax will BYC pay in year 2 if it reports taxable income from operations of $35,000 in year 2 before any loss carryovers?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the tax impact to a C corporation or an S corporation when it makes a (noncash) property distribution to a shareholder?
A) Recognizes either gain or loss.
B) Does not recognize gain or loss.
C) Recognizes gain but not loss.
D) Recognizes loss only.
A) Recognizes either gain or loss.
B) Does not recognize gain or loss.
C) Recognizes gain but not loss.
D) Recognizes loss only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The excess loss limitations apply to owners of all of the following entities except which of the following?
A) C corporations.
B) S corporations.
C) Entities taxed as partnerships.
D) Single member LLCs (owned by an individual taxpayer).
A) C corporations.
B) S corporations.
C) Entities taxed as partnerships.
D) Single member LLCs (owned by an individual taxpayer).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In its first year of existence (2018) Aspen Corp. (a C corporation) reported a loss for tax purposes of $60,000. In 2019, it reports a $40,000 loss. For 2020, it reports taxable income from operations of $120,000. How much tax will Aspen Corp. pay for year 3?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following statements is true for entity owners who pay the self-employment tax and the additional Medicare tax?
A) Both the self-employment tax and the additional Medicare tax are deductible for AGI in full.
B) Half of the self-employment tax and all of the additional Medicare tax are deductible for AGI.
C) Half of the self-employment tax and none of the additional Medicare tax are deductible for AGI.
D) None of the self-employment tax and none of the additional Medicare tax are deductible for AGI.
A) Both the self-employment tax and the additional Medicare tax are deductible for AGI in full.
B) Half of the self-employment tax and all of the additional Medicare tax are deductible for AGI.
C) Half of the self-employment tax and none of the additional Medicare tax are deductible for AGI.
D) None of the self-employment tax and none of the additional Medicare tax are deductible for AGI.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
P corporation owns 60 percent of the stock of S corporation. If S corporation distributes a dividend to P corporation, what is tax rate on the dividend after the dividends received deduction (DRD) if P is entitled to a 65 percent DRD?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
David would like to organize HOS (a business entity) as either an S corporation or as a corporation (taxed as a C corporation) generating a 12 percent annual before-tax return on a $300,000 investment. David's marginal tax rate is 24 percent and the corporate tax rate is 21 percent. David's marginal tax rate on individual capital gains and dividends is 15 percent. HOS will pay out its after-tax earnings every year to either its members or its shareholders. If HOS is taxed as an S corporation, David's business income allocation would be subject to a 3.8 percent net investment income tax (he is a passive investor in the business) and the business income allocation would qualify for the deduction for qualified business income.
a. How much would David keep after taxes if HOS is organized as either an S corporation or a C corporation?
b. What are the overall tax rates (combined owner and entity level) if HOS is organized as either an S corporation or a C corporation?
a. How much would David keep after taxes if HOS is organized as either an S corporation or a C corporation?
b. What are the overall tax rates (combined owner and entity level) if HOS is organized as either an S corporation or a C corporation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Stacy would like to have SST (a business entity) organized as either an LLC (taxed as a partnership) or as a corporation (taxed as a C corporation) generating a 10 percent annual before-tax return on a $600,000 investment. Stacy's marginal tax rate on ordinary income is 37 percent. Stacy's marginal tax rate on individual capital gains and dividends is 23.8 percent, including the net investment income tax. SST will pay out its after-tax earnings every year to either its members or its shareholders. If SST is taxed as a partnership, Stacy would be subject to a 2.9 percent self-employment tax rate and a .9 percent additional Medicare tax. Assume that SST's income is not qualified business income for purposes of the qualified business income deduction. How much would Stacy have after taxes if SST is organized as either an LLC or a C corporation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Rodger owns 100% of the shares in Trevor Inc., a C corporation. Assume the following for the current year:
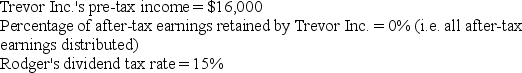 Given these assumptions, how much cash does Rodger have from the dividend after all taxes have been paid?
Given these assumptions, how much cash does Rodger have from the dividend after all taxes have been paid?
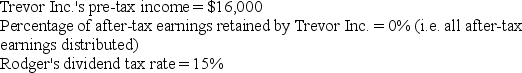 Given these assumptions, how much cash does Rodger have from the dividend after all taxes have been paid?
Given these assumptions, how much cash does Rodger have from the dividend after all taxes have been paid?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Corporation A owns 10% of Corporation C. The marginal tax rate on non-dividend income for both A and C is 21%. Corporation C earns a total of $200 million before taxes in the current year, pays corporate tax on this income and distributes the remainder proportionately to its shareholders as a dividend. In addition, Corporation A owns 40% of partnership P that earns $500 million in the current year. Given this fact pattern, answer the following questions:
a. How much cash from the Corporation C dividend remains after Corporation A pays the tax on the dividend assuming Corporation A is eligible for the 50 percent dividends received deduction?
b. If Partnership P distributes all of its current year earnings in proportion to the partner's ownership percentages, how much cash from Partnership P does Corporation A have after paying taxes on its share of income from the partnership?
c. If you were to replace Corporation A with individual A [her marginal tax rate on ordinary income is 37% and on qualified dividends is 23.8 percent (including the net investment income tax)] in the original fact pattern above, how much cash does individual A have from the Corporation C dividend after all taxes assuming the dividends are qualified dividends? Consistent with the original facts, assume that Corporation C distributes all of its after-tax income to its shareholders.
a. How much cash from the Corporation C dividend remains after Corporation A pays the tax on the dividend assuming Corporation A is eligible for the 50 percent dividends received deduction?
b. If Partnership P distributes all of its current year earnings in proportion to the partner's ownership percentages, how much cash from Partnership P does Corporation A have after paying taxes on its share of income from the partnership?
c. If you were to replace Corporation A with individual A [her marginal tax rate on ordinary income is 37% and on qualified dividends is 23.8 percent (including the net investment income tax)] in the original fact pattern above, how much cash does individual A have from the Corporation C dividend after all taxes assuming the dividends are qualified dividends? Consistent with the original facts, assume that Corporation C distributes all of its after-tax income to its shareholders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If you were seeking an entity with the most favorable tax treatment regarding (1) the number of owners allowed, (2) the flexibility to select your accounting period, and (3) the availability of preferential capital gains rates when selling your ownership interest, which entity should you decide to use?
A) C corporation.
B) S corporation.
C) Partnership.
D) Sole proprietorship.
A) C corporation.
B) S corporation.
C) Partnership.
D) Sole proprietorship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Jorge is a 60 percent owner of JJ LLC (taxed as a partnership). He is a passive investor in JJ (he doesn't perform any work for JJ) and his marginal ordinary tax rate is 37 percent. Which of the following statements is true regarding Jorge's tax treatment of business income allocated to him from JJ?
A) Business income allocations are not subject to self-employment tax.
B) Business income allocations are not subject to the net investment income tax.
C) Business income allocations are subject to the additional Medicare tax.
D) Business income allocations are taxed at a maximum 23.8 percent tax rate.
A) Business income allocations are not subject to self-employment tax.
B) Business income allocations are not subject to the net investment income tax.
C) Business income allocations are subject to the additional Medicare tax.
D) Business income allocations are taxed at a maximum 23.8 percent tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following statements is true regarding compensation paid to an owner of an entity taxed as a partnership who works for the entity?
A) The compensation is deductible by the entity.
B) The compensation is self-employment income to the owner-worker.
C) The entity is not required to withhold FICA tax on the compensation it pays to the owner.
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) The compensation is deductible by the entity.
B) The compensation is self-employment income to the owner-worker.
C) The entity is not required to withhold FICA tax on the compensation it pays to the owner.
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Owners of which of the following entity types could potentially increase their after-tax cash flow from the entity by reducing the compensation they receive in order to increase the amount of business income that flows-through to them from the entity?
A) Sole-proprietorship.
B) Entity taxed as a partnership.
C) S corporation.
D) "Entity taxed as a partnership" and "S corporation".
A) Sole-proprietorship.
B) Entity taxed as a partnership.
C) S corporation.
D) "Entity taxed as a partnership" and "S corporation".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
From a tax perspective, which entity choice is preferred when a liquidating distribution occurs and the entity has assets that have declined in value?
A) Partnership.
B) S corporation.
C) LLC.
D) Partnership and S corporation.
E) S corporation and LLC.
A) Partnership.
B) S corporation.
C) LLC.
D) Partnership and S corporation.
E) S corporation and LLC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Jorge is a 100 percent owner of JJ LLC (taxed as an S Corporation). He works full-time for JJ and his marginal ordinary tax rate is 37 percent. Which of the following statements is true regarding Jorge's tax treatment of business income allocated to him from JJ?
A) Business income allocations are subject to self-employment tax.
B) Business income allocations are not subject to the net investment income tax.
C) Business income allocations are subject to the additional Medicare tax.
D) Business income allocations are taxed at a maximum 23.8 percent tax rate.
A) Business income allocations are subject to self-employment tax.
B) Business income allocations are not subject to the net investment income tax.
C) Business income allocations are subject to the additional Medicare tax.
D) Business income allocations are taxed at a maximum 23.8 percent tax rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the maximum number of unrelated shareholders a C corporation can have, the maximum number of unrelated shareholders an S corporation can have, and the maximum number of partners a partnership may have respectively?
A) 100; no limit; no limit
B) no limit; 100; 2
C) no limit; 100; no limit
D) 100; 100; no limit
A) 100; no limit; no limit
B) no limit; 100; 2
C) no limit; 100; no limit
D) 100; 100; no limit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
For which type of entity does the entity not pay compensation to an owner who is working for the entity?
A) S corporation.
B) C corporation.
C) Entity taxed as a partnership.
D) None of the choices are correct.
A) S corporation.
B) C corporation.
C) Entity taxed as a partnership.
D) None of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 80 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



