Deck 21: Caring for the Patient With an Acute Brain or Cranial Nerve Disorder
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 21: Caring for the Patient With an Acute Brain or Cranial Nerve Disorder
1
A patient with increased intracranial pressure ICP) is being repositioned. The nurse would incorporate which actions into this intervention? Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
A) Inform the patient regarding what is going to occur during the intervention.
B) Reposition the patient every 1 to 2 hours.
C) Accompany each repositioning with passive range-of-motion exercises.
D) Elevate the head of the bed to 30 degrees.
E) Manage the repositioning with slow, smooth, and gentle movements.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
A) Inform the patient regarding what is going to occur during the intervention.
B) Reposition the patient every 1 to 2 hours.
C) Accompany each repositioning with passive range-of-motion exercises.
D) Elevate the head of the bed to 30 degrees.
E) Manage the repositioning with slow, smooth, and gentle movements.
Inform the patient regarding what is going to occur during the intervention.
Elevate the head of the bed to 30 degrees.
Manage the repositioning with slow, smooth, and gentle movements.
Elevate the head of the bed to 30 degrees.
Manage the repositioning with slow, smooth, and gentle movements.
2
Which neurologic assessment is being performed in the exhibit? 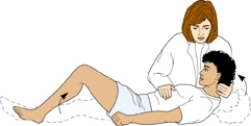
A) Kernig's sign
B) Babinski reflex
C) Brudzinski sign
D) Decorticate posturing

A) Kernig's sign
B) Babinski reflex
C) Brudzinski sign
D) Decorticate posturing
Brudzinski sign
3
A patient is in the emergency department following a head injury. The nurse would assess for which sign indicating early increased intracranial pressure?
A) Decreasing level of consciousness
B) Elevated diastolic blood pressure
C) Decreasing respiratory rate
D) Tachycardia
A) Decreasing level of consciousness
B) Elevated diastolic blood pressure
C) Decreasing respiratory rate
D) Tachycardia
Decreasing level of consciousness
4
Which nursing diagnosis is most applicable to a patient with new-onset seizures?
A) Anxiety
B) Self-Care Deficit
C) Activity Intolerance
D) Impaired Mobility
A) Anxiety
B) Self-Care Deficit
C) Activity Intolerance
D) Impaired Mobility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A patient comes to the clinic complaining of repetitive episodes of sudden severe pain on the right side of the face. The nurse anticipates additional testing for which disorder?
A) Trigeminal neuralgia
B) Parkinson's disease
C) Bell's palsy
D) Myasthenia gravis
A) Trigeminal neuralgia
B) Parkinson's disease
C) Bell's palsy
D) Myasthenia gravis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Decerebrate posturing is present in an unconscious patient following a motor vehicle accident. The nurse expects to see which position?
A) The arms and legs are hyperextended, and arms are hyperpronated.
B) The arms are folded over the chest and spasms are rhythmic.
C) The arms are pulled inward and the head is turned to the side.
D) The arms and legs have tonic-clonic seizure activity.
A) The arms and legs are hyperextended, and arms are hyperpronated.
B) The arms are folded over the chest and spasms are rhythmic.
C) The arms are pulled inward and the head is turned to the side.
D) The arms and legs have tonic-clonic seizure activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The nurse is caring for a patient with an intracranial pressure monitoring device. What is the priority nursing diagnosis NDX) for this patient?
A) Risk for Infection
B) Ineffective Thermoregulation
C) Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity
D) Impaired Physical Mobility
A) Risk for Infection
B) Ineffective Thermoregulation
C) Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity
D) Impaired Physical Mobility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The patient was an unrestrained front-seat passenger in a motor vehicle crash and struck his forehead on the inside of the windshield. Diagnostic testing in the emergency department reveals coup-contrecoup injury. The nurse identifies which area as the contrecoup injury?
A) The frontal area of the brain
B) The posterior or occipital part of the brain
C) Both the anterior and posterior areas of the brain
D) The midpoint of the brainstem
A) The frontal area of the brain
B) The posterior or occipital part of the brain
C) Both the anterior and posterior areas of the brain
D) The midpoint of the brainstem

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The patient was riding in a car that hit a tree. The head hit the windshield, and then the brain rebounded within the skull toward the opposite side. This injury represents which mechanism of injury?
A) An acceleration-deceleration injury
B) A penetrating head injury
C) An acceleration injury
D) A deceleration injury
A) An acceleration-deceleration injury
B) A penetrating head injury
C) An acceleration injury
D) A deceleration injury

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A patient is having a seizure that involves a blank stare, unresponsiveness to questions, and smacking of the lips. The seizure lasts less than a minute. How would the nurse categorize this seizure?
A) Absence seizure
B) Partial seizure
C) Tonic-clonic seizure
D) Status epilepticus seizure
A) Absence seizure
B) Partial seizure
C) Tonic-clonic seizure
D) Status epilepticus seizure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Following a fall, a patient is brought to the emergency department. There was a brief loss of consciousness; the patient complains of headache, has vomited twice, has a dilated pupil on the same side as a hematoma over the temporal area, and is currently having a seizure. The nurse prepares to care for this patient based on which evaluation of this assessment?
A) This is an emergency situation likely involving an epidural hematoma and requires surgery.
B) This is a controlled situation once the seizure stops.
C) This is a serious situation in which a subdural hematoma is developing and requires surgery.
D) This is a typical situation seen with most patients who fall, and symptoms will subside with observation.
A) This is an emergency situation likely involving an epidural hematoma and requires surgery.
B) This is a controlled situation once the seizure stops.
C) This is a serious situation in which a subdural hematoma is developing and requires surgery.
D) This is a typical situation seen with most patients who fall, and symptoms will subside with observation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The nurse anticipates that which medication will be ordered to halt status epilepticus in a patient?
A) Lorazepam Ativan) IV
B) Oral glucose
C) Phenytoin Dilantin) orally
D) Gabapentin Neurontin) and lamotrigine Lamictal)
A) Lorazepam Ativan) IV
B) Oral glucose
C) Phenytoin Dilantin) orally
D) Gabapentin Neurontin) and lamotrigine Lamictal)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A 25-year-old female is diagnosed with tic douloureux. How should the nurse describe this disorder to the patient? Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
A) "This condition is also called Bell's palsy."
B) "You are the typical age for onset of this condition."
C) "More women than men have this condition."
D) "More testing will be necessary."
E) "The treatment for this condition is to allow it to run its course, which is typically 5 to 7 days."
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
A) "This condition is also called Bell's palsy."
B) "You are the typical age for onset of this condition."
C) "More women than men have this condition."
D) "More testing will be necessary."
E) "The treatment for this condition is to allow it to run its course, which is typically 5 to 7 days."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The patient sustains a subdural hematoma after falling. How would the nurse explain this injury to the patient's family?
A) "Bleeding has occurred between the skull and the covering of the brain."
B) "Bleeding has occurred in the center of the brain."
C) "Bleeding has occurred between the layers of the scalp."
D) "Bleeding is occurring between the brain and its covering."
A) "Bleeding has occurred between the skull and the covering of the brain."
B) "Bleeding has occurred in the center of the brain."
C) "Bleeding has occurred between the layers of the scalp."
D) "Bleeding is occurring between the brain and its covering."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The patient is supine and the head is flexed to the chest without pain, resistance, or flexion of the hips or knees. The nurse is observing for which finding?
A) Doll's eyes reflex
B) Brudzinski sign
C) Babinski reflex
D) Kernig's sign
A) Doll's eyes reflex
B) Brudzinski sign
C) Babinski reflex
D) Kernig's sign

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The nurse is assessing the patient using the technique shown. What is considered a normal finding using this technique? 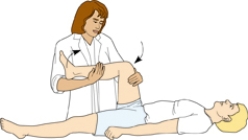
A) Pain only at the hip during flexion
B) Resistance in the hip joint
C) A clicking sound in the knee upon flexion
D) No pain or resistance in either joint

A) Pain only at the hip during flexion
B) Resistance in the hip joint
C) A clicking sound in the knee upon flexion
D) No pain or resistance in either joint

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A patient without a history of previous seizures experiences two tonic-clonic seizures in succession while the nurse is in the patient's room. List in priority order the actions the nurse should take. Standard Text: Click and drag the options below to move them up or down.
Choice
A) Turn the patient on his or her side. Choice
B) Protect the patient from environmental harm. Choice
C) Start oxygen via face mask. Choice
D) Reorient the patient to time, person, and place.
Choice
A) Turn the patient on his or her side. Choice
B) Protect the patient from environmental harm. Choice
C) Start oxygen via face mask. Choice
D) Reorient the patient to time, person, and place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A patient has experienced a subarachnoid hemorrhage and is at risk for increased intracranial pressure ICP) due to the initiation of the vasodilatory cascade. The nurse plans care for this patient to avoid which primary initiating factor?
A) Vasoconstriction of cerebral vessels
B) Cerebral tissue ischemia
C) Decreased cerebral perfusion pressure
D) Cerebral edema
A) Vasoconstriction of cerebral vessels
B) Cerebral tissue ischemia
C) Decreased cerebral perfusion pressure
D) Cerebral edema

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A patient has just been diagnosed with trigeminal neuralgia. What would the nurse teach this patient about treatment for this disorder?
A) Drugs used to treat seizure disorders are generally effective.
B) Drug therapy will begin with a trial of antiviral drugs.
C) The primary treatment focus will be on supporting respiratory function until the condition resolves.
D) Gargling with hot salt water will help reduce pain and keep tissues moistened.
A) Drugs used to treat seizure disorders are generally effective.
B) Drug therapy will begin with a trial of antiviral drugs.
C) The primary treatment focus will be on supporting respiratory function until the condition resolves.
D) Gargling with hot salt water will help reduce pain and keep tissues moistened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Reviewing a patient's report of laboratory test results see accompanying box), the nurse realizes that which values are critical for the patient with a decreased level of consciousness? 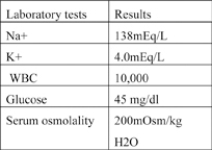
A) Glucose and serum osmolality
B) Sodium and potassium levels
C) Sodium and white blood cell count
D) Glucose and white blood cell count

A) Glucose and serum osmolality
B) Sodium and potassium levels
C) Sodium and white blood cell count
D) Glucose and white blood cell count

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A patient has been diagnosed with a pituitary adenoma. Which assessment finding supports that it is a nonfunctioning form?
A) 20/60 vision using a Snellen chart
B) A round, moon-shaped face
C) A protruding lower jaw
D) Report of insomnia
A) 20/60 vision using a Snellen chart
B) A round, moon-shaped face
C) A protruding lower jaw
D) Report of insomnia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A patient has developed severe postsurgical muscle weakness in the lower extremities after the removal of a brain tumor. The nurse takes which initial intervention to minimize the patient's risk of developing a deep vein thrombosis DVT)?
A) Ask the patient questions to determine if there is a history of DVT.
B) Add regular leg massages to the patient's care plan.
C) Instruct the patient to perform leg exercises at least twice daily.
D) Apply well-fitted antiembolism hose.
A) Ask the patient questions to determine if there is a history of DVT.
B) Add regular leg massages to the patient's care plan.
C) Instruct the patient to perform leg exercises at least twice daily.
D) Apply well-fitted antiembolism hose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A patient at risk for increased intracranial pressure ICP) is likely to experience involuntary compensatory mechanisms. The nurse would monitor this patient for signs of which involuntary compensation? Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
A) Vasoconstriction of cardiac vessels
B) Vasodilation of the cerebral vessels
C) Decreased production of cerebral spinal fluid CSF)
D) Decreased metabolic energy needs
E) Increased absorption of cerebral spinal fluid CSF)
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
A) Vasoconstriction of cardiac vessels
B) Vasodilation of the cerebral vessels
C) Decreased production of cerebral spinal fluid CSF)
D) Decreased metabolic energy needs
E) Increased absorption of cerebral spinal fluid CSF)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A patient is recovering from a lumbar puncture, and the nurse is concerned that the patient may contract bacterial meningitis. The nurse should be alert for which common early symptoms? Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
A) Fever
B) Seizures
C) Rhinorrhea
D) Headache
E) Confusion
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
A) Fever
B) Seizures
C) Rhinorrhea
D) Headache
E) Confusion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A patient is being admitted for possible early-stage viral meningitis. The nurse would assess for which significant findings to help confirm the diagnosis?
A) A history of flulike symptoms resolving 5 days ago
B) Sluggish pupils bilaterally
C) Blood pressure of 100/62
D) A cervical lymph node palpable on physical examination
A) A history of flulike symptoms resolving 5 days ago
B) Sluggish pupils bilaterally
C) Blood pressure of 100/62
D) A cervical lymph node palpable on physical examination

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A patient has had a surgical resection of an acoustic neuroma. The nurse would prioritize which postoperative assessment?
A) Timing how long it takes for tinnitus to return
B) Measuring urine output hourly
C) Determining the degree of hearing loss
D) Identifying damage to cranial nerves VII, IX, X, and XII
A) Timing how long it takes for tinnitus to return
B) Measuring urine output hourly
C) Determining the degree of hearing loss
D) Identifying damage to cranial nerves VII, IX, X, and XII

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A nurse is providing care to a patient with increased intracranial pressure following a closed head injury. The nurse would determine that adequate cerebral perfusion pressure exists if the CPP is at least ____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A patient diagnosed with a brain tumor is reluctant to agree to a surgical excision of the lesion. How can the nurse best address the patient's concerns?
A) Notifying the neurosurgeon of the patient's concerns
B) Assuring the patient that the procedure is necessary
C) Providing detailed written information on the benefits of the proposed procedure
D) Asking the patient to be more specific about the concerns
A) Notifying the neurosurgeon of the patient's concerns
B) Assuring the patient that the procedure is necessary
C) Providing detailed written information on the benefits of the proposed procedure
D) Asking the patient to be more specific about the concerns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A 2-year-old child fell and sustained a scalp laceration that will require suturing. The parents ask the nurse, "How serious an injury is this?" How should the nurse respond?
A) "There is a lot of bleeding, but it is really a rather superficial injury."
B) "From the description of the fall it doesn't appear serious, but the X-ray will tell us for sure."
C) "He'll need a few stitches and a tetanus injection, but that should do it."
D) "Children this age are really resilient, but you never know until the X-rays are read."
A) "There is a lot of bleeding, but it is really a rather superficial injury."
B) "From the description of the fall it doesn't appear serious, but the X-ray will tell us for sure."
C) "He'll need a few stitches and a tetanus injection, but that should do it."
D) "Children this age are really resilient, but you never know until the X-rays are read."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The nurse is planning a community education session regarding prevention of traumatic brain injury TBI). The nurse would discuss which risk factors? Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
A) Age over 65
B) Male gender
C) Age under 18
D) High alcohol intake
E) Serving in the military
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
A) Age over 65
B) Male gender
C) Age under 18
D) High alcohol intake
E) Serving in the military

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A patient with a right temporal lobe hematoma is displaying Cheyne-Stokes respirations. How should this nurse interpret this assessment finding?
A) The next sign will likely be sluggish pupil reaction ipsilaterally.
B) This type of brain pathophysiology is usually self-limiting.
C) This patient requires surgical decompression of the brain.
D) There is no medical treatment appropriate for this symptomology.
A) The next sign will likely be sluggish pupil reaction ipsilaterally.
B) This type of brain pathophysiology is usually self-limiting.
C) This patient requires surgical decompression of the brain.
D) There is no medical treatment appropriate for this symptomology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A patient has been diagnosed with a grade 1 astrocytoma, an intra-axial brain tumor. The patient asks, "What are my chances of surviving this thing?" The nurse's response is based on which information?
A) A grade 1 astrocytoma is a very aggressive form of this type of tumor.
B) It depends on whether the tumor metastasizes outside the brain.
C) Age is the greatest predictor of patient survival.
D) This type of tumor has a survival rate of 10 years.
A) A grade 1 astrocytoma is a very aggressive form of this type of tumor.
B) It depends on whether the tumor metastasizes outside the brain.
C) Age is the greatest predictor of patient survival.
D) This type of tumor has a survival rate of 10 years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A patient diagnosed with a benign brain tumor is scheduled for gamma knife surgery. How would the nurse explain this procedure?
A) "A radioactive seed or capsule will be implanted into the tumor."
B) "A robotic arm device will deliver multiple beams of radiation to the tumor."
C) "This is the traditional method of delivering radiation to a tumor."
D) "The gamma knife is a method of delivering a focused dose of radiation at your tumor."
A) "A radioactive seed or capsule will be implanted into the tumor."
B) "A robotic arm device will deliver multiple beams of radiation to the tumor."
C) "This is the traditional method of delivering radiation to a tumor."
D) "The gamma knife is a method of delivering a focused dose of radiation at your tumor."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which observations by the nurse are representative of the symptomology of an epidural hematoma EDH)? Note: Credit will be given only if all correct choices and no incorrect choices are selected.
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
A) History of unconsciousness immediately after trauma
B) Muscle weakness on the side opposite the head injury
C) Rapid deterioration in level of consciousness
D) Period of lucidity prior to onset of symptoms
E) Dilated pupil on the same side as the injury
Standard Text: Select all that apply.
A) History of unconsciousness immediately after trauma
B) Muscle weakness on the side opposite the head injury
C) Rapid deterioration in level of consciousness
D) Period of lucidity prior to onset of symptoms
E) Dilated pupil on the same side as the injury

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A patient is being tested for bacterial meningitis. Which finding would the nurse evaluate as supporting that diagnosis?
A) The CSF is negative for glucose.
B) CSF is high in sodium.
C) The CSF is turbid in appearance.
D) The potassium level in the CSF is low.
A) The CSF is negative for glucose.
B) CSF is high in sodium.
C) The CSF is turbid in appearance.
D) The potassium level in the CSF is low.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



