Deck 7: Production and Cost in the Firm
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/218
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Production and Cost in the Firm
1
A young chef is considering opening his own sushi bar. To do so, he would have to quit his current job, which pays $20,000 a year, and take over a store building that he owns and currently rents to his brother for $6,000 a year. His expenses at the sushi bar would be $50,000 for food and $2,000 for gas and electricity. What are his explicit costs?
A) $26,000
B) $66,000
C) $78,000
D) $52,000
E) $72,000
A) $26,000
B) $66,000
C) $78,000
D) $52,000
E) $72,000
D
2
Implicit cost involves a direct cash payment for the use of a resource.
False
3
Which of the following is not an explicit cost?
A) salaries
B) sales taxes
C) the cost of utilities, such as gas and electricity
D) insurance premiums
E) the value of a firm owner's time
A) salaries
B) sales taxes
C) the cost of utilities, such as gas and electricity
D) insurance premiums
E) the value of a firm owner's time
E
4
The difference between a firm's total revenue and what must be paid to attract resources from their best alternative use is called
A) total revenue
B) utility
C) economic profit
D) cost
E) production efficiency
A) total revenue
B) utility
C) economic profit
D) cost
E) production efficiency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The opportunity cost of a resource
A) includes both explicit and implicit cost
B) includes explicit cost only
C) includes implicit cost only
D) is equal to the market price of the resource
E) is not related to the market price of the resource
A) includes both explicit and implicit cost
B) includes explicit cost only
C) includes implicit cost only
D) is equal to the market price of the resource
E) is not related to the market price of the resource

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If a firm's economic profit is positive, its accounting profit must also be positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The reason economists assume that firms try to maximize economic profit is
A) over time, firms that don't earn profits will have difficulty securing financing to survive
B) firms in the real world always maximize profit
C) profit is easier to calculate than revenues
D) if a firm fails to earn a profit in its first year, it will go out of business
E) profit maximization is easier for firms than revenue maximization
A) over time, firms that don't earn profits will have difficulty securing financing to survive
B) firms in the real world always maximize profit
C) profit is easier to calculate than revenues
D) if a firm fails to earn a profit in its first year, it will go out of business
E) profit maximization is easier for firms than revenue maximization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Opportunity cost usually
A) cannot be measured
B) applies to labor but not to capital
C) is involved in calculating economic profit
D) is greater than the cash payment made to a resource
E) is less than the cash payment made to a resource
A) cannot be measured
B) applies to labor but not to capital
C) is involved in calculating economic profit
D) is greater than the cash payment made to a resource
E) is less than the cash payment made to a resource

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
All other things constant, higher implicit cost results in lower accounting profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following are implicit costs for a typical firm?
A) insurance costs
B) electricity costs
C) opportunity costs of capital owned and used by the firm
D) cost of labor hired by the firm
E) the cost of raw materials
A) insurance costs
B) electricity costs
C) opportunity costs of capital owned and used by the firm
D) cost of labor hired by the firm
E) the cost of raw materials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If Ripco owns the building where it operates, then if
A) the firm pays no rent, there is no opportunity cost
B) the firm does not rent the building to anyone else, there is no opportunity cost
C) the firm pays no rent, there is an opportunity cost
D) its usage of the building precludes it from renting to anyone else, there is an opportunity cost
E) the firm could use the building for other things, there is no opportunity cost
A) the firm pays no rent, there is no opportunity cost
B) the firm does not rent the building to anyone else, there is no opportunity cost
C) the firm pays no rent, there is an opportunity cost
D) its usage of the building precludes it from renting to anyone else, there is an opportunity cost
E) the firm could use the building for other things, there is no opportunity cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A firm's opportunity costs of using resources provided by the firm's owners are called
A) sunk costs
B) fixed costs
C) explicit costs
D) implicit costs
E) entrepreneurial costs
A) sunk costs
B) fixed costs
C) explicit costs
D) implicit costs
E) entrepreneurial costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An implicit cost is
A) any cost a firm cannot avoid in the short run
B) any expenditure a firm makes
C) an opportunity cost
D) accurately measured in accounting statements
E) ignored by economists
A) any cost a firm cannot avoid in the short run
B) any expenditure a firm makes
C) an opportunity cost
D) accurately measured in accounting statements
E) ignored by economists

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A young chef is considering opening his own sushi bar. To do so, he would have to quit his current job, which pays $20,000 a year, and take over a store building that he owns and currently rents to his brother for $6,000 a year. His expenses at the sushi bar would be $50,000 for food and $2,000 for gas and electricity. What are his implicit costs?
A) $26,000
B) $66,000
C) $78,000
D) $52,000
E) $72,000
A) $26,000
B) $66,000
C) $78,000
D) $52,000
E) $72,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Explicit costs are
A) not part of opportunity cost
B) the only cost considered in opportunity cost
C) exactly the same as implicit costs
D) actual monetary payments for resources purchased
E) the opportunity costs of using resources owned by the firm
A) not part of opportunity cost
B) the only cost considered in opportunity cost
C) exactly the same as implicit costs
D) actual monetary payments for resources purchased
E) the opportunity costs of using resources owned by the firm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Cash payments for steel to be used in production would be an example of
A) sunk costs
B) fixed costs
C) explicit costs
D) implicit costs
E) entrepreneurial costs
A) sunk costs
B) fixed costs
C) explicit costs
D) implicit costs
E) entrepreneurial costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If all my savings are invested in my consulting company, an increase in the interest rate increases my implicit costs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Two friends, Diane and Sam, own and run a bar. Diane tends bar on Monday, Wednesday, and Friday and receives a wage in addition to tips. Sam tends bar on Tuesday, Thursday, and Saturday and receives only tips. Which of the following represents an implicit cost of operating the bar?
A) Diane's wage
B) Sam's time
C) Diane's tips
D) Sam's tips
E) both Diane's and Sam's tips
A) Diane's wage
B) Sam's time
C) Diane's tips
D) Sam's tips
E) both Diane's and Sam's tips

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
John moved his office from a building he was renting downtown to the carriage house he owns in back of his house. How will his costs change?
A) explicit and implicit costs rise
B) explicit costs rise; implicit costs fall
C) explicit and implicit costs fall
D) explicit costs fall; implicit costs rise
E) not enough information is given
A) explicit and implicit costs rise
B) explicit costs rise; implicit costs fall
C) explicit and implicit costs fall
D) explicit costs fall; implicit costs rise
E) not enough information is given

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Unlike implicit costs, explicit costs
A) reflect opportunity costs
B) include the value of the owner's time
C) are not included in a firm's accounting statements
D) are actual cash payments
E) do not change as a firm's output changes
A) reflect opportunity costs
B) include the value of the owner's time
C) are not included in a firm's accounting statements
D) are actual cash payments
E) do not change as a firm's output changes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Zipco's accounting profit is equal to its
A) total revenue minus opportunity costs
B) total revenue plus opportunity costs
C) total revenue minus imputed costs
D) total revenue minus explicit costs
E) total revenue minus explicit and implicit costs
A) total revenue minus opportunity costs
B) total revenue plus opportunity costs
C) total revenue minus imputed costs
D) total revenue minus explicit costs
E) total revenue minus explicit and implicit costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following would be shown on IBM's accounting statement?
A) revenue, implicit costs, explicit costs, and economic profit
B) revenue, implicit costs, explicit costs, and accounting profit
C) revenue, explicit costs, and economic profit
D) revenue, explicit costs, and accounting profit
E) revenue, implicit costs, and accounting profit
A) revenue, implicit costs, explicit costs, and economic profit
B) revenue, implicit costs, explicit costs, and accounting profit
C) revenue, explicit costs, and economic profit
D) revenue, explicit costs, and accounting profit
E) revenue, implicit costs, and accounting profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose Ernie gives up his job as financial advisor for P.E.T.S., at which he earned $30,000 per year, to open up a store selling spot remover to Dalmatians. He invested $10,000 in the store, which had been in savings earning 5 percent interest. This year's revenues in the new business were $50,000, and explicit costs were $10,000. Calculate Ernie's economic profit.
A) $10,000
B) $50,000
C) $20,000
D) $40,000
E) $9,500
A) $10,000
B) $50,000
C) $20,000
D) $40,000
E) $9,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If General Motors is earning only a normal profit,
A) it is making economic profit
B) it is breaking even
C) it is suffering an economic loss
D) it is covering only explicit costs
E) it is covering only implicit costs
A) it is making economic profit
B) it is breaking even
C) it is suffering an economic loss
D) it is covering only explicit costs
E) it is covering only implicit costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose a lawyer leaves his $50,000-a-year job and starts his own firm breeding pit bulls. In the first year, his accounting profit is $70,000. The lawyer finances his new business with $100,000 from his savings account, which had earned 10 percent interest. His economic profit is
A) $10,000
B) $60,000
C) $70,000
D) -$80,000
E) -$90,000
A) $10,000
B) $60,000
C) $70,000
D) -$80,000
E) -$90,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Economic profit is defined as
A) total revenue minus price
B) price minus quantity
C) total revenue minus what must be paid to resources to attract them from their best alternative use
D) total revenue divided by what must be paid to resources to attract them from their best alternative use
E) total revenue plus what must be paid to resources to attract them from their best alternative use
A) total revenue minus price
B) price minus quantity
C) total revenue minus what must be paid to resources to attract them from their best alternative use
D) total revenue divided by what must be paid to resources to attract them from their best alternative use
E) total revenue plus what must be paid to resources to attract them from their best alternative use

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Accounting profit equals
A) explicit costs minus implicit costs
B) economic profit minus implicit costs
C) economic profit minus explicit costs
D) economic profit minus explicit costs and implicit costs
E) economic profit plus implicit costs
A) explicit costs minus implicit costs
B) economic profit minus implicit costs
C) economic profit minus explicit costs
D) economic profit minus explicit costs and implicit costs
E) economic profit plus implicit costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Suppose Bob leaves his $50,000-a-year job as a financial advisor to P.E.T.S. and starts his own business selling spot remover for Dalmatians. In the first year his accounting profit is $70,000. Based on this level of success, Bob should
A) return to his old job because his economic profit is negative
B) return to his old job because his economic profit is smaller than his accounting profit
C) return to his old job because his economic profit is less than his old salary
D) stay with his new firm because his economic profit is positive
E) stay with his new firm because accounting profit is positive
A) return to his old job because his economic profit is negative
B) return to his old job because his economic profit is smaller than his accounting profit
C) return to his old job because his economic profit is less than his old salary
D) stay with his new firm because his economic profit is positive
E) stay with his new firm because accounting profit is positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Economic profit is defined as total revenue
A) plus total costs
B) minus marginal costs
C) minus variable costs
D) minus total costs
E) minus fixed costs
A) plus total costs
B) minus marginal costs
C) minus variable costs
D) minus total costs
E) minus fixed costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Suppose Ben buys out Jerry's ownership in the firm but retains him as a salaried employee. If so,
A) economic profit increases
B) economic profit decreases
C) there is no change in economic profit
D) there is no change in accounting profit
E) accounting profit increases
A) economic profit increases
B) economic profit decreases
C) there is no change in economic profit
D) there is no change in accounting profit
E) accounting profit increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppose Ernie gives up his job as financial advisor for P.E.T.S., at which he earned $30,000 per year, to open up a store selling spot remover to Dalmatians. He invested $10,000 in the store, which had been in savings earning 5 percent interest. This year's revenues in the new business were $50,000, and explicit costs were $10,000. Calculate Ernie's accounting profit.
A) $10,000
B) $50,000
C) $20,000
D) $40,000
E) $9,500
A) $10,000
B) $50,000
C) $20,000
D) $40,000
E) $9,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following would not appear on a firm's accounting statement?
A) sunk costs
B) fixed costs
C) explicit costs
D) implicit costs
E) insurance costs
A) sunk costs
B) fixed costs
C) explicit costs
D) implicit costs
E) insurance costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Accounting profit is
A) always less than economic profit
B) never less than economic profit
C) equal to economic profit if a normal profit is earned
D) less than economic profit only when implicit costs are greater than explicit costs
E) greater than economic profit only when implicit costs are greater than explicit costs
A) always less than economic profit
B) never less than economic profit
C) equal to economic profit if a normal profit is earned
D) less than economic profit only when implicit costs are greater than explicit costs
E) greater than economic profit only when implicit costs are greater than explicit costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Zipco's economic profit is equal to its
A) total revenue minus accounting profit
B) total revenue minus explicit costs
C) total revenue plus accounting profit
D) total revenue plus opportunity costs
E) accounting profit minus implicit costs
A) total revenue minus accounting profit
B) total revenue minus explicit costs
C) total revenue plus accounting profit
D) total revenue plus opportunity costs
E) accounting profit minus implicit costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Maryann and Don want to open their own deli. To do so, Maryann must give up her job, at which she earns $20,000 per year, and Don must give up his part-time job, at which he earns $10,000 per year. They must liquidate their money market fund, which earns $1,000 interest annually. The rent on the building is $10,000 per year, and expenses for such necessities as utilities, corned beef, and pickles are $35,000 annually. What minimum amount of revenue per year would make it worthwhile, financially, for Maryann and Don to operate the deli?
A) $10,000
B) $35,000
C) $45,000
D) $31,000
E) $76,000
A) $10,000
B) $35,000
C) $45,000
D) $31,000
E) $76,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Economic profit is defined as
A) total revenue minus implicit costs
B) total revenue plus explicit costs
C) total revenue plus implicit costs
D) wages plus interest minus rent
E) total revenue minus implicit and explicit costs
A) total revenue minus implicit costs
B) total revenue plus explicit costs
C) total revenue plus implicit costs
D) wages plus interest minus rent
E) total revenue minus implicit and explicit costs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Amanda, age 6, opens a lemonade stand. She makes all the lemonade from a mix she found in her parents' pantry. Her stand is an old box she found in the garage. The pitcher and paper cups were taken from the kitchen. Which of the following is true?
A) The opportunity cost of the lemonade is zero.
B) The only opportunity cost of the lemonade is Amanda's time.
C) Amanda's explicit costs are zero.
D) The implicit costs of Amanda's lemonade are zero.
E) Whatever revenue Amanda gets will be pure economic profit.
A) The opportunity cost of the lemonade is zero.
B) The only opportunity cost of the lemonade is Amanda's time.
C) Amanda's explicit costs are zero.
D) The implicit costs of Amanda's lemonade are zero.
E) Whatever revenue Amanda gets will be pure economic profit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Normal profit is defined as
A) accounting profit
B) economic profit
C) profit necessary to ensure that opportunity costs are covered
D) accounting profit minus economic profit
E) economic profit minus accounting profit
A) accounting profit
B) economic profit
C) profit necessary to ensure that opportunity costs are covered
D) accounting profit minus economic profit
E) economic profit minus accounting profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Maryann and Don want to open their own deli. To do so, Maryann must give up her job, at which she earns $20,000 per year, and Don must give up his part-time job, at which he earns $10,000 per year. They must liquidate their money market fund, which earns $1,000 interest annually. The rent on the building is $10,000 per year, and expenses for such necessities as utilities, corned beef, and pickles are $35,000 annually. What is the explicit cost per year of operating the deli?
A) $10,000
B) $35,000
C) $45,000
D) $31,000
E) $76,000
A) $10,000
B) $35,000
C) $45,000
D) $31,000
E) $76,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Suppose a soccer coach has been making $25,000 per year but gives up his coaching job in order to make lace doilies. If his revenue from the sale of these doilies is $50,000 and his materials cost $20,000, then his economic profit is
A) $5,000
B) $25,000
C) $30,000
D) $50,000
E) $80,000
A) $5,000
B) $25,000
C) $30,000
D) $50,000
E) $80,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Suppose I have $1,000 to put into a one-year CD. Community Bank offers 5 percent interest, Floatbank offers 5.25 percent, and Squidbank offers 5.40 percent. If I place my money in Squidbank, my economic profit on the investment is
A) 5.40 percent
B) 5 percent
C) 0.40 percent
D) 0.15 percent
E) -0.40 percent
A) 5.40 percent
B) 5 percent
C) 0.40 percent
D) 0.15 percent
E) -0.40 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Exhibit 7-1

Sally owns a small business that she operates in a small building she owns. Given the information in Exhibit 7-1, Sally's normal profit is
A) $80,000
B) $41,000
C) $65,000
D) $35,000
E) $24,000

Sally owns a small business that she operates in a small building she owns. Given the information in Exhibit 7-1, Sally's normal profit is
A) $80,000
B) $41,000
C) $65,000
D) $35,000
E) $24,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Exhibit 7-1

Sally owns a small business that she operates in a small building she owns. Given the information in Exhibit 7-1, Sally's accounting profit is
A) $80,000
B) $50,000
C) $65,000
D) $35,000
E) $24,000

Sally owns a small business that she operates in a small building she owns. Given the information in Exhibit 7-1, Sally's accounting profit is
A) $80,000
B) $50,000
C) $65,000
D) $35,000
E) $24,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Bart operates a lemonade stand in front of his house. His father works at the Springfield Nuclear Power Plant. Which of the following is most likely to be true?
A) The long run is the same for the power plant as it is for the lemonade stand.
B) The long run is longer for the power plant than it is for the lemonade stand.
C) The long run is shorter for the power plant than it is for the lemonade stand.
D) We cannot compare the long runs because these are different businesses.
E) It's impossible for the power plant short run to be shorter than the lemonade stand's long run.
A) The long run is the same for the power plant as it is for the lemonade stand.
B) The long run is longer for the power plant than it is for the lemonade stand.
C) The long run is shorter for the power plant than it is for the lemonade stand.
D) We cannot compare the long runs because these are different businesses.
E) It's impossible for the power plant short run to be shorter than the lemonade stand's long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In the long run, all inputs are variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the Baloney Store earns more than a normal profit, its
A) economic profit must be greater than its accounting profit
B) economic profit is positive
C) economic profit is, therefore, equal to its accounting profit
D) accounting profit is zero
E) accounting profit is less than its economic profit
A) economic profit must be greater than its accounting profit
B) economic profit is positive
C) economic profit is, therefore, equal to its accounting profit
D) accounting profit is zero
E) accounting profit is less than its economic profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the short run, all costs are fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following is most likely to be a fixed resource for the City Slicker's Dude Ranch?
A) the lodge where the guests stay
B) food for the guests
C) stable hands to take care of the horses
D) hay for the horses
E) water for the horses
A) the lodge where the guests stay
B) food for the guests
C) stable hands to take care of the horses
D) hay for the horses
E) water for the horses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Suppose Joan uses her savings to purchase computer equipment for her new consulting business. Soon after this, the market interest rate rises. As a result, her
A) explicit costs rise immediately
B) accounting profit falls immediately
C) accounting profit rises immediately
D) economic profit rises immediately
E) economic profit falls immediately
A) explicit costs rise immediately
B) accounting profit falls immediately
C) accounting profit rises immediately
D) economic profit rises immediately
E) economic profit falls immediately

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
John moved his office from a building he was renting downtown to the carriage house he owns in back of his house. How will his profit change?
A) Implicit costs fall.
B) Explicit costs remain unchanged while implicit costs rise.
C) Economic profit must fall.
D) Explicit costs rise.
E) Accounting profit will rise.
A) Implicit costs fall.
B) Explicit costs remain unchanged while implicit costs rise.
C) Economic profit must fall.
D) Explicit costs rise.
E) Accounting profit will rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The short run is a period of time
A) equal to or less than six months
B) during which all resources may be varied
C) during which all resources are fixed
D) during which at least one resource is fixed
E) during which at least one resource may be varied
A) equal to or less than six months
B) during which all resources may be varied
C) during which all resources are fixed
D) during which at least one resource is fixed
E) during which at least one resource may be varied

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Inputs that can be increased or decreased in the short run are called
A) fixed inputs
B) variable inputs
C) economic inputs
D) accounting inputs
E) normal inputs
A) fixed inputs
B) variable inputs
C) economic inputs
D) accounting inputs
E) normal inputs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In the long run, all of a firm's inputs are variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Suppose that at the current level of output, Pat's Hats has fixed costs of $500, variable costs of $1,000, and $2,000 in total revenue. Which of the following is true?
A) Profit is currently $500 and, in the long run, it will be $1,000 because there will be no fixed costs.
B) Profit is currently $500 and, in the long run, it will be $1,500 because there will be no variable costs.
C) Profit is currently $500.
D) Profit is currently $500, and Pat's Hats will want to decrease its plant size in the long run to lower its fixed costs.
E) Pat's Hats will continue to operate as long as revenue is greater than $500.
A) Profit is currently $500 and, in the long run, it will be $1,000 because there will be no fixed costs.
B) Profit is currently $500 and, in the long run, it will be $1,500 because there will be no variable costs.
C) Profit is currently $500.
D) Profit is currently $500, and Pat's Hats will want to decrease its plant size in the long run to lower its fixed costs.
E) Pat's Hats will continue to operate as long as revenue is greater than $500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose a professor gives up her teaching job to devote her time to writing textbooks. If salaries of professors rise,
A) her accounting profit will rise
B) her accounting profit will fall
C) her explicit costs will rise
D) her economic profit from textbooks will fall
E) her economic profit from textbooks will rise
A) her accounting profit will rise
B) her accounting profit will fall
C) her explicit costs will rise
D) her economic profit from textbooks will fall
E) her economic profit from textbooks will rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If the Money Store earns a normal profit this year, its
A) economic profit is equal to its accounting profit
B) economic profit is zero
C) economic profit is equal to the average accounting profit in other industries
D) accounting profit is zero
E) accounting profit is less than its economic profit
A) economic profit is equal to its accounting profit
B) economic profit is zero
C) economic profit is equal to the average accounting profit in other industries
D) accounting profit is zero
E) accounting profit is less than its economic profit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A young chef is considering opening his own sushi bar. To do so, he would have to quit his current job, which pays $20,000 a year, and take over a store building he owns and currently rents for $6,000 a year. His expenses at the sushi bar would be $50,000 for food and $2,000 for gas and electricity. What is the minimum revenue he must earn per year in order for it to be worth his while to open his sushi bar?
A) $26,000
B) $66,000
C) $78,000
D) $52,000
E) $72,000
A) $26,000
B) $66,000
C) $78,000
D) $52,000
E) $72,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The graph of average fixed cost is a horizontal line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Exhibit 7-1

Sally owns a small business that she operates in a small building she owns. Given the information in Exhibit 7-1, Sally's economic profit is
A) $80,000
B) $50,000
C) $65,000
D) $35,000
E) $24,000

Sally owns a small business that she operates in a small building she owns. Given the information in Exhibit 7-1, Sally's economic profit is
A) $80,000
B) $50,000
C) $65,000
D) $35,000
E) $24,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is most likely to be a fixed resource for Paul's Country Fresh Pies, Inc.?
A) berries
B) flour
C) bakers
D) eggs
E) ovens
A) berries
B) flour
C) bakers
D) eggs
E) ovens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The length of time that represents the long run
A) is greater than one year
B) is greater than six months
C) is longer in service industries than in manufacturing
D) is the same for all industries
E) varies from industry to industry
A) is greater than one year
B) is greater than six months
C) is longer in service industries than in manufacturing
D) is the same for all industries
E) varies from industry to industry

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is a long-run adjustment?
A) A new economics professor is hired on campus.
B) General Motors increases its orders for steel.
C) Microsoft cuts back its hiring of new graduates.
D) Glow Electric disassembles one of its nuclear power plants.
E) Texaco buys more crude oil to refine into gasoline.
A) A new economics professor is hired on campus.
B) General Motors increases its orders for steel.
C) Microsoft cuts back its hiring of new graduates.
D) Glow Electric disassembles one of its nuclear power plants.
E) Texaco buys more crude oil to refine into gasoline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Exhibit 7-2
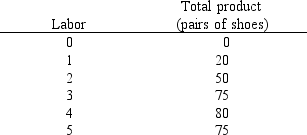
Given the information in Exhibit 7-2, at what point do diminishing marginal returns set in?
A) before the first unit of labor
B) between the first and second units of labor
C) between the second and third units of labor
D) between the third and fourth units of labor
E) between the fourth and fifth units of labor

Given the information in Exhibit 7-2, at what point do diminishing marginal returns set in?
A) before the first unit of labor
B) between the first and second units of labor
C) between the second and third units of labor
D) between the third and fourth units of labor
E) between the fourth and fifth units of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
As Product Co. adds the first four workers to its production process in the short run, its output rises from 0 to 12 to 25 to 35 to 43. Addition of the fifth worker will most likely lead to an output rate
A) greater than 51
B) equal to 51
C) less than 51
D) greater than 51 if the firm experiences diseconomies of scale
E) none of the above
A) greater than 51
B) equal to 51
C) less than 51
D) greater than 51 if the firm experiences diseconomies of scale
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
If marginal product is negative, total product must be negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Marginal product is defined as
A) the increase in revenue that occurs when an additional unit of a resource is added
B) the increase in output that occurs when all resources are increased by the same proportion
C) the increase in output that occurs when an additional unit of a resource is added, holding all other resources constant
D) the amount of additional resources needed to increase output by one unit when all resources are increased by the same amount
E) the amount of additional money needed to increase output by one unit when all resources are held constant
A) the increase in revenue that occurs when an additional unit of a resource is added
B) the increase in output that occurs when all resources are increased by the same proportion
C) the increase in output that occurs when an additional unit of a resource is added, holding all other resources constant
D) the amount of additional resources needed to increase output by one unit when all resources are increased by the same amount
E) the amount of additional money needed to increase output by one unit when all resources are held constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is a short-run adjustment?
A) Toyota builds an automobile plant in Kentucky.
B) Faced with increasing enrollment, a private college builds a new School of Business building.
C) Because of staggering losses, three insurance companies exit the industry.
D) People's Bank hires two new tellers to meet increased demand for customer services.
E) Shaveco enters the razor blade market with a new product, produced in the United States.
A) Toyota builds an automobile plant in Kentucky.
B) Faced with increasing enrollment, a private college builds a new School of Business building.
C) Because of staggering losses, three insurance companies exit the industry.
D) People's Bank hires two new tellers to meet increased demand for customer services.
E) Shaveco enters the razor blade market with a new product, produced in the United States.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following would most likely reach the long run most rapidly?
A) a nuclear power plant
B) a college
C) a lumber mill
D) a shopping mall
E) a hot dog stand
A) a nuclear power plant
B) a college
C) a lumber mill
D) a shopping mall
E) a hot dog stand

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is most likely to be a fixed resource for the Speedy Word Processing and Résumé Company?
A) floppy disks
B) typists
C) computer terminals
D) electricity
E) paper
A) floppy disks
B) typists
C) computer terminals
D) electricity
E) paper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If a firm is experiencing diminishing marginal returns, its marginal product is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Exhibit 7-2

Given the information in Exhibit 7-2, what is the marginal product of the fourth unit of labor?
A) 5 pairs of shoes
B) 10 pairs of shoes
C) 20 pairs of shoes
D) 50 pairs of shoes
E) 80 pairs of shoes

Given the information in Exhibit 7-2, what is the marginal product of the fourth unit of labor?
A) 5 pairs of shoes
B) 10 pairs of shoes
C) 20 pairs of shoes
D) 50 pairs of shoes
E) 80 pairs of shoes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following probably has the shortest long run?
A) a law firm
B) a steel mill
C) an automobile plant
D) a tire factory
E) an aircraft engine factory
A) a law firm
B) a steel mill
C) an automobile plant
D) a tire factory
E) an aircraft engine factory

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Exhibit 7-2

Given the information in Exhibit 7-2, what is the marginal product of the third unit of labor?
A) 45 pairs of shoes
B) 25 pairs of shoes
C) 15 pairs of shoes
D) $45
E) $25

Given the information in Exhibit 7-2, what is the marginal product of the third unit of labor?
A) 45 pairs of shoes
B) 25 pairs of shoes
C) 15 pairs of shoes
D) $45
E) $25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The short run is a period of time
A) less than one year
B) greater than one year
C) during which all resources are variable
D) during which at least one resource is fixed
E) during which at least one resource is variable
A) less than one year
B) greater than one year
C) during which all resources are variable
D) during which at least one resource is fixed
E) during which at least one resource is variable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Exhibit 7-2

Given the information in Exhibit 7-2, what is the average product of the fourth unit of labor?
A) 5 pairs of shoes
B) 10 pairs of shoes
C) 20 pairs of shoes
D) 50 pairs of shoes
E) 80 pairs of shoes

Given the information in Exhibit 7-2, what is the average product of the fourth unit of labor?
A) 5 pairs of shoes
B) 10 pairs of shoes
C) 20 pairs of shoes
D) 50 pairs of shoes
E) 80 pairs of shoes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Exhibit 7-2

Given the information in Exhibit 7-2, at what point do negative marginal returns set in?
A) before the first unit of labor
B) between the first and second units of labor
C) between the second and third units of labor
D) between the third and fourth units of labor
E) between the fourth and fifth units of labor

Given the information in Exhibit 7-2, at what point do negative marginal returns set in?
A) before the first unit of labor
B) between the first and second units of labor
C) between the second and third units of labor
D) between the third and fourth units of labor
E) between the fourth and fifth units of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The additional output obtained by adding another unit of labor to the production process is called
A) the marginal cost of labor
B) the average output of labor
C) a variable cost
D) the marginal product of labor
E) the marginal utility of labor
A) the marginal cost of labor
B) the average output of labor
C) a variable cost
D) the marginal product of labor
E) the marginal utility of labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Increasing marginal returns are generally the result of
A) diseconomies of scale
B) increasing costs
C) specialization and division of labor
D) labor unions
E) technology
A) diseconomies of scale
B) increasing costs
C) specialization and division of labor
D) labor unions
E) technology

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If a firm is experiencing diminishing marginal returns, its marginal product is declining.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The long run is a period of time
A) during which at least one resource is fixed
B) during which all resources are variable
C) during which all resources are fixed
D) less than one year
E) greater than one year
A) during which at least one resource is fixed
B) during which all resources are variable
C) during which all resources are fixed
D) less than one year
E) greater than one year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 218 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



