Deck 6: Production
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/123
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Production
1
We manufacturer automobiles given the production function q = 5KL where q is the number of autos assembled per eight-hour shift, K is the number of robots used on the assembly line (capital) and L is the number of workers hired per hour (labor). If we use K=10 robots and L=10 workers in order to produce q = 450 autos per shift, then we know that production is:
A) technologically efficient.
B) technologically inefficient.
C) maximized.
D) optimal.
A) technologically efficient.
B) technologically inefficient.
C) maximized.
D) optimal.
B
2
The short run is
A) less than a year.
B) three years.
C) however long it takes to produce the planned output.
D) a time period in which at least one input is fixed.
E) a time period in which at least one set of outputs has been decided upon.
A) less than a year.
B) three years.
C) however long it takes to produce the planned output.
D) a time period in which at least one input is fixed.
E) a time period in which at least one set of outputs has been decided upon.
D
3
Some economists conduct empirical research on the theory of the firm by measuring the degree of technical efficiency achieved by actual firms. What type of research contributions are provided by these studies?
A) Normative
B) Positive
C) Administrative
D) Executive
A) Normative
B) Positive
C) Administrative
D) Executive
B
4
For many firms, capital is the production input that is typically fixed in the short run. Which of the following firms would face the longest time required to adjust its capital inputs?
A) Firm that makes DVD players.
B) Computer chip fabricator
C) Flat-screen TV manufacturer
D) Nuclear power plant
A) Firm that makes DVD players.
B) Computer chip fabricator
C) Flat-screen TV manufacturer
D) Nuclear power plant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A production function assumes a given
A) technology.
B) set of input prices.
C) ratio of input prices.
D) amount of capital and labor.
E) amount of output.
A) technology.
B) set of input prices.
C) ratio of input prices.
D) amount of capital and labor.
E) amount of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Writing total output as Q, change in output as Q, total labor employment as L, and change in labor employment as L, the marginal product of labor can be written algebraically as
A) Q ∙ L.
B) Q / L.
C) ΔL / ΔQ.
D) ΔQ / ΔL.
A) Q ∙ L.
B) Q / L.
C) ΔL / ΔQ.
D) ΔQ / ΔL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following equations based on capital (K) and labor (L) inputs does not represent a plausible production function?
A) F(K,L) = 3KL
B) F(K,L) = 3K
C) F(K,L) = K + L - 1
D) F(K,L) = 10(KL)0.5
A) F(K,L) = 3KL
B) F(K,L) = 3K
C) F(K,L) = K + L - 1
D) F(K,L) = 10(KL)0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The law of diminishing returns refers to diminishing
A) total returns.
B) marginal returns.
C) average returns.
D) all of these.
A) total returns.
B) marginal returns.
C) average returns.
D) all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A function that indicates the maximum output per unit of time that a firm can produce, for every combination of inputs with a given technology, is called
A) an isoquant.
B) a production possibility curve.
C) a production function.
D) an isocost function.
A) an isoquant.
B) a production possibility curve.
C) a production function.
D) an isocost function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Joe owns a small coffee shop, and his production function is q = 3KL where q is total output in cups per hour, K is the number of coffee machines (capital), and L is the number of employees hired per hour (labor). If Joe's capital is currently fixed at K=3 machines, what is his short-run production function?
A) q = 3L
B) q = 3L2
C) q = 9L
D) q = 3K2
A) q = 3L
B) q = 3L2
C) q = 9L
D) q = 3K2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following inputs are variable in the long run?
A) labor.
B) capital and equipment.
C) plant size.
D) all of these.
A) labor.
B) capital and equipment.
C) plant size.
D) all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Ronald's Outboard Motor Manufacturing plant production function is y(K, L) = 25 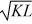
. Ronald is investigating a new outboard motor manufacturing technique. Ronald believes that if he adopts the new technique, his production function for outboard motors will become: y(K, L) = 36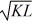
. Given that Ronald uses 4 units of machine hours, sketch his production function with the old technique and the new technique as he increases labor hours. With the new technique, do labor hours contribute more to production?
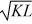
. Ronald is investigating a new outboard motor manufacturing technique. Ronald believes that if he adopts the new technique, his production function for outboard motors will become: y(K, L) = 36
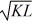
. Given that Ronald uses 4 units of machine hours, sketch his production function with the old technique and the new technique as he increases labor hours. With the new technique, do labor hours contribute more to production?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Use the following two statements to answer this question:
I) Production functions describe what is technically feasible when the firm operates efficiently.
II) The production function shows the least cost method of producing a given level of output.
A) Both I and II are true.
B) I is true, and II is false.
C) I is false, and II is true.
D) Both I and II are false.
I) Production functions describe what is technically feasible when the firm operates efficiently.
II) The production function shows the least cost method of producing a given level of output.
A) Both I and II are true.
B) I is true, and II is false.
C) I is false, and II is true.
D) Both I and II are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Wally describes himself as a resilient fundamentalist when it comes to making investments in the stock market. At the moment, Wally uses only periodicals from the library when analyzing corporate fundamentals. The number of firms he can analyze in a day is given by the function: y(L) = 2 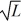
, where L is the number of hours a day he works. Sketch Wally's total number of firms analyzed as he increases his hours of work. If Wally begins using internet sources to learn about corporate fundamentals, the number of firms he can analyze in a day is given by the function: y(L) = 5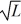
Sketch Wally's total number of firms analyzed as he increases his hours of work and uses the internet.
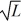
, where L is the number of hours a day he works. Sketch Wally's total number of firms analyzed as he increases his hours of work. If Wally begins using internet sources to learn about corporate fundamentals, the number of firms he can analyze in a day is given by the function: y(L) = 5
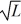
Sketch Wally's total number of firms analyzed as he increases his hours of work and uses the internet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When labor usage is at 12 units, output is 36 units. From this we may infer that
A) the marginal product of labor is 3.
B) the total product of labor is 1/3.
C) the average product of labor is 3.
D) none of the above
A) the marginal product of labor is 3.
B) the total product of labor is 1/3.
C) the average product of labor is 3.
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A farmer uses L units of labor and K units of capital to produce Q units of corn using a production function F(K,L). A production plan that uses K' = L' = 10 to produce Q' units of corn where
Q' < F(10, 10) is said to be
A) technically feasible and efficient.
B) technically unfeasible and efficient.
C) technically feasible and inefficient.
D) technically unfeasible and inefficient.
E) none of the above
Q' < F(10, 10) is said to be
A) technically feasible and efficient.
B) technically unfeasible and efficient.
C) technically feasible and inefficient.
D) technically unfeasible and inefficient.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The slope of the total product curve is the
A) average product.
B) slope of a line from the origin to the point.
C) marginal product.
D) marginal rate of technical substitution.
A) average product.
B) slope of a line from the origin to the point.
C) marginal product.
D) marginal rate of technical substitution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A production function defines the output that can be produced
A) at the lowest cost, given the inputs available.
B) for the average firm.
C) if the firm is technically efficient.
D) in a given time period if no additional inputs are hired.
E) as technology changes over time.
A) at the lowest cost, given the inputs available.
B) for the average firm.
C) if the firm is technically efficient.
D) in a given time period if no additional inputs are hired.
E) as technology changes over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following actions is not an example of the production coordination provided by firms?
A) Manage production activities of workers
B) Pay wages to workers
C) Establish industry safety regulations
D) Set the production schedule for each week
A) Manage production activities of workers
B) Pay wages to workers
C) Establish industry safety regulations
D) Set the production schedule for each week

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Suppose there are ten identical manufacturing firms that produce computer chips with machinery (capital, K) and labor (L), and each firm has a production function of the form q = 10KL0.5. What is the industry-level production function?
A) Q = 10K10L5
B) Q = 100KL0.5
C) Q = 100L0.5
D) none of the above
A) Q = 10K10L5
B) Q = 100KL0.5
C) Q = 100L0.5
D) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Technological improvement
A) can hide the presence of diminishing returns.
B) can be shown as a shift in the total product curve.
C) allows more output to be produced with the same combination of inputs.
D) All of the above are true.
A) can hide the presence of diminishing returns.
B) can be shown as a shift in the total product curve.
C) allows more output to be produced with the same combination of inputs.
D) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The law of diminishing returns applies to
A) the short run only.
B) the long run only.
C) both the short and the long run.
D) neither the short nor the long run.
E) all inputs, with no reference to the time period.
A) the short run only.
B) the long run only.
C) both the short and the long run.
D) neither the short nor the long run.
E) all inputs, with no reference to the time period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
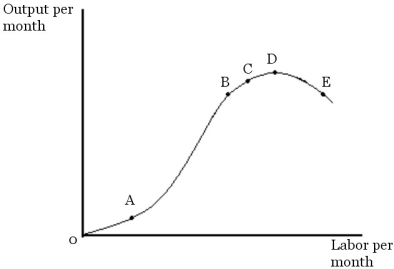 Figure 6.1
Figure 6.1Refer to Figure 6.1. At point C
A) the marginal product of labor is greater than the average product of labor.
B) the average product of labor is greater than the marginal product of labor.
C) the marginal product of labor and the average product of labor are equal.
D) the marginal product of labor and the average product of labor are both increasing.
E) Both B and D are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
At a given level of labor employment, knowing the difference between the average product of labor and the marginal product of labor tells you
A) whether increasing labor use raises output.
B) whether increasing labor use changes the marginal product of labor.
C) whether economies of scale exist.
D) whether the law of diminishing returns applies.
E) how increasing labor use alters the average product of labor.
A) whether increasing labor use raises output.
B) whether increasing labor use changes the marginal product of labor.
C) whether economies of scale exist.
D) whether the law of diminishing returns applies.
E) how increasing labor use alters the average product of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The Malthusian dilemma relates to marginal product in that
A) starvation can be averted only if marginal product is constant.
B) because of diminishing marginal product, the amount of food produced by each additional member of the population increases.
C) because of diminishing marginal product, the amount of food produced by each additional member of the population decreases.
D) because of diminishing marginal product, the wage falls as the population decreases.
E) because of diminishing average product, the population will not have additional capital to work with.
A) starvation can be averted only if marginal product is constant.
B) because of diminishing marginal product, the amount of food produced by each additional member of the population increases.
C) because of diminishing marginal product, the amount of food produced by each additional member of the population decreases.
D) because of diminishing marginal product, the wage falls as the population decreases.
E) because of diminishing average product, the population will not have additional capital to work with.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The marginal product of an input is
A) total product divided by the amount of the input used to produce this amount of output.
B) the addition to total output that adds nothing to total revenue.
C) the addition to total output that adds nothing to profit.
D) the addition to total output due to the addition of one unit of all other inputs.
E) the addition to total output due to the addition of the last unit of an input, holding all other inputs constant.
A) total product divided by the amount of the input used to produce this amount of output.
B) the addition to total output that adds nothing to total revenue.
C) the addition to total output that adds nothing to profit.
D) the addition to total output due to the addition of one unit of all other inputs.
E) the addition to total output due to the addition of the last unit of an input, holding all other inputs constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The law of diminishing returns assumes that
A) there is at least one fixed input.
B) all inputs are changed by the same percentage.
C) additional inputs are added in smaller and smaller increments.
D) all inputs are held constant.
A) there is at least one fixed input.
B) all inputs are changed by the same percentage.
C) additional inputs are added in smaller and smaller increments.
D) all inputs are held constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the following two statements to answer this question:
I) The marginal product of labor is the slope of the line from the origin to the total product curve at that level of labor usage.
II The average product of labor is the slope of the line that is tangent to the total product curve at that level of labor usage.
A) Both I and II are true.
B) I is true, and II is false.
C) I is false, and II is true.
D) Both I and II are false.
I) The marginal product of labor is the slope of the line from the origin to the total product curve at that level of labor usage.
II The average product of labor is the slope of the line that is tangent to the total product curve at that level of labor usage.
A) Both I and II are true.
B) I is true, and II is false.
C) I is false, and II is true.
D) Both I and II are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
According to the law of diminishing returns
A) the total product of an input will eventually be negative.
B) the total product of an input will eventually decline.
C) the marginal product of an input will eventually be negative.
D) the marginal product of an input will eventually decline.
E) none of the above
A) the total product of an input will eventually be negative.
B) the total product of an input will eventually decline.
C) the marginal product of an input will eventually be negative.
D) the marginal product of an input will eventually decline.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In a certain textile firm, labor is the only short term variable input. The manager notices that the marginal product of labor is the same for each unit of labor, which implies that
A) the average product of labor is always greater that the marginal product of labor
B) the average product of labor is always equal to the marginal product of labor
C) the average product of labor is always less than the marginal product of labor
D) as more labor is used, the average product of labor falls
E) there is no unambiguous relationship between labor's marginal and average products.
A) the average product of labor is always greater that the marginal product of labor
B) the average product of labor is always equal to the marginal product of labor
C) the average product of labor is always less than the marginal product of labor
D) as more labor is used, the average product of labor falls
E) there is no unambiguous relationship between labor's marginal and average products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
For consideration of such issues as labor's productivity growth nationwide, the relevant measure is the
A) marginal product of labor.
B) average product of labor.
C) total product of labor.
D) wage.
E) cost of capital.
A) marginal product of labor.
B) average product of labor.
C) total product of labor.
D) wage.
E) cost of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
 Figure 6.1
Figure 6.1Refer to Figure 6.1. Which of the following statements is false?
A) At point E the marginal product of labor is decreasing.
B) At point E the marginal product of labor is negative.
C) At point E the average product of labor is decreasing.
D) At point E the average product of labor is negative.
E) At point E the marginal product of labor is less than the average product of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the law of diminishing returns applies to labor then
A) the marginal product of labor must eventually become negative.
B) the average product of labor must eventually become negative.
C) the marginal product of labor must rise and then fall as employment rises.
D) the average product of labor must rise and then fall as employment increases.
E) after some level of employment, the marginal product of labor must fall.
A) the marginal product of labor must eventually become negative.
B) the average product of labor must eventually become negative.
C) the marginal product of labor must rise and then fall as employment rises.
D) the average product of labor must rise and then fall as employment increases.
E) after some level of employment, the marginal product of labor must fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The link between the productivity of labor and the standard of living is
A) tenuous and changing.
B) inverse.
C) that over the long run, consumers as a whole can increase their rate of consumption only by increasing labor productivity.
D) that over the long run, consumers' rate of consumption is not related to labor productivity.
E) that the productivity of labor grows much more erratically than the standard of living.
A) tenuous and changing.
B) inverse.
C) that over the long run, consumers as a whole can increase their rate of consumption only by increasing labor productivity.
D) that over the long run, consumers' rate of consumption is not related to labor productivity.
E) that the productivity of labor grows much more erratically than the standard of living.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Assume that average product for six workers is fifteen. If the marginal product of the seventh worker is eighteen,
A) marginal product is rising.
B) marginal product is falling.
C) average product is rising.
D) average product is falling.
A) marginal product is rising.
B) marginal product is falling.
C) average product is rising.
D) average product is falling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following ideas were central to the conclusions drawn by Thomas Malthus in his 1798 "Essay on the Principle of Population"?
A) Short-run time period
B) Shortage of labor
C) Law of diminishing resource availability
D) Law of diminishing returns
A) Short-run time period
B) Shortage of labor
C) Law of diminishing resource availability
D) Law of diminishing returns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
 Figure 6.1
Figure 6.1Refer to Figure 6.1. At which point on the total product curve is the average product of labor the highest?
A) point A.
B) point B.
C) point C.
D) point D.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When the average product is decreasing, marginal product
A) equals average product.
B) is increasing.
C) exceeds average product.
D) is decreasing.
E) is less than average product.
A) equals average product.
B) is increasing.
C) exceeds average product.
D) is decreasing.
E) is less than average product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
 Figure 6.1
Figure 6.1Refer to Figure 6.1. At point A, the marginal product of labor is
A) rising.
B) at its minimum.
C) at its maximum.
D) diminishing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Marginal product crosses the horizontal axis (is equal to zero) at the point where
A) average product is maximized.
B) total product is maximized.
C) diminishing returns set in.
D) output per worker reaches a maximum.
E) All of the above are true.
A) average product is maximized.
B) total product is maximized.
C) diminishing returns set in.
D) output per worker reaches a maximum.
E) All of the above are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which would not increase the productivity of labor?
A) An increase in the size of the labor force
B) An increase in the quality of capital
C) An increase in the quantity of capital
D) An increase in technology
E) An increase in the efficiency of energy
A) An increase in the size of the labor force
B) An increase in the quality of capital
C) An increase in the quantity of capital
D) An increase in technology
E) An increase in the efficiency of energy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following statements does not explain why US health care expenditures are higher than in other countries?
A) Government policies have shifted the health care production function downward over time.
B) Consumer incomes have increased, which allows consumers to purchase more health care.
C) The US health care system is relatively inefficient compared to other countries.
D) Demand for health care in the US has increased, so health care production occurs at a higher point on the total product curve than in other countries.
A) Government policies have shifted the health care production function downward over time.
B) Consumer incomes have increased, which allows consumers to purchase more health care.
C) The US health care system is relatively inefficient compared to other countries.
D) Demand for health care in the US has increased, so health care production occurs at a higher point on the total product curve than in other countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Tad's Baitshop currently uses no computers in determining inventory. The number of items that can be inventoried in a day is given by y(L) = 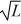
, where L is the number of labor hours used. If Tad purchases a computer to be used for inventory purposes, the number of items that can be inventoried in a day becomes y(L) = 2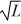
. Use the information in the table below to sketch Tad's marginal product of labor curves before and after the use of the computer for inventory purposes.
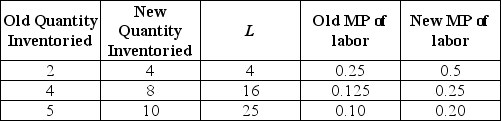
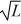
, where L is the number of labor hours used. If Tad purchases a computer to be used for inventory purposes, the number of items that can be inventoried in a day becomes y(L) = 2
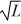
. Use the information in the table below to sketch Tad's marginal product of labor curves before and after the use of the computer for inventory purposes.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An important factor that contributes to labor productivity growth is:
A) growth in the capital stock.
B) technological change.
C) the standard of living.
D) A and B only
E) A, B, and C are correct.
A) growth in the capital stock.
B) technological change.
C) the standard of living.
D) A and B only
E) A, B, and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
One of the factors contributing to the fact that labor productivity is higher in the U.S. than in the People's Republic of China is
A) China's larger stock of capital.
B) the higher capital/labor ratio in China.
C) the higher capital/labor ratio in the U.S.
D) China's smaller stock of fossil fuels.
E) the fact that much labor in the U.S. is in management.
A) China's larger stock of capital.
B) the higher capital/labor ratio in China.
C) the higher capital/labor ratio in the U.S.
D) China's smaller stock of fossil fuels.
E) the fact that much labor in the U.S. is in management.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The production function for Cogswell Cogs is y(K, L) = 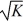
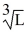
. K represents the number of robot hours used in the production process while L represents the number of labor hours. The marginal productivity of a labor hour is MPL =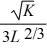
Fill in the empty columns in the table below. Use the information in the table to sketch Cogswell's marginal product of labor curve while robot hours are fixed at 9.
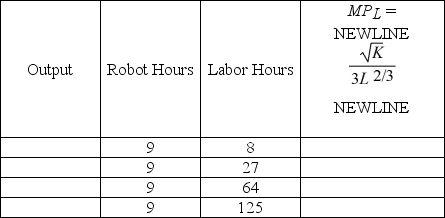
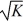
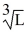
. K represents the number of robot hours used in the production process while L represents the number of labor hours. The marginal productivity of a labor hour is MPL =
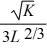
Fill in the empty columns in the table below. Use the information in the table to sketch Cogswell's marginal product of labor curve while robot hours are fixed at 9.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The concerns about world food production raised by Malthus have not materialized because:
A) input prices have fallen over time.
B) crop prices have risen over time.
C) Malthus was wrong about the diminishing returns to labor in agriculture.
D) technological improvements have increased our ability to produce food over time.
A) input prices have fallen over time.
B) crop prices have risen over time.
C) Malthus was wrong about the diminishing returns to labor in agriculture.
D) technological improvements have increased our ability to produce food over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Joe owns a coffee house and produces coffee drinks under the production function q = 5KL where q is the number of cups generated per hour, K is the number of coffee machines (capital), and L is the number of employees hired per hour (labor). What is the average product of labor?
A) AP = 5
B) AP = 5K
C) AP = 5L
D) AP = 5K/L
A) AP = 5
B) AP = 5K
C) AP = 5L
D) AP = 5K/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
You operate a car detailing business with a fixed amount of machinery (capital), but you have recently altered the number of workers that you employ per hour. As you increased the number of employees hired per hour from three to five, your total output increased by 5 cars to 15 cars per hour. What is the average product of labor at the new levels of labor?
A) AP = 3 cars per worker
B) AP = 5 cars per worker
C) AP = 4 cars per worker
D) We do not have enough information to answer this question.
A) AP = 3 cars per worker
B) AP = 5 cars per worker
C) AP = 4 cars per worker
D) We do not have enough information to answer this question.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A bakery operating in the short run has found that when the level of employment in its baking room was increased from 4 to 10, in increments of one, its corresponding levels of production of bread were 110, 115, 122, 127, 130, 132, and 133.
a. Calculate the marginal product of labor.
b. Explain whether this production function exhibits diminishing marginal productivity of labor.
a. Calculate the marginal product of labor.
b. Explain whether this production function exhibits diminishing marginal productivity of labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The production function of pizzas for One Guy's Pizza shop is y(K, L) = 4 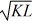
. K represents the number of ovens One Guy's Pizza uses and is fixed in the short-run at 4 ovens. L represents the number of labor hours One Guy's Pizza employees and is variable in the short and long-run. Fill in the empty columns in the table below.
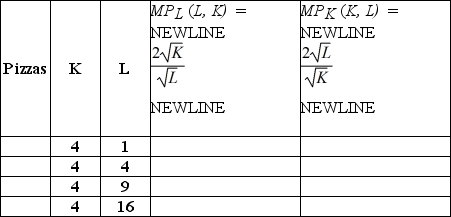
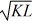
. K represents the number of ovens One Guy's Pizza uses and is fixed in the short-run at 4 ovens. L represents the number of labor hours One Guy's Pizza employees and is variable in the short and long-run. Fill in the empty columns in the table below.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Consider the following statements when answering this question;
I) Suppose a semiconductor chip factory uses a technology where the average product of labor is constant for all employment levels. This technology obeys the law of diminishing returns.
II) Suppose a semiconductor chip factory uses a technology where the marginal product of labor rises, then is constant and finally falls as employment increases. This technology obeys the law of diminishing returns.
A) I is true, and II is false.
B) I is false, and II is true.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Both I and II are false.
I) Suppose a semiconductor chip factory uses a technology where the average product of labor is constant for all employment levels. This technology obeys the law of diminishing returns.
II) Suppose a semiconductor chip factory uses a technology where the marginal product of labor rises, then is constant and finally falls as employment increases. This technology obeys the law of diminishing returns.
A) I is true, and II is false.
B) I is false, and II is true.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Both I and II are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Complete the following table: 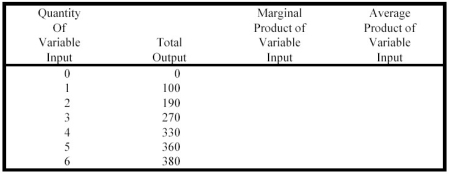


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Joe owns a coffee house and produces coffee drinks under the production function q = 5KL where q is the number of cups generated per hour, K is the number of coffee machines (capital), and L is the number of employees hired per hour (labor). The average product of labor and the marginal product of labor are both equal to AP = MP = 5K. Does labor exhibit diminishing marginal returns in this case?
A) Yes, if capital also exhibits diminishing marginal returns.
B) Yes, this is true for all values of K.
C) No, the marginal product of labor is constant (for a given K).
D) No, the marginal product of labor is increasing (for a given K).
A) Yes, if capital also exhibits diminishing marginal returns.
B) Yes, this is true for all values of K.
C) No, the marginal product of labor is constant (for a given K).
D) No, the marginal product of labor is increasing (for a given K).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
You operate a car detailing business with a fixed amount of machinery (capital), but you have recently altered the number of workers that you employ per hour. Three employees can generate an average product of 4 cars per person in each hour, and five employees can generate an average product of 3 cars per person in each hour. What is the marginal product of labor as you increase the labor from three to five employees?
A) MP = 3 cars
B) MP = 1.5 cars
C) MP = 15 cars
D) MP = -1 cars
A) MP = 3 cars
B) MP = 1.5 cars
C) MP = 15 cars
D) MP = -1 cars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
As an economy recovers from a recession, the observed level of labor productivity tends to decline. Why?
A) The total product remains the same during the recovery, but the number of workers declines.
B) The total product increases during the recovery, but the number of workers declines.
C) The marginal product of labor declines as new workers enter the expanding work force.
D) The marginal product of labor increases at a slower rate than the decline in employment.
A) The total product remains the same during the recovery, but the number of workers declines.
B) The total product increases during the recovery, but the number of workers declines.
C) The marginal product of labor declines as new workers enter the expanding work force.
D) The marginal product of labor increases at a slower rate than the decline in employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Joe owns a coffee house and produces coffee drinks under the production function q = 5KL where q is the number of cups generated per hour, K is the number of coffee machines (capital), and L is the number of employees hired per hour (labor). What is the marginal product of labor?
A) MP = 5
B) MP = 5K
C) MP = 5L
D) MP = 5K/L
A) MP = 5
B) MP = 5K
C) MP = 5L
D) MP = 5K/L

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Consider the following statements when answering this question;
I) Whenever the marginal product of labor curve is a downward sloping curve, the average product of labor curve is also a downward sloping curve that lies above the marginal product of labor curve.
II) If a firm uses only labor to produce, and the production function is given by a straight line, then the marginal product of labor always equals the average product of labor as labor employment expands.
A) I is true, and II is false.
B) I is false, and II is true.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Both I and II are false.
I) Whenever the marginal product of labor curve is a downward sloping curve, the average product of labor curve is also a downward sloping curve that lies above the marginal product of labor curve.
II) If a firm uses only labor to produce, and the production function is given by a straight line, then the marginal product of labor always equals the average product of labor as labor employment expands.
A) I is true, and II is false.
B) I is false, and II is true.
C) Both I and II are true.
D) Both I and II are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Complete the following table: 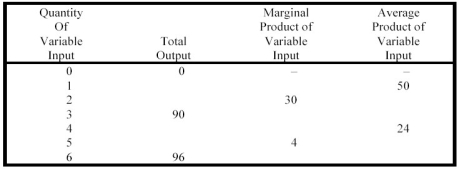


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What describes the graphical relationship between average product and marginal product?
A) Average product cuts marginal product from above, at the maximum point of marginal product.
B) Average product cuts marginal product from below, at the maximum point of marginal product.
C) Marginal product cuts average product from above, at the maximum point of average product.
D) Marginal product cuts average product from below, at the maximum point of average product.
E) Average and marginal product do not intersect.
A) Average product cuts marginal product from above, at the maximum point of marginal product.
B) Average product cuts marginal product from below, at the maximum point of marginal product.
C) Marginal product cuts average product from above, at the maximum point of average product.
D) Marginal product cuts average product from below, at the maximum point of average product.
E) Average and marginal product do not intersect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The function which shows combinations of inputs that yield the same output is called a(n)
A) isoquant curve.
B) isocost curve.
C) production function.
D) production possibilities frontier.
A) isoquant curve.
B) isocost curve.
C) production function.
D) production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A production function in which the inputs are perfectly substitutable would have isoquants that are
A) convex to the origin.
B) L-shaped.
C) linear.
D) concave to the origin.
A) convex to the origin.
B) L-shaped.
C) linear.
D) concave to the origin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the following two statements to answer this question:
I) Isoquants cannot cross one another.
II) An isoquant that is twice the distance from the origin represents twice the level of output.
A) Both I and II are true.
B) I is true, and II is false.
C) I is false, and II is true.
D) Both I and II are false.
I) Isoquants cannot cross one another.
II) An isoquant that is twice the distance from the origin represents twice the level of output.
A) Both I and II are true.
B) I is true, and II is false.
C) I is false, and II is true.
D) Both I and II are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
If we take the production function and hold the level of output constant, allowing the amounts of capital and labor to vary, the curve that is traced out is called:
A) the total product.
B) an isoquant.
C) the average product.
D) the marginal product.
E) none of the above
A) the total product.
B) an isoquant.
C) the average product.
D) the marginal product.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
An upward sloping isoquant
A) can be derived from a production function with one input
B) can be derived from a production function that uses more than one input where reductions in the use of any input always reduces output
C) cannot be derived from a production function when a firm is assumed to maximize profits
D) can be derived whenever one input to production is available at zero cost to the firm
E) none of the above
A) can be derived from a production function with one input
B) can be derived from a production function that uses more than one input where reductions in the use of any input always reduces output
C) cannot be derived from a production function when a firm is assumed to maximize profits
D) can be derived whenever one input to production is available at zero cost to the firm
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Sarah's Pretzel Plant produces pretzels according to the function y(K, L) = 100 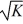
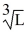
. K is the number of ovens, and L is the number of labor hours Sarah uses to produce her pretzels. At the moment, Sarah uses 9 ovens. Also, she plans to hire 64 labor hours. Sarah can sell each unit of pretzels produced for $3.50. Fill in the table below. If Sarah increased her use of labor hours to 65, would the value of the marginal product of labor exceed the wage rate of $8.50?
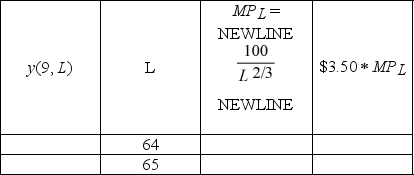
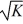
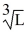
. K is the number of ovens, and L is the number of labor hours Sarah uses to produce her pretzels. At the moment, Sarah uses 9 ovens. Also, she plans to hire 64 labor hours. Sarah can sell each unit of pretzels produced for $3.50. Fill in the table below. If Sarah increased her use of labor hours to 65, would the value of the marginal product of labor exceed the wage rate of $8.50?


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
As we move downward along a typical isoquant, the slope of the isoquant
A) becomes flatter.
B) becomes steeper.
C) remains constant.
D) becomes linear.
A) becomes flatter.
B) becomes steeper.
C) remains constant.
D) becomes linear.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If capital is measured on the vertical axis and labor is measured on the horizontal axis, the slope of an isoquant can be interpreted as the
A) rate at which the firm can replace capital with labor without changing the output rate.
B) average rate at which the firm can replace capital with labor without changing the output rate.
C) marginal product of labor.
D) marginal product of capital.
A) rate at which the firm can replace capital with labor without changing the output rate.
B) average rate at which the firm can replace capital with labor without changing the output rate.
C) marginal product of labor.
D) marginal product of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
An examination of the production isoquants in the diagram below reveals that: 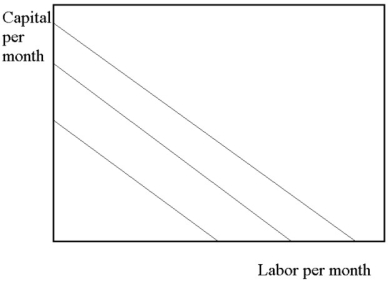
A) capital and labor must be used in fixed proportions.
B) capital and labor are perfectly substitutable.
C) except at the corners of the isoquants the MRTS is constant.
D) Both B and C are correct.
E) none of the above

A) capital and labor must be used in fixed proportions.
B) capital and labor are perfectly substitutable.
C) except at the corners of the isoquants the MRTS is constant.
D) Both B and C are correct.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the following two statements to answer this question:
I) If the marginal product of labor is zero, the total product of labor is at its maximum.
II If the marginal product of labor is at its maximum, the average product of labor is falling.
A) Both I and II are true.
B) I is true, and II is false.
C) I is false, and II is true.
D) Both I and II are false.
I) If the marginal product of labor is zero, the total product of labor is at its maximum.
II If the marginal product of labor is at its maximum, the average product of labor is falling.
A) Both I and II are true.
B) I is true, and II is false.
C) I is false, and II is true.
D) Both I and II are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
An examination of the production isoquants in the diagram below reveals that: 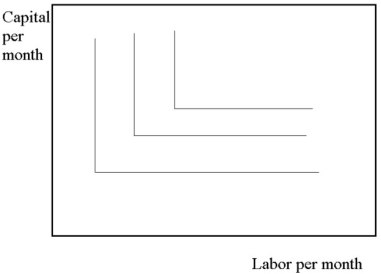
A) capital and labor will be used in fixed proportions.
B) capital and labor are perfectly substitutable.
C) the MRTS is constant.
D) Both B and C are correct.
E) none of the above

A) capital and labor will be used in fixed proportions.
B) capital and labor are perfectly substitutable.
C) the MRTS is constant.
D) Both B and C are correct.
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
If the isoquants are straight lines, then
A) inputs have fixed costs at all use rates.
B) the marginal rate of technical substitution of inputs is constant.
C) only one combination of inputs is possible.
D) there are constant returns to scale.
A) inputs have fixed costs at all use rates.
B) the marginal rate of technical substitution of inputs is constant.
C) only one combination of inputs is possible.
D) there are constant returns to scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the following statements to answer this question.
I) The numerical labels attached to indifference curves are meaningful only in an ordinal way.
II) The numerical labels attached to isoquants are meaningful only in an ordinal way.
A) both I and II are true.
B) I is true, and II is false.
C) I is false, and II is true.
D) both I and II are false.
I) The numerical labels attached to indifference curves are meaningful only in an ordinal way.
II) The numerical labels attached to isoquants are meaningful only in an ordinal way.
A) both I and II are true.
B) I is true, and II is false.
C) I is false, and II is true.
D) both I and II are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A firm uses two factors of production. Irrespective of how much of each factor is used, both factors always have positive marginal products which imply that
A) isoquants are relevant only in the long run
B) isoquants have negative slope
C) isoquants are convex
D) isoquants can become vertical or horizontal
E) none of the above
A) isoquants are relevant only in the long run
B) isoquants have negative slope
C) isoquants are convex
D) isoquants can become vertical or horizontal
E) none of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
An isoquant
A) must be linear.
B) cannot have a negative slope.
C) is a curve that shows all the combinations of inputs that yield the same total output.
D) is a curve that shows the maximum total output as a function of the level of labor input.
E) is a curve that shows all possible output levels that can be produced at the same cost.
A) must be linear.
B) cannot have a negative slope.
C) is a curve that shows all the combinations of inputs that yield the same total output.
D) is a curve that shows the maximum total output as a function of the level of labor input.
E) is a curve that shows all possible output levels that can be produced at the same cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Two isoquants, which represent different output levels but are derived from the same production function, cannot cross because
A) isoquants represent different utility levels
B) this would violate a technical efficiency condition
C) isoquants are downward sloping
D) additional inputs will not be used by profit maximizing firms if those inputs decrease output
E) Both B and D are true.
A) isoquants represent different utility levels
B) this would violate a technical efficiency condition
C) isoquants are downward sloping
D) additional inputs will not be used by profit maximizing firms if those inputs decrease output
E) Both B and D are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The marginal rate of technical substitution is equal to the
A) slope of the total product curve.
B) change in output minus the change in labor.
C) change in output divided by the change in labor.
D) ratio of the marginal products of the inputs.
A) slope of the total product curve.
B) change in output minus the change in labor.
C) change in output divided by the change in labor.
D) ratio of the marginal products of the inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The rate at which one input can be reduced per additional unit of the other input, while holding output constant, is measured by the
A) marginal rate of substitution.
B) marginal rate of technical substitution.
C) slope of the isocost curve.
D) average product of the input.
A) marginal rate of substitution.
B) marginal rate of technical substitution.
C) slope of the isocost curve.
D) average product of the input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Trisha's Fashion Boutique production function for dresses is y(K, L) = K1/2L1/3, where K is the number of sewing machines and L is the amount of labor hours employed. Trisha pays $15 per labor hour and sells each dress for $87.50. Also, Trisha currently has 4 sewing machines. Fill in the table below. How many units of labor will Trisha employ before the value of the marginal product of labor is less than the cost of a labor hour?
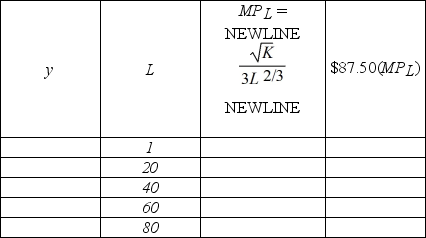


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Laura's Internet Services firm can design computer systems according to the function y(K, L) = 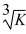
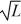
, where K is the amount of gigabyte storage she has available and L is the amount of labor hours she employs. Currently, Laura has 125 gigabytes of storage. Sketch the change in the marginal product of labor curve for Laura's firm for values of L= 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, if she increases her gigabyte storage capacity to 216.
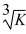
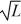
, where K is the amount of gigabyte storage she has available and L is the amount of labor hours she employs. Currently, Laura has 125 gigabytes of storage. Sketch the change in the marginal product of labor curve for Laura's firm for values of L= 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, if she increases her gigabyte storage capacity to 216.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 123 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



