Deck 16: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/46
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions
1
What is the order of decreasing reactivity towards nucleophilic acyl substitution for the carboxylic acid derivatives? (most reactive first) 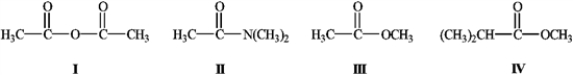
A) I, II, III, IV
B) I, III, IV, II
C) II, IV, III, I
D) II, I, III, IV
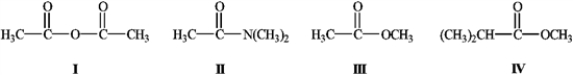
A) I, II, III, IV
B) I, III, IV, II
C) II, IV, III, I
D) II, I, III, IV
I, III, IV, II
2
What is the correct structure for phenylbenzoate?
A)
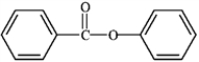
B)
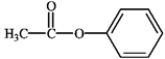
C)
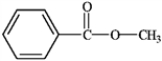
D)
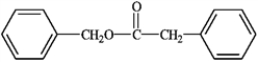
A)

B)

C)

D)
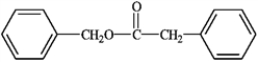

3
Draw the structure of prop-2-enamide.
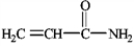
4
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 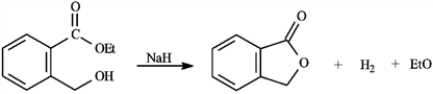
Refer to instructions. The purpose of the base catalyst in this reaction is:
A) to polarize the carbonyl group to make it more electrophilic
B) to convert the ester to an intermediate carboxylic acid
C) to convert the alcohol group to an alkoxide anion, which is a better nucleophile
D) all of these

Refer to instructions. The purpose of the base catalyst in this reaction is:
A) to polarize the carbonyl group to make it more electrophilic
B) to convert the ester to an intermediate carboxylic acid
C) to convert the alcohol group to an alkoxide anion, which is a better nucleophile
D) all of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Consider the information below to answer the following question(s).
The reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of acid is termed a Fischer esterification.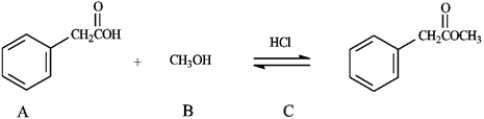
Refer to instructions. What would be the identity of A, B and C needed to produce the following compound?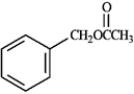
The reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of acid is termed a Fischer esterification.

Refer to instructions. What would be the identity of A, B and C needed to produce the following compound?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Consider the information below to answer the following question(s).
The reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of acid is termed a Fischer esterification.
Refer to instructions. The nucleophile in this reaction is indicated by letter _____.
A)A
B)B
C)C
The reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of acid is termed a Fischer esterification.

Refer to instructions. The nucleophile in this reaction is indicated by letter _____.
A)A
B)B
C)C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Consider the information below to answer the following question(s).
The reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of acid is termed a Fischer esterification.
Refer to instructions. Compound C functions as _____ in this reaction.
A) a base scavenger
B) a solvent
C) a catalyst
D) a neutralizer
The reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol in the presence of acid is termed a Fischer esterification.

Refer to instructions. Compound C functions as _____ in this reaction.
A) a base scavenger
B) a solvent
C) a catalyst
D) a neutralizer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Circle any of the following structures that are not considered to be derivatives of carboxylic acids. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Of the following, which represents a possible direct conversion of the reactant to product shown?
A) ester to acid chloride
B) thioester to acid anhydride
C) ester to amide
D) acid anhydride to acid chloride
A) ester to acid chloride
B) thioester to acid anhydride
C) ester to amide
D) acid anhydride to acid chloride

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Provide IUPAC names for the structures in the following question(s).
Name: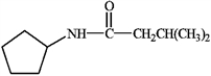
Name:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Rank the following compounds in order of increasing reactivity with a nucleophile. 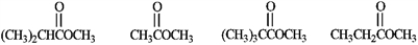
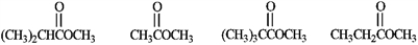

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 
Refer to instructions. The product of this reaction is:
A) a lactone
B) an anhydride
C) a lactam
D) an ether

Refer to instructions. The product of this reaction is:
A) a lactone
B) an anhydride
C) a lactam
D) an ether

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Provide the missing structure(s) or reagent(s) for each reaction or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry.
Provide missing structure(s):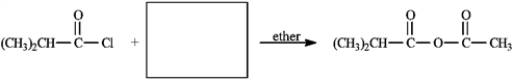
Provide missing structure(s):


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Provide IUPAC names for the structures in the following question(s).
Name: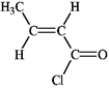
Name:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 
Refer to instructions. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for this reaction. Show intermediate structures and all electron flow with arrows.

Refer to instructions. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for this reaction. Show intermediate structures and all electron flow with arrows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Provide the missing structure(s) or reagent(s) for each reaction or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry.
Provide missing structure(s):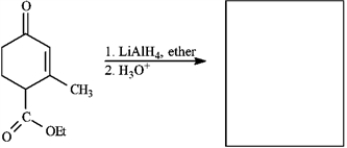
Provide missing structure(s):


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s). 
Refer to instructions. This reaction is an example of:
A) an intermolecular nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction
B) an intramolecular nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction
C) an intermolecular SN2 reaction
D) an intramolecular SN2 reaction

Refer to instructions. This reaction is an example of:
A) an intermolecular nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction
B) an intramolecular nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction
C) an intermolecular SN2 reaction
D) an intramolecular SN2 reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Provide the missing structure(s) or reagent(s) for each reaction or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry.
Provide missing structure(s):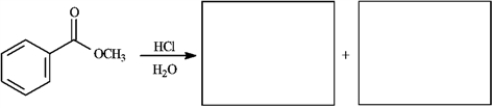
Provide missing structure(s):


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Provide the missing structure(s) or reagent(s) for each reaction or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry.
Provide missing structure(s):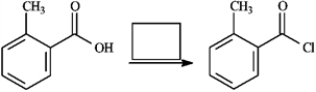
Provide missing structure(s):


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Provide IUPAC names for the structures in the following question(s).
Name: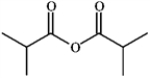
Name:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Tell which spectroscopic technique you would use to distinguish between the two members of the pair. Tell what differences you would expect to see.
Identify spectroscopic technique: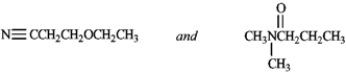
Identify spectroscopic technique:
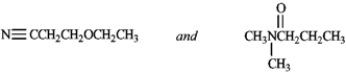

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following compounds is a 2° amide?
A)
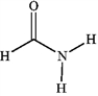
B)
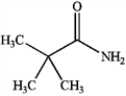
C)
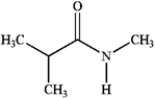
D)
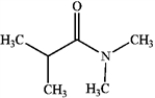
A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The product of the following reaction is a primary essence contained within bananas. 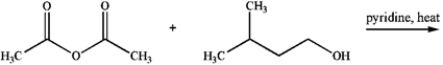 a)Draw its structure.
a)Draw its structure.
b)The product of the above reaction could also be produced by the reaction of an acid and an alcohol. Draw their structures.
 a)Draw its structure.
a)Draw its structure.b)The product of the above reaction could also be produced by the reaction of an acid and an alcohol. Draw their structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Provide the missing structure(s) or reagent(s) for each reaction or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry.
Provide missing structure(s):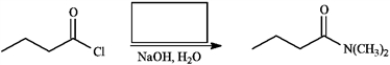
Provide missing structure(s):


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Tell which spectroscopic technique you would use to distinguish between the two members of the pair. Tell what differences you would expect to see.
Identify spectroscopic technique:
Identify spectroscopic technique:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Provide the missing structure(s) or reagent(s) for each reaction or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry.
Provide missing structure(s):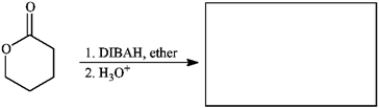
Provide missing structure(s):


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? 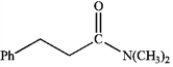
A) dimethylamino 3-phenylpropanoic acid
B) N,N-dimethyl 2-phenylethyl amide
C) N,N-dimethyl 3-phenylpropanamide
D) dimethyl 2-phenylpropanoylamine

A) dimethylamino 3-phenylpropanoic acid
B) N,N-dimethyl 2-phenylethyl amide
C) N,N-dimethyl 3-phenylpropanamide
D) dimethyl 2-phenylpropanoylamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Draw the major product of the following reaction. 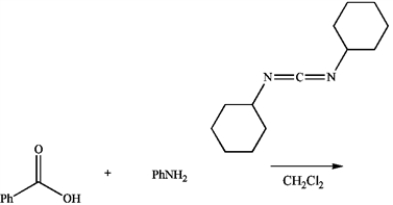


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the major organic product produced by the following reaction? 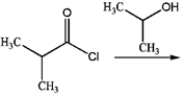
A)
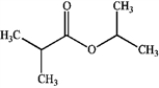
B)
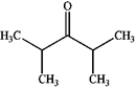
C)
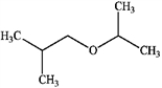
D)
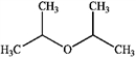

A)

B)

C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is the correct assignment of the classes of the following compounds? 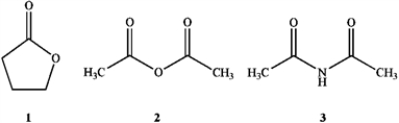
A) 1 = lactone; 2 = ester; 3 = amide
B) 1 = ester; 2 = ester; 3 = imide
C) 1 = ester; 2 = imide; 3 = amide
D) 1 = lactone; 2 = anhydride; 3 = imide

A) 1 = lactone; 2 = ester; 3 = amide
B) 1 = ester; 2 = ester; 3 = imide
C) 1 = ester; 2 = imide; 3 = amide
D) 1 = lactone; 2 = anhydride; 3 = imide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Tell which spectroscopic technique you would use to distinguish between the two members of the pair. Tell what differences you would expect to see.
Identify spectroscopic technique: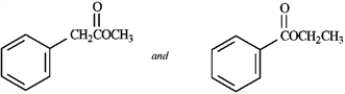
Identify spectroscopic technique:


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Rank the following from highest to lowest reactivity toward reaction with EtOH. 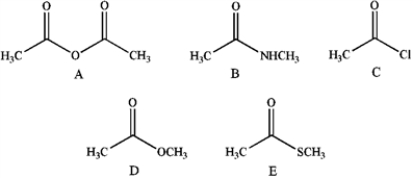


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What is the major organic product produced by the following reaction? 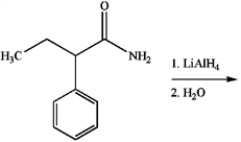


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Draw the major products of the following biochemical reaction (where R = a fatty acid chain). 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds (more acidic > less acidic)? 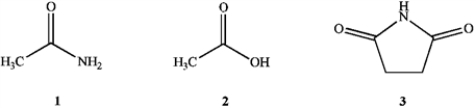
A) 1 > 2 > 3
B) 2 > 3 > 1
C) 1 > 3 > 2
D) 3 > 2 > 1

A) 1 > 2 > 3
B) 2 > 3 > 1
C) 1 > 3 > 2
D) 3 > 2 > 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following best describes the key mechanistic steps in the reaction of an acid chloride and an alcohol to form an ester?
A) elimination followed by addition
B) addition followed by decarboxylation
C) addition followed by elimination
D) substitution followed by addition
A) elimination followed by addition
B) addition followed by decarboxylation
C) addition followed by elimination
D) substitution followed by addition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
What is the correct assignment of the functional groups in the following compounds? 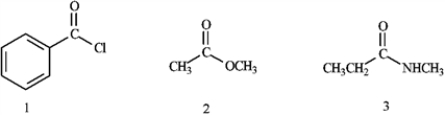
A) 1 = acid chloride; 2 = ester; 3 = nitrile
B) 1 = carboxylic acid; 2 = ester; 3 = imide
C) 1 = acid chloride; 2 = ester; 3 = amide
D) 1 = acid anhydride; 2 = ester; 3 = imide

A) 1 = acid chloride; 2 = ester; 3 = nitrile
B) 1 = carboxylic acid; 2 = ester; 3 = imide
C) 1 = acid chloride; 2 = ester; 3 = amide
D) 1 = acid anhydride; 2 = ester; 3 = imide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the correct assignment of the names of the following substituted benzenes? 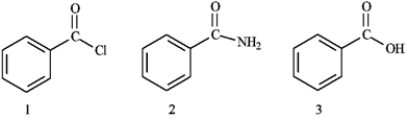
A) 1 = benzoyl chloride; 2 = benzyl amine; 3 = benzyl alcohol
B) 1 = benzyl amine; 2 = benzoyl chloride; 3 = benzamide
C) 1 = benzamide; 2 = benzoyl chloride; 3 = benzoic acid
D) 1 = benzoyl chloride; 2 = benzamide; 3 = benzoic acid

A) 1 = benzoyl chloride; 2 = benzyl amine; 3 = benzyl alcohol
B) 1 = benzyl amine; 2 = benzoyl chloride; 3 = benzamide
C) 1 = benzamide; 2 = benzoyl chloride; 3 = benzoic acid
D) 1 = benzoyl chloride; 2 = benzamide; 3 = benzoic acid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Provide the missing structure(s) or reagent(s) for each reaction or sequences of reactions. Show all relevant stereochemistry.
Provide missing structure(s):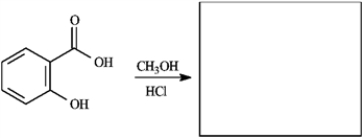
Provide missing structure(s):


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is the correct order of decreasing reactivity in hydrolysis reactions (more reactive > less reactive)?
A) anhydrides > amides > acid chlorides
B) amides > acid chlorides > anhydrides
C) anhydrides > acid chlorides > amides
D) acid chlorides > anhydrides > amides
A) anhydrides > amides > acid chlorides
B) amides > acid chlorides > anhydrides
C) anhydrides > acid chlorides > amides
D) acid chlorides > anhydrides > amides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The two spectra below belong to acetic acid (ethanoic acid) and its isomer, methyl formate (methyl methanoate). Which spectrum corresponds to which compound? Explain your answer. 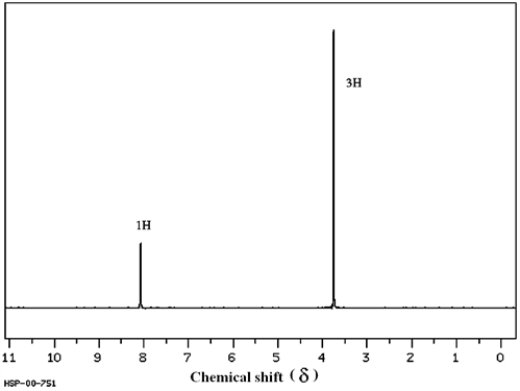
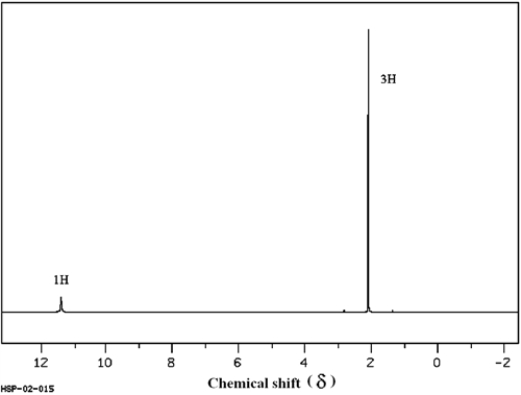 (Spectra obtained from SDBSWeb: http://www.aist.go.jp/RIODB/SDBS)
(Spectra obtained from SDBSWeb: http://www.aist.go.jp/RIODB/SDBS)

 (Spectra obtained from SDBSWeb: http://www.aist.go.jp/RIODB/SDBS)
(Spectra obtained from SDBSWeb: http://www.aist.go.jp/RIODB/SDBS)
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Draw the structure of polymer formed in the following reaction. Show only a single monomer. 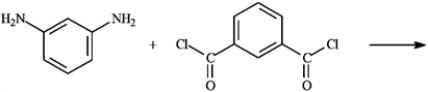


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Draw the major product of the following reaction (which affords a penicillin derivative). 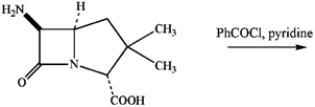


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Draw the structure of the lactone product of the following reaction. 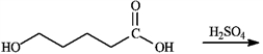


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The following a monomer of the polymer used in biodegradable sutures called Lactomerâ. Upon hydrolysis what product(s) form(s)? Draw the appropriate structure(s). 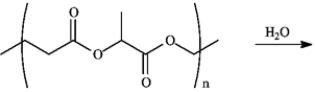


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Draw the structure of polymer formed in the following reaction. Show only a single monomer. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 46 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



