Deck 22: Carbohydrate Metabolism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/45
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Carbohydrate Metabolism
1
Which enzyme catalyzes a reaction that is a major control point for glycolysis?
A) Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
B) Enolase
C) Phosphofructokinase
D) Aldolase
A) Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
B) Enolase
C) Phosphofructokinase
D) Aldolase
Phosphofructokinase
2
In the course of the conversion of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
A) an alcohol group is phosphorylated
B) an alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde
C) an alcohol is oxidized to a carboxylic acid
D) an aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid
A) an alcohol group is phosphorylated
B) an alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde
C) an alcohol is oxidized to a carboxylic acid
D) an aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid
an aldehyde is oxidized to a carboxylic acid
3
Which group of small molecules best fit the boxes associated with the reaction shown? 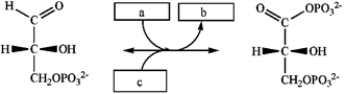 a b c
a b c
A) ATP ADP H2O
B) NADH NAD+ Pi
C) NAD+ NADH H2O
D) NAD+ NADH Pi
 a b c
a b cA) ATP ADP H2O
B) NADH NAD+ Pi
C) NAD+ NADH H2O
D) NAD+ NADH Pi
NAD+ NADH Pi
4
Consider the following reaction. 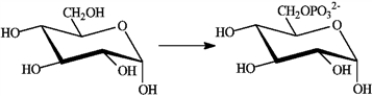 Which of the following describes this reaction?
Which of the following describes this reaction?
A) is so strongly exergonic that it does not require a catalyst
B) is an exergonic reaction not coupled to any other reaction
C) is an endergonic reaction that takes place because it is coupled to the exergonic hydrolysis of ATP
D) is an exergonic reaction that is coupled to the endergonic hydrolysis of ATP
 Which of the following describes this reaction?
Which of the following describes this reaction?A) is so strongly exergonic that it does not require a catalyst
B) is an exergonic reaction not coupled to any other reaction
C) is an endergonic reaction that takes place because it is coupled to the exergonic hydrolysis of ATP
D) is an exergonic reaction that is coupled to the endergonic hydrolysis of ATP

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider the following reversible reaction.  This reaction:
This reaction:
A) is catalyzed by the enzyme triose phosphate isomerase
B) requires several enzymes
C) requires coenzyme A
D) requires thiamine pyrophosphate
 This reaction:
This reaction:A) is catalyzed by the enzyme triose phosphate isomerase
B) requires several enzymes
C) requires coenzyme A
D) requires thiamine pyrophosphate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the reaction catalyzed by aldolase, the substrate is bound to the enzyme
A) by an ester linkage
B) as a Schiff base
C) by a peptide bond
D) by hydrogen bonds
A) by an ester linkage
B) as a Schiff base
C) by a peptide bond
D) by hydrogen bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Biotin is important in gluconeogenesis for all of these reasons, except:
A) It is necessary to add CO2 to certain intermediates in this pathway.
B) CO2 becomes one or more of the 6 carbons in the glucose product.
C) Biotin is capable of binding covalently to CO2.
D) Biotin helps synthesize an important precursor of phosphoenolpyruvate.
E) All of these reactions require the vitamin coenzyme.
A) It is necessary to add CO2 to certain intermediates in this pathway.
B) CO2 becomes one or more of the 6 carbons in the glucose product.
C) Biotin is capable of binding covalently to CO2.
D) Biotin helps synthesize an important precursor of phosphoenolpyruvate.
E) All of these reactions require the vitamin coenzyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
During the complete catabolism of a molecule of glucose, the ultimate fate of the carbon atoms are
A) pyruvate
B) AcetylCoA
C) carbon dioxide
D) fructose-6-phosphate
E) a, b or c
A) pyruvate
B) AcetylCoA
C) carbon dioxide
D) fructose-6-phosphate
E) a, b or c

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which enzyme is used in gluconeogenesis, but NOT in glycolysis?
A) PEP carboxykinase
B) enolase
C) phosphohexose isomerase
D) 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase
A) PEP carboxykinase
B) enolase
C) phosphohexose isomerase
D) 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The order of compounds in the conversion of glucose to pyruvic acid is as follows: (PEP = phosphoenolpyruvate)
A) Fructose-bisphosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, 1,3-phosphoglyceric acid, 3-phosphoglyceric acid, PEP.
B) Fructose-6-phosphate, fructose-bisphosphate, PEP, 1,3-phosphoglyceric acid, 3-phosphoglyceric acid.
C) Fructose-6-phosphate, fructose-bisphosphate, 1,3-phosphoglyceric acid, 3-phosphoglyceric acid, PEP.
D) Fructose-6-phosphate, fructose-bisphosphate, 3-phosphoglyceric acid, 1,3-phosphoglyceric acid, PEP.
E) Fructose-bisphosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, 3-phosphoglyceric acid, 1,3-phosphoglyceric acid, PEP.
A) Fructose-bisphosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, 1,3-phosphoglyceric acid, 3-phosphoglyceric acid, PEP.
B) Fructose-6-phosphate, fructose-bisphosphate, PEP, 1,3-phosphoglyceric acid, 3-phosphoglyceric acid.
C) Fructose-6-phosphate, fructose-bisphosphate, 1,3-phosphoglyceric acid, 3-phosphoglyceric acid, PEP.
D) Fructose-6-phosphate, fructose-bisphosphate, 3-phosphoglyceric acid, 1,3-phosphoglyceric acid, PEP.
E) Fructose-bisphosphate, fructose-6-phosphate, 3-phosphoglyceric acid, 1,3-phosphoglyceric acid, PEP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following are not involved in both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis?
A) pyruvate
B) oxaloacetate
C) glucose-6-phosphate
D) fructose-6-phosphate
E) all of these
A) pyruvate
B) oxaloacetate
C) glucose-6-phosphate
D) fructose-6-phosphate
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The reaction of fructose 1,6-bisphosphate to give glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate is an example of
A) a reverse aldol condensation
B) hydrolysis
C) oxidation
D) dehydration
A) a reverse aldol condensation
B) hydrolysis
C) oxidation
D) dehydration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Thiamin diphosphate (TPP) is a coenzyme
A) frequently encountered in oxidation-reduction reactions
B) required for the phosphorylation of ADP
C) involved in transfers of two-carbon groups
D) involved in transfers of one-carbon groups
A) frequently encountered in oxidation-reduction reactions
B) required for the phosphorylation of ADP
C) involved in transfers of two-carbon groups
D) involved in transfers of one-carbon groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In humans, what aspect(s) are the mechanism of glycosidase hydrolysis of starch by inversion and retention of stereochemistry similar?
A) formation of an oxomium ion intermediate
B) involve two inversions
C) SN2-like inversion
D) occurs only in the small intestine
E) all of these
A) formation of an oxomium ion intermediate
B) involve two inversions
C) SN2-like inversion
D) occurs only in the small intestine
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The first reaction of gluconeogenesis is  This reaction is classified as:
This reaction is classified as:
A) an oxidative decarboxylation
B) a carboxylation
C) a redox reaction
D) a phosphate transfer
 This reaction is classified as:
This reaction is classified as:A) an oxidative decarboxylation
B) a carboxylation
C) a redox reaction
D) a phosphate transfer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If gluconeogenesis were the exact reverse of glycolysis, which of the following would not be possible?
A) production and breakdown of glucose involving simpler precursors
B) formation of phosphorylated intermediates in both anabolism and catabolism of glucose
C) endergonic anabolism and catabolism of glucose
D) independent control of the anabolism and catabolism of glucose
E) c and d
A) production and breakdown of glucose involving simpler precursors
B) formation of phosphorylated intermediates in both anabolism and catabolism of glucose
C) endergonic anabolism and catabolism of glucose
D) independent control of the anabolism and catabolism of glucose
E) c and d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
At the beginning of polysaccharide catabolism, α-amylase catalyzes:
A) internal (1→6) links
B) internal (1→4) links
C) terminal (1→6) links
D) terminal (1→4) links
E) all of these
A) internal (1→6) links
B) internal (1→4) links
C) terminal (1→6) links
D) terminal (1→4) links
E) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction shown? 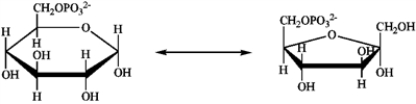
A) an epimerase
B) an isomerase
C) a mutase
D) a dehydrogenase

A) an epimerase
B) an isomerase
C) a mutase
D) a dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Gluconeogenesis differs from glycolysis because
A) it does not produce ATP
B) different enzymes are involved
C) biotin is required for gluconeogenesis and not for glycolysis
D) all of these
A) it does not produce ATP
B) different enzymes are involved
C) biotin is required for gluconeogenesis and not for glycolysis
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The citric acid cycle is linked to the electron transport chain via:
A) NADH
B) FAD+
C) O2
D) all of these
E) a and b
A) NADH
B) FAD+
C) O2
D) all of these
E) a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 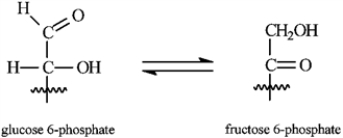
Refer to instructions. This reaction proceeds through a common enol structure. Draw the structure of the glucose/fructose enol.

Refer to instructions. This reaction proceeds through a common enol structure. Draw the structure of the glucose/fructose enol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following types of reactions are involved in glycolysis? Select all that apply.
A)nucleophilic acyl substitution
B)oxidation
C)aldol
D)reduction
E)hydrolysis
F)isomerization
A)nucleophilic acyl substitution
B)oxidation
C)aldol
D)reduction
E)hydrolysis
F)isomerization

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which enzymes in the citric acid cycle catalyze oxidative decarboxylation reactions?
A) isocitrate dehydrogenase and the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
B) aconitase and succinate dehydrogenase
C) the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex and succinate thiokinase
D) fumarase and succinate dehydrogenase
A) isocitrate dehydrogenase and the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex
B) aconitase and succinate dehydrogenase
C) the α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex and succinate thiokinase
D) fumarase and succinate dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Circle the carbon atoms in the molecule of glucose shown that enter the citric acid cycle as −CH3 groups. 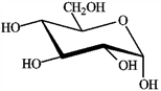


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which group of small molecules best fit the boxes associated with the reaction shown?  a b
a b
A) ADP + 2 Pi ATP
B) NAD+ NADH
C) ATP ADP + 2 Pi
D) FAD FADH2
 a b
a bA) ADP + 2 Pi ATP
B) NAD+ NADH
C) ATP ADP + 2 Pi
D) FAD FADH2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Draw and name the major product of the reaction of α-glucose with ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 
Refer to instructions. This reaction:
A) is catalyzed by an oxidase.
B) involves a ring opening
C) requires ATP
D) occurs in the citric acid cycle

Refer to instructions. This reaction:
A) is catalyzed by an oxidase.
B) involves a ring opening
C) requires ATP
D) occurs in the citric acid cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate reacts with the SH group of a cysteine residue (abbreviated (Enz-SH)) of a dehydrogenase to produce a hemithioaectal intermediate. Draw its structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Consider the structure of amylopectin below to answer the following questions. 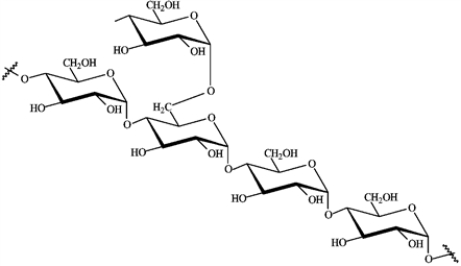 a)Circle the glycosidic links that are hydrolyzed in the small intestine.
a)Circle the glycosidic links that are hydrolyzed in the small intestine.
b)What is the final product of complete hydrolysis of amylpectin?
 a)Circle the glycosidic links that are hydrolyzed in the small intestine.
a)Circle the glycosidic links that are hydrolyzed in the small intestine.b)What is the final product of complete hydrolysis of amylpectin?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which group of small molecules best fit the boxes associated with the reaction shown? 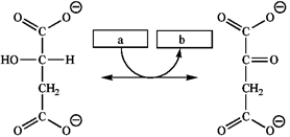 a b
a b
A) ADP + 2 Pi ATP
B) NAD+ NADH
C) NADP+ NADPH
D) FAD FADH2
 a b
a bA) ADP + 2 Pi ATP
B) NAD+ NADH
C) NADP+ NADPH
D) FAD FADH2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The enzyme pyruvate carboxylase
A) is not subject to allosteric control
B) requires biotin for activity
C) catalyzes a reaction that does not require ATP
D) is inhibited by acetyl-CoA
A) is not subject to allosteric control
B) requires biotin for activity
C) catalyzes a reaction that does not require ATP
D) is inhibited by acetyl-CoA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The citric acid cycle is considered to be the central metabolic pathway for all the following reasons, except:
A) It is involved in the metabolism of sugars and amino acids.
B) It is involved in the metabolism of amino acids and lipids.
C) It links anaerobic metabolism to aerobic metabolism.
D) Many of its intermediates are starting points for synthesis of a variety of compounds.
E) All of these are reasons why the citric acid cycle is considered to be the central pathway.
A) It is involved in the metabolism of sugars and amino acids.
B) It is involved in the metabolism of amino acids and lipids.
C) It links anaerobic metabolism to aerobic metabolism.
D) Many of its intermediates are starting points for synthesis of a variety of compounds.
E) All of these are reasons why the citric acid cycle is considered to be the central pathway.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Consider the glycolytic intermediate below to answer the following questions. 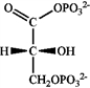 a)What is the name of the glycolytic intermediate?
a)What is the name of the glycolytic intermediate?
a. 1-phosphoglycerate
b. glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
c. dihydroxyacetone phosphate
d. 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
b)
Draw the structure of the product of the reaction of this intermediate with ADP.
 a)What is the name of the glycolytic intermediate?
a)What is the name of the glycolytic intermediate? a. 1-phosphoglycerate
b. glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate
c. dihydroxyacetone phosphate
d. 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate
b)
Draw the structure of the product of the reaction of this intermediate with ADP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The order of compounds and intermediates found in the citric acid cycle is as follows:
A) Iso-Citrate → Aconitate → α-Ketoglutarate → Fumarate → Malate → Oxaloacetate
B) Aconitate → iso-Citrate → Oxaloacetate → α-Ketoglutarate → Malate → Fumarate
C) Aconitate → iso-Citrate → α-Ketoglutarate → Fumarate → Malate → Oxaloacetate
D) Aconitate → iso-Citrate → α-Ketoglutarate → Malate → Fumarate → Oxaloacetate
E) Iso-Citrate → Aconitate → α-Ketoglutarate → Malate → Oxaloacetate → Fumarate
A) Iso-Citrate → Aconitate → α-Ketoglutarate → Fumarate → Malate → Oxaloacetate
B) Aconitate → iso-Citrate → Oxaloacetate → α-Ketoglutarate → Malate → Fumarate
C) Aconitate → iso-Citrate → α-Ketoglutarate → Fumarate → Malate → Oxaloacetate
D) Aconitate → iso-Citrate → α-Ketoglutarate → Malate → Fumarate → Oxaloacetate
E) Iso-Citrate → Aconitate → α-Ketoglutarate → Malate → Oxaloacetate → Fumarate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which group of small molecules best fit the boxes associated with the reaction shown? 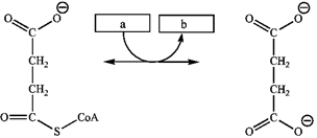 a b
a b
A) GDP GTP
B) NADP+ NADPH
C) ADP + Pi ATP
D) FAD FADH2
 a b
a bA) GDP GTP
B) NADP+ NADPH
C) ADP + Pi ATP
D) FAD FADH2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The following reactions all occur during oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate, except:
A) Removal of CO2.
B) Oxidation of an acetate group.
C) Addition of Coenzyme A to a 2-carbon fragment.
D) Reduction of NAD+
E) All of these reactions take place during oxidative decarboxylation.
A) Removal of CO2.
B) Oxidation of an acetate group.
C) Addition of Coenzyme A to a 2-carbon fragment.
D) Reduction of NAD+
E) All of these reactions take place during oxidative decarboxylation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the reactions of the citric acid cycle requires FAD as a coenzyme?
A) the conversion of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate
B) the conversion of α-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA
C) the conversion of succinate to fumarate
D) the conversion of malate to oxaloacetate
A) the conversion of isocitrate to α-ketoglutarate
B) the conversion of α-ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA
C) the conversion of succinate to fumarate
D) the conversion of malate to oxaloacetate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When acetyl-CoA reacts with oxaloacetate to form citrate
A) a new carbon-carbon bond is formed
B) an oxidative decarboxylation reaction takes place
C) a dehydration reaction takes place
D) a rearrangement takes place
A) a new carbon-carbon bond is formed
B) an oxidative decarboxylation reaction takes place
C) a dehydration reaction takes place
D) a rearrangement takes place

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Draw the structure of the ultimate organic glycolysis product of α-glucose. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which enzyme catalyzes the reaction shown? 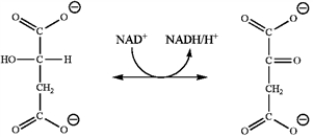
A) isocitrate dehydrogenase
B) malate dehydrogenase
C) fumarase
D) succinate dehydrogenase

A) isocitrate dehydrogenase
B) malate dehydrogenase
C) fumarase
D) succinate dehydrogenase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Match a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.
Embden-Meyerhoff
Embden-Meyerhoff
Pathways that break down larger biomolecules into smaller ones.
A)electron-transport chain
B)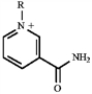
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)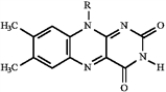
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)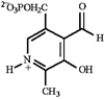
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)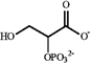
O)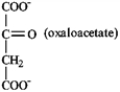
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
Embden-Meyerhoff
Embden-Meyerhoff
Pathways that break down larger biomolecules into smaller ones.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
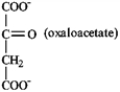
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Match a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.
Embden-Meyerhoff
Embden-Meyerhoff
The product of the citric acid cycle, which is a reactant in the first step.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)
O)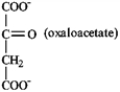
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
Embden-Meyerhoff
Embden-Meyerhoff
The product of the citric acid cycle, which is a reactant in the first step.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
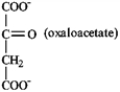
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Match a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.
Embden-Meyerhoff
Embden-Meyerhoff
Uses the energy produced in the citric acid cycle to make ATP.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)
O)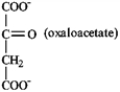
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
Embden-Meyerhoff
Embden-Meyerhoff
Uses the energy produced in the citric acid cycle to make ATP.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
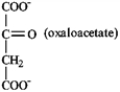
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Match a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.
Embden-Meyerhoff
Embden-Meyerhoff
Acetyl groups are oxidized to yield carbon dioxide and water.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)
O)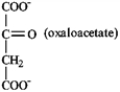
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
Embden-Meyerhoff
Embden-Meyerhoff
Acetyl groups are oxidized to yield carbon dioxide and water.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
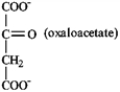
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Match a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.
Embden-Meyerhoff
Embden-Meyerhoff
The pathway by which organisms make glucose from simple precursors.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)
O)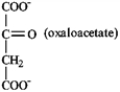
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
Embden-Meyerhoff
Embden-Meyerhoff
The pathway by which organisms make glucose from simple precursors.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
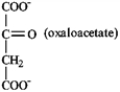
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 45 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



