Deck 2: Solar Energy to Earth and the Seasons
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/83
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Solar Energy to Earth and the Seasons
1
Earth's orbit around the Sun
A)is perfectly circular.
B)is elliptical.
C)has been constant since the birth of the Solar System.
D)results in a constant distance from the Sun throughout the year.
E)takes approximately the same amount of time as the orbit of other planets around the Sun.
A)is perfectly circular.
B)is elliptical.
C)has been constant since the birth of the Solar System.
D)results in a constant distance from the Sun throughout the year.
E)takes approximately the same amount of time as the orbit of other planets around the Sun.
B
2
On its way to Earth,solar winds first encounter
A)the ionosphere.
B)the lower atmosphere.
C)the stratosphere.
D)the magnetosphere.
E)Earth's surface.
A)the ionosphere.
B)the lower atmosphere.
C)the stratosphere.
D)the magnetosphere.
E)Earth's surface.
D
3
The basic idea behind the planetesimal hypothesis is that
A)small grains of cosmic dust and other solids gradual accrete to form planetesimals that may grow to become protoplanets and eventually planets.
B)cosmic debris from the Big Bang coalesced to form planets as they neared the gravitational pull of the Sun.
C)planets form as a direct result of the nuclear fusion of nebular gases.
D)early in the Solar System's history,a star passed near the Sun and pulled off gases that eventually condensed to form planets.
E)planets form from the remains of super-giant planetesimals that blow apart,thereby creating smaller objects-the planets.
A)small grains of cosmic dust and other solids gradual accrete to form planetesimals that may grow to become protoplanets and eventually planets.
B)cosmic debris from the Big Bang coalesced to form planets as they neared the gravitational pull of the Sun.
C)planets form as a direct result of the nuclear fusion of nebular gases.
D)early in the Solar System's history,a star passed near the Sun and pulled off gases that eventually condensed to form planets.
E)planets form from the remains of super-giant planetesimals that blow apart,thereby creating smaller objects-the planets.
A
4
Our Solar System is embedded in the _ of the Milky Way.
A)Scutum-Centaurus Arm
B)Perseus Arm
C)Cygnus X complex
D)Orion Spur of the Sagittarius Arm
E)Vela Molecular Ridge
A)Scutum-Centaurus Arm
B)Perseus Arm
C)Cygnus X complex
D)Orion Spur of the Sagittarius Arm
E)Vela Molecular Ridge

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The electromagnetic spectrum encompasses
A)all possible wavelengths of electromagnetic energy.
B)only radiant energy within the visible light wavelength range.
C)thermal infrared through radiowaves only.
D)those wavelengths of electromagnetic energy greater than 3.00 μm.
E)those wavelengths of electromagnetic energy smaller than 0.01 μm.
A)all possible wavelengths of electromagnetic energy.
B)only radiant energy within the visible light wavelength range.
C)thermal infrared through radiowaves only.
D)those wavelengths of electromagnetic energy greater than 3.00 μm.
E)those wavelengths of electromagnetic energy smaller than 0.01 μm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The auroras in the upper atmosphere are caused by
A)UV and visible light interaction with the asthenosphere.
B)interaction of the solar wind and upper layers of Earth's atmosphere.
C)sun spot activity and gravitational accretion.
D)coronal mass ejections entering the atmosphere at lower latitudes (below 30°).
E)stratospheric ozone depletion.
A)UV and visible light interaction with the asthenosphere.
B)interaction of the solar wind and upper layers of Earth's atmosphere.
C)sun spot activity and gravitational accretion.
D)coronal mass ejections entering the atmosphere at lower latitudes (below 30°).
E)stratospheric ozone depletion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is not true about the Milky Way Galaxy in which we live?
A)It is one of millions of galaxies in the universe.
B)It is the largest galaxy in the universe.
C)It is a spiral-shaped galaxy.
D)It contains approximately 300 billion stars.
E)A supermassive black hole sits in the galactic center.
A)It is one of millions of galaxies in the universe.
B)It is the largest galaxy in the universe.
C)It is a spiral-shaped galaxy.
D)It contains approximately 300 billion stars.
E)A supermassive black hole sits in the galactic center.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The sun emits radiant energy composed of
A)mainly visible light and infrared energy.
B)mainly ultraviolet and X-rays.
C)thermal infrared through radiowaves only.
D)only radiant energy within the visible light wavelength range.
E)those wavelengths of electromagnetic energy smaller than 0.01 μm.
A)mainly visible light and infrared energy.
B)mainly ultraviolet and X-rays.
C)thermal infrared through radiowaves only.
D)only radiant energy within the visible light wavelength range.
E)those wavelengths of electromagnetic energy smaller than 0.01 μm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A surface disturbance on the Sun's surface caused by magnetic storms is called a(n)
A)magnetic cyclone.
B)aurora.
C)solar wind.
D)sunspot.
E)electromagnetic spectrum.
A)magnetic cyclone.
B)aurora.
C)solar wind.
D)sunspot.
E)electromagnetic spectrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Earth and the Sun formed specifically from
A)black holes.
B)unknown origins.
C)a nebula of dust and gases.
D)the Milky Way Galaxy.
E)other planets.
A)black holes.
B)unknown origins.
C)a nebula of dust and gases.
D)the Milky Way Galaxy.
E)other planets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following about the Sun is false?
A)The Sun is the largest star in the Milky Way Galaxy.
B)The principal outputs of the Sun consists of solar wind and radiant energy.
C)The Sun produces energy through fusion.
D)The Sun has average temperature,size,and color when compared to other Stars in our galaxy.
E)The Sun and Solar System are part of the Milky Way Galaxy.
A)The Sun is the largest star in the Milky Way Galaxy.
B)The principal outputs of the Sun consists of solar wind and radiant energy.
C)The Sun produces energy through fusion.
D)The Sun has average temperature,size,and color when compared to other Stars in our galaxy.
E)The Sun and Solar System are part of the Milky Way Galaxy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following is true?
A)The Sun is also a planet.
B)The Milky Way Galaxy contains over 300 million stars.
C)Earth is the fourth planet from the Sun in our Solar System.
D)The Sun is the largest star in the Milky Way Galaxy.
E)The Milky Way is part of our Solar System
A)The Sun is also a planet.
B)The Milky Way Galaxy contains over 300 million stars.
C)Earth is the fourth planet from the Sun in our Solar System.
D)The Sun is the largest star in the Milky Way Galaxy.
E)The Milky Way is part of our Solar System

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The Goldilocks zone is best described as
A)any area on a planet in our solar system in ample solar radiation is received,enabling conditions in which rudimentary life may yet evolve.
B)the regions on Earth that receives the "just right" combination of solar energy and precipitation,enabling life to flourish.
C)an area of orbit about a star where conditions make it "just right" for living organisms,i.e.a habitable zone.
D)orbital zones in other solar systems in which the "three bears," i.e.a star,a moon,and an Earth-sized planet are found.
E)regions of space in which Earth-size planets are found and,therefore,may be "just right" for human colonization.
A)any area on a planet in our solar system in ample solar radiation is received,enabling conditions in which rudimentary life may yet evolve.
B)the regions on Earth that receives the "just right" combination of solar energy and precipitation,enabling life to flourish.
C)an area of orbit about a star where conditions make it "just right" for living organisms,i.e.a habitable zone.
D)orbital zones in other solar systems in which the "three bears," i.e.a star,a moon,and an Earth-sized planet are found.
E)regions of space in which Earth-size planets are found and,therefore,may be "just right" for human colonization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following does not accurately describe Earth's distance from the Sun?
A)Earth is closest to the Sun in January (perihelion).
B)The Earth-Sun distance averages 150 million kilometers (93 million miles).
C)Due to Earth's circular orbit,it is always equidistant from the sun throughout the year.
D)Earth is farthest away from the Sun in July (aphelion).
E)It takes light an average of 8 minutes and 20 seconds to travel from the Sun to Earth.
A)Earth is closest to the Sun in January (perihelion).
B)The Earth-Sun distance averages 150 million kilometers (93 million miles).
C)Due to Earth's circular orbit,it is always equidistant from the sun throughout the year.
D)Earth is farthest away from the Sun in July (aphelion).
E)It takes light an average of 8 minutes and 20 seconds to travel from the Sun to Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is not true of sunspots?
A)More sunspots indicate increased solar radiation.
B)Sunspots are brighter than the rest of the Sun's surface.
C)Sunspots can be up to 12 times larger than Earth.
D)Sunspots are surface disturbances caused by magnetic storms.
E)Sunspots can produce flares and prominences.
A)More sunspots indicate increased solar radiation.
B)Sunspots are brighter than the rest of the Sun's surface.
C)Sunspots can be up to 12 times larger than Earth.
D)Sunspots are surface disturbances caused by magnetic storms.
E)Sunspots can produce flares and prominences.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
On average,solar maximums occur every .
A)32 years
B)365 days
C)182 days
D)11 years
E)300 years
A)32 years
B)365 days
C)182 days
D)11 years
E)300 years

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The planetesimal hypothesis pertains to the formation of the
A)ocean basins.
B)universe.
C)galaxies.
D)planets.
E)black holes.
A)ocean basins.
B)universe.
C)galaxies.
D)planets.
E)black holes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Light travels at a speed of approximately
A)80,500 kilometers per minute (50,000 miles per minute).
B)80,500 kilometers per hour (50,000 mph).
C)300,000 kilometers per hour (186,336 mph).
D)1,000,000,000 kilometers per second (621,118,012 miles per second).
E)300,000 kilometers per second (186,333 miles per second).
A)80,500 kilometers per minute (50,000 miles per minute).
B)80,500 kilometers per hour (50,000 mph).
C)300,000 kilometers per hour (186,336 mph).
D)1,000,000,000 kilometers per second (621,118,012 miles per second).
E)300,000 kilometers per second (186,333 miles per second).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Most of the processes in our biosphere are fueled by
A)energy derived from inside Earth.
B)radiant energy from the Sun.
C)tidal action of the Oceans and large lakes.
D)the moon.
E)utilities and oil companies.
A)energy derived from inside Earth.
B)radiant energy from the Sun.
C)tidal action of the Oceans and large lakes.
D)the moon.
E)utilities and oil companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Earth's magnetosphere is generated by
A)nuclear fission in Earth's core.
B)nuclear fusion in Earth's core.
C)dynamo-like motions in Earth's interior.
D)gravitational accretion.
E)sun spot activity.
A)nuclear fission in Earth's core.
B)nuclear fusion in Earth's core.
C)dynamo-like motions in Earth's interior.
D)gravitational accretion.
E)sun spot activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Solar radiation that is intercept by Earth is called
A)insolation.
B)thermopause.
C)thermal infrared radiation.
D)solar constant.
E)solar wind.
A)insolation.
B)thermopause.
C)thermal infrared radiation.
D)solar constant.
E)solar wind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The term "net radiation" refers to the
A)total amount of energy radiated by Earth.
B)total amount of energy received by Earth.
C)difference in the amount of incoming and outgoing radiation.
D)variations in insolation latitudinally due to solar wind activity.
E)variations in insolation latitudinally due to sun spot cycles.
A)total amount of energy radiated by Earth.
B)total amount of energy received by Earth.
C)difference in the amount of incoming and outgoing radiation.
D)variations in insolation latitudinally due to solar wind activity.
E)variations in insolation latitudinally due to sun spot cycles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
refers to changes in daylength and the Sun's altitude over the course of the year.
A)Sphericity
B)Declination
C)Eccentricty
D)Parallelism
E)Seasonality
A)Sphericity
B)Declination
C)Eccentricty
D)Parallelism
E)Seasonality

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
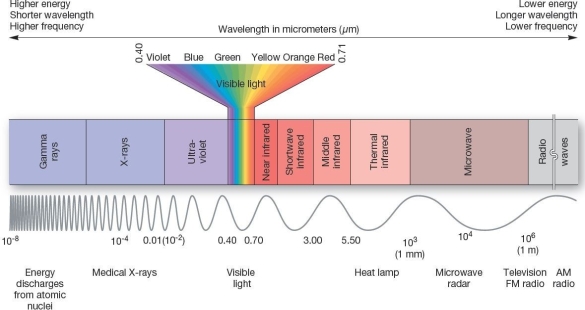 A portion of the electromagnetic spectrum of radiant energy from the Sun Which of the following is characterized by the longest wavelengths
A portion of the electromagnetic spectrum of radiant energy from the Sun Which of the following is characterized by the longest wavelengthsA)X-rays
B)thermal infrared
C)radio waves
D)gamma rays
E)visible

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
is a measure of the average kinetic energy of individual molecules in matter.
A)Heat
B)Visible light
C)Temperature
D)Electromagnetic radiation
E)Thermal infrared through radiation
A)Heat
B)Visible light
C)Temperature
D)Electromagnetic radiation
E)Thermal infrared through radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The dominant wavelength emitted by Earth is
A)visible light.
B)X-ray radiation.
C)infrared.
D)gamma radiation.
E)microwave.
A)visible light.
B)X-ray radiation.
C)infrared.
D)gamma radiation.
E)microwave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What is the name of the location on Earth's surface that receives the Sun's perpendicular rays?
A)zenith
B)sun spot
C)azimuth
D)subsolar point
E)solar constant
A)zenith
B)sun spot
C)azimuth
D)subsolar point
E)solar constant

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
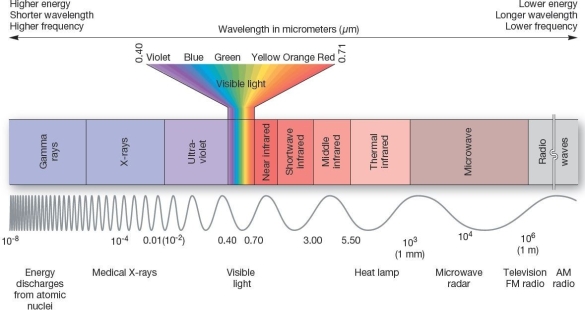 A portion of the electromagnetic spectrum of radiant energy from the Sun Which of the following sequences is arranged in order from shorter wavelength to longer wavelength?
A portion of the electromagnetic spectrum of radiant energy from the Sun Which of the following sequences is arranged in order from shorter wavelength to longer wavelength?A)visible,gamma rays,radio waves,infrared
B)gamma rays,microwaves,visible,X-rays
C)radio waves,visible,heat,X-rays
D)infrared,visible,ultraviolet,X-rays
E)X-rays,ultraviolet,visible,infrared

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The uneven distribution of insolation by latitude is primarily a result of
A)Earth's curvature.
B)sun spot cycles.
C)variability in the Sun's output.
D)solar wind activity.
E)the changing distance of Earth from the Sun.
A)Earth's curvature.
B)sun spot cycles.
C)variability in the Sun's output.
D)solar wind activity.
E)the changing distance of Earth from the Sun.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is true?
A)The Sun emits shortwave radiation,whereas Earth emits longwave radiation
B)Because the Sun is so far away,it is impossible to measure the wavelengths of its radiation.
C)While the wavelengths emitted by the Sun and Earth are mostly the same,Earth tends to emit more shortwave radiation than the Sun.
D)The radiation emitted by the Sun and Earth are roughly the same wavelength.
E)The Sun emits longwave radiation,whereas Earth emits shortwave radiation.
A)The Sun emits shortwave radiation,whereas Earth emits longwave radiation
B)Because the Sun is so far away,it is impossible to measure the wavelengths of its radiation.
C)While the wavelengths emitted by the Sun and Earth are mostly the same,Earth tends to emit more shortwave radiation than the Sun.
D)The radiation emitted by the Sun and Earth are roughly the same wavelength.
E)The Sun emits longwave radiation,whereas Earth emits shortwave radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The average insolation received by the thermopause when Earth is at its average distance from the sun is known as the
A)insolation.
B)energy balance.
C)solar constant.
D)aurora.
E)solar wind.
A)insolation.
B)energy balance.
C)solar constant.
D)aurora.
E)solar wind.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
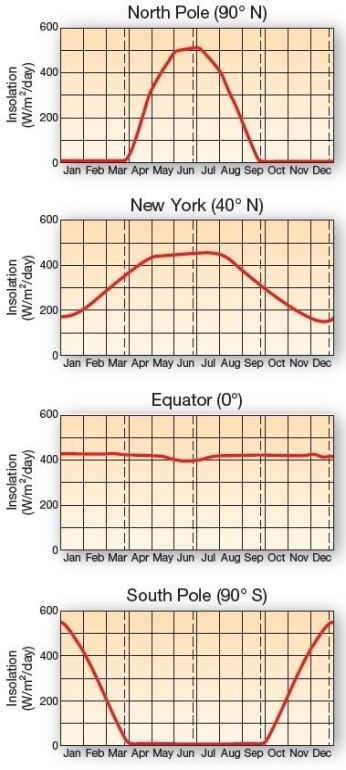 Daily insolation received at the top of the atmosphere.The total daily insolation received at the top of the atmosphere is charted in watts per square meter per day for four locations (1 W/m2/day = 2.064 cal/cm2/day).The vertical dashed lines mark the equinoxes and solstices,two of each during the year. Which of the following is true relative to insolation at the thermopause relative to latitude?
Daily insolation received at the top of the atmosphere.The total daily insolation received at the top of the atmosphere is charted in watts per square meter per day for four locations (1 W/m2/day = 2.064 cal/cm2/day).The vertical dashed lines mark the equinoxes and solstices,two of each during the year. Which of the following is true relative to insolation at the thermopause relative to latitude?A)Annually,higher latitudes receive more insolation than lower latitudes.
B)Annually,insolation is evenly distributed with little change by latitude.
C)Annually,lower latitudes receive more insolation than the high latitudes.
D)Insolation can only be measured longitudinally,not latitudinally.
E)Insolation variations is governed by elevation,not latitude.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The sun radiates concentrated around .
A)longer wavelength;3.00 μm.
B)longer wavelength;103 μm.
C)shorter wavelength;0.5 μm.
D)shorter wavelength;10-8 μm.
E)shorter wavelength;0.001 μm.
A)longer wavelength;3.00 μm.
B)longer wavelength;103 μm.
C)shorter wavelength;0.5 μm.
D)shorter wavelength;10-8 μm.
E)shorter wavelength;0.001 μm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The solar constant is measured at
A)the thermopause.
B)the edge of the Sun's atmosphere.
C)Earth's surface.
D)the Sun's surface.
E)sea level.
A)the thermopause.
B)the edge of the Sun's atmosphere.
C)Earth's surface.
D)the Sun's surface.
E)sea level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Comparing the three temperature scales,absolute zero is
A)-273° K.
A)0° F.
B)0° K.
B)32° F.
E)32° C.
A)-273° K.
A)0° F.
B)0° K.
B)32° F.
E)32° C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The Sun's altitude refers to
A)the angular distance from the equator to the latitude to the subsolar point.
B)the latitude of the subsolar point.
C)the angular height of the Sun above the horizon.
D)the distance of the sun from Earth.
E)the difference between the angles of insolation at the equator and the poles.
A)the angular distance from the equator to the latitude to the subsolar point.
B)the latitude of the subsolar point.
C)the angular height of the Sun above the horizon.
D)the distance of the sun from Earth.
E)the difference between the angles of insolation at the equator and the poles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The subsolar point occurs
A)only within a few degrees north or south of the equator.
B)at all latitudes at least once throughout the year.
C)only at lower latitudes between the Tropics (23.5° N/S).
D)at all latitudes between 60° N and S.
E)primarily in the Northern Hemisphere to 33.5° N.
A)only within a few degrees north or south of the equator.
B)at all latitudes at least once throughout the year.
C)only at lower latitudes between the Tropics (23.5° N/S).
D)at all latitudes between 60° N and S.
E)primarily in the Northern Hemisphere to 33.5° N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
![<strong> Daily net radiation patterns at the top of the atmosphere.Averaged daily net radiation flows measured at the top of the atmosphere by the Earth Radiation Budget Experiment (ERBE).Units are W/m2.[Data for map courtesy of GSFC/NASA.] Average daily net radiation flows tend to be</strong> A)lowest in the midlatitudes (40° to 60° N/S). B)equal at all latitudes. C)positive at lower latitudes. D)negative at lower latitudes E)highest in the midlatitudes (40° to 60° N/S).](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB5538/11eab6b6_9b81_f610_a5f2_6b9c5594bca2_TB5538_00.jpg) Daily net radiation patterns at the top of the atmosphere.Averaged daily net radiation flows measured at the top of the atmosphere by the Earth Radiation Budget Experiment (ERBE).Units are W/m2.[Data for map courtesy of GSFC/NASA.] Average daily net radiation flows tend to be
Daily net radiation patterns at the top of the atmosphere.Averaged daily net radiation flows measured at the top of the atmosphere by the Earth Radiation Budget Experiment (ERBE).Units are W/m2.[Data for map courtesy of GSFC/NASA.] Average daily net radiation flows tend to beA)lowest in the midlatitudes (40° to 60° N/S).
B)equal at all latitudes.
C)positive at lower latitudes.
D)negative at lower latitudes
E)highest in the midlatitudes (40° to 60° N/S).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The region at the top of the atmosphere located approximately 480 km (300 mi)above Earth's surface is known as the
A)perihelion.
B)apihelion.
C)sun spot.
D)aurora.
E)thermopause.
A)perihelion.
B)apihelion.
C)sun spot.
D)aurora.
E)thermopause.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
is the flow of kinetic energy between molecules or from one body or substance to another resulting from a temperature difference between them.
A)Electromagnetic radiation
B)Visible light
C)Temperature
D)Heat
E)Thermal infrared through radiation
A)Electromagnetic radiation
B)Visible light
C)Temperature
D)Heat
E)Thermal infrared through radiation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is true of the number of hours of daylight?
A)The poles always experience equal hours of day and night.
B)Annually,the hours of daylight varies the least at higher latitudes.
C)The hours of daylight varies depending on the latitude of the observer.
D)Annually,the hours of daylight is constant at each latitude.
E)Annually,the hours of daylight varies the most along the equator.
A)The poles always experience equal hours of day and night.
B)Annually,the hours of daylight varies the least at higher latitudes.
C)The hours of daylight varies depending on the latitude of the observer.
D)Annually,the hours of daylight is constant at each latitude.
E)Annually,the hours of daylight varies the most along the equator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is not true?
A)The axial tilt ranges roughly between 22° and 24.5° over a 41,000 year cycle.
B)Earth's axis is tilted 23.5° relative to the plane of the ecliptic.
C)Throughout the year,Earth's axis maintains the same alignment relative to the plane of the ecliptic.
D)During the winter months,Earth's axis is aligned towards Southern Cross.
E)The axis through Earth's two poles points just slightly off Polaris.
A)The axial tilt ranges roughly between 22° and 24.5° over a 41,000 year cycle.
B)Earth's axis is tilted 23.5° relative to the plane of the ecliptic.
C)Throughout the year,Earth's axis maintains the same alignment relative to the plane of the ecliptic.
D)During the winter months,Earth's axis is aligned towards Southern Cross.
E)The axis through Earth's two poles points just slightly off Polaris.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
As viewed from the equator,Earth's rotation is described as
A)east to west.
B)north to south.
C)counterclockwise.
D)west to east.
E)clockwise.
A)east to west.
B)north to south.
C)counterclockwise.
D)west to east.
E)clockwise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The Southern Hemisphere's summer solstice occurs
A)on or around June 21.
B)when the subsolar point is at the Tropic of Cancer.
C)on or around December 21.
D)at the same time as the Northern Hemisphere's summer solstice.
E)during the Northern Hemisphere's equinox.
A)on or around June 21.
B)when the subsolar point is at the Tropic of Cancer.
C)on or around December 21.
D)at the same time as the Northern Hemisphere's summer solstice.
E)during the Northern Hemisphere's equinox.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The plane of Earth's orbit about the Sun is called
A)the great circle.
B)perihelion.
C)aphelion.
D)the subsolar point.
E)the plane of the ecliptic.
A)the great circle.
B)perihelion.
C)aphelion.
D)the subsolar point.
E)the plane of the ecliptic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
59) 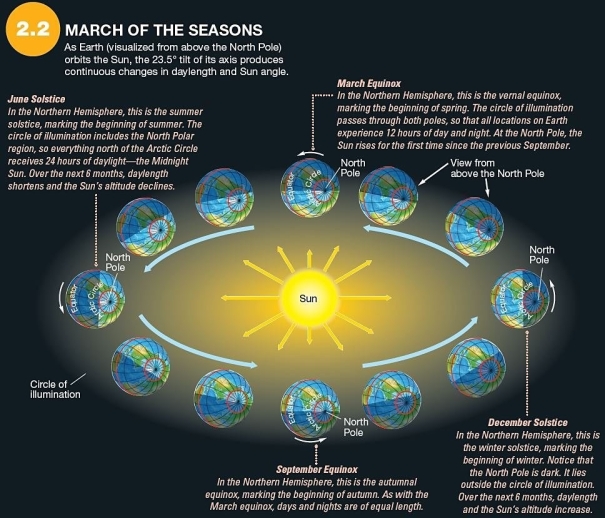 Which is true of the March equinox?
Which is true of the March equinox?
A)The subsolar point is at the equator.
B)The subsolar point is at the South Pole.
C)The subsolar point is at the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° N).
D)The subsolar point is at the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° S).
E)The subsolar point is at the North Pole.
 Which is true of the March equinox?
Which is true of the March equinox?A)The subsolar point is at the equator.
B)The subsolar point is at the South Pole.
C)The subsolar point is at the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° N).
D)The subsolar point is at the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° S).
E)The subsolar point is at the North Pole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
57) 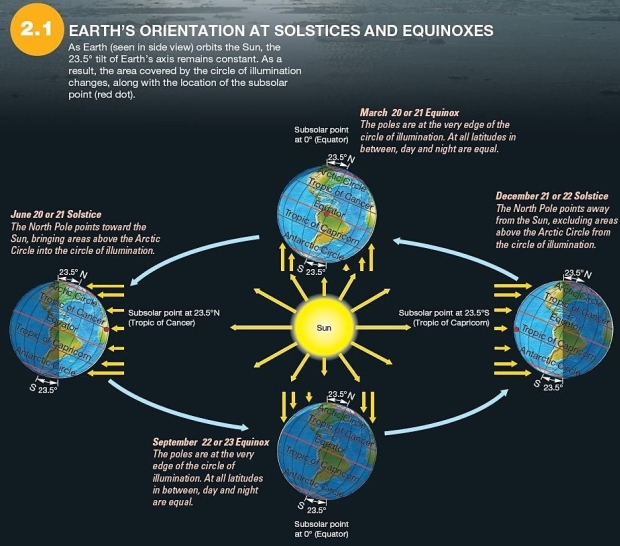 Which is true of the December solstice?
Which is true of the December solstice?
A)The Arctic Circle is completely within the circle of illumination.
B)The subsolar point is at the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° N)
C)The subsolar point is at the equator.
D)The North Pole experiences 24 hours of daylight.
E)The Antarctic Circle is completely within the circle of illumination.
 Which is true of the December solstice?
Which is true of the December solstice?A)The Arctic Circle is completely within the circle of illumination.
B)The subsolar point is at the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° N)
C)The subsolar point is at the equator.
D)The North Pole experiences 24 hours of daylight.
E)The Antarctic Circle is completely within the circle of illumination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
On the March equinox
A)all latitudes on Earth except the equator experience unequal daylengths.
B)all latitudes between the poles experience equal daylength.
C)the Sun's direct rays strike perpendicular to the Tropic of Capricorn(23.5° S).
D)the subsolar point is at the South Pole.
E)the Arctic Circle is completely within the circle of illumination.
A)all latitudes on Earth except the equator experience unequal daylengths.
B)all latitudes between the poles experience equal daylength.
C)the Sun's direct rays strike perpendicular to the Tropic of Capricorn(23.5° S).
D)the subsolar point is at the South Pole.
E)the Arctic Circle is completely within the circle of illumination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Sun's declination migrates through of latitude annually.
A)30°
B)23.5°
C)47°
D)90°
E)66.5°
A)30°
B)23.5°
C)47°
D)90°
E)66.5°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
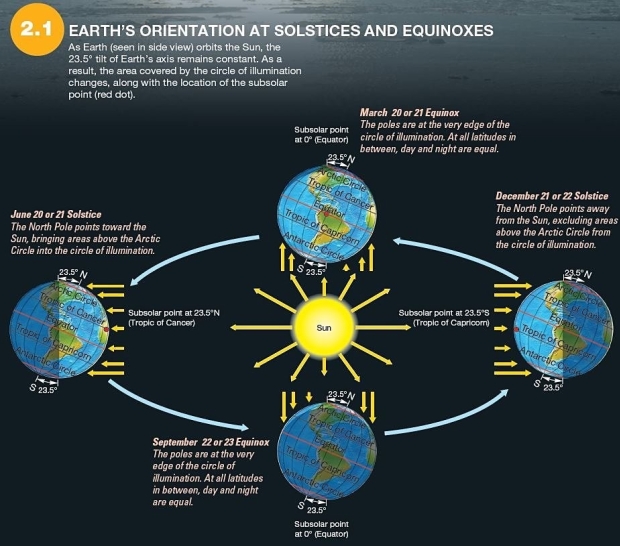 Which is true of the June solstice?
Which is true of the June solstice?A)The subsolar point is at the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° N).
B)The Arctic Circle is completely within the circle of illumination.
C)The South Pole experiences 24 hours of daylight.
D)The Antarctic Circle is completely within the circle of illumination.
E)The subsolar point is at the equator.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which of the following characterizes Earth's revolution?
A)The orbital shape is best described as circular.
B)It takes approximately 24 hours.
C)It determines the timing of seasons and length of the year.
D)It is responsible for creating the circle of illumination and,hence,day/night relationships.
E)The orbit has been constant since the formation of the Solar System.
A)The orbital shape is best described as circular.
B)It takes approximately 24 hours.
C)It determines the timing of seasons and length of the year.
D)It is responsible for creating the circle of illumination and,hence,day/night relationships.
E)The orbit has been constant since the formation of the Solar System.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is not true regarding rotational velocities at different latitudes?
A)At 0° latitude,the rotational velocity is 1675 kmph (1040 mph).
B)At 30° latitude,the rotational velocity is 1452 kmph (902 mph).
C)At 90° latitude,the rotational velocity is 1452 kmph (902 mph).
D)The linear velocity of rotation varies with latitude.
E)At 60° latitude,the rotational velocity is 838 kmph (521 mph).
A)At 0° latitude,the rotational velocity is 1675 kmph (1040 mph).
B)At 30° latitude,the rotational velocity is 1452 kmph (902 mph).
C)At 90° latitude,the rotational velocity is 1452 kmph (902 mph).
D)The linear velocity of rotation varies with latitude.
E)At 60° latitude,the rotational velocity is 838 kmph (521 mph).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following cannot be attributed to the effects of Earth's rotation?
A)latitudinal variations in net radiation
B)deflection of the ocean currents
C)daylength
D)rise and fall of the tides
E)deflection of the winds
A)latitudinal variations in net radiation
B)deflection of the ocean currents
C)daylength
D)rise and fall of the tides
E)deflection of the winds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Axial parallelism refers to
A)the "wobble" of Earth on its axis during its annual revolution.
B)the curvature of Earth's surface relative to insolation.
C)the alignment of Earth's axis relative to the plane of ecliptic,Polaris,and other stars.
D)variations in the axial tilt over a 41,000 year period.
E)the "wobble" of Earth on its axis during its daily rotation.
A)the "wobble" of Earth on its axis during its annual revolution.
B)the curvature of Earth's surface relative to insolation.
C)the alignment of Earth's axis relative to the plane of ecliptic,Polaris,and other stars.
D)variations in the axial tilt over a 41,000 year period.
E)the "wobble" of Earth on its axis during its daily rotation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is correct regarding daylength?
A)The equator experiences 6 hours differences in daylength between summer and winter.
B)Day length is always 12 hours long at the equator.
C)Daylength is uniform at al latitudes throughout the year.
D)The range of daylength is shortest in the polar regions.
E)The poles always experience equal hours of day and night.
A)The equator experiences 6 hours differences in daylength between summer and winter.
B)Day length is always 12 hours long at the equator.
C)Daylength is uniform at al latitudes throughout the year.
D)The range of daylength is shortest in the polar regions.
E)The poles always experience equal hours of day and night.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
At all times during the year,the circle of illumination
A)divides Earth between Northern and Southern hemispheres.
B)divides between day and night.
C)divides Earth between Eastern and Western hemispheres.
D)separates winter from summer.
E)separates spring from autumn.
A)divides Earth between Northern and Southern hemispheres.
B)divides between day and night.
C)divides Earth between Eastern and Western hemispheres.
D)separates winter from summer.
E)separates spring from autumn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The Sun's declination refers to
A)the angular height of the Sun above the horizon.
B)the altitude,in thousands of feet,of the Sun above the horizon.
C)the difference between the angles of insolation at the equator and the poles.
D)the latitude of the subsolar point.
E)the distance of the sun from Earth.
A)the angular height of the Sun above the horizon.
B)the altitude,in thousands of feet,of the Sun above the horizon.
C)the difference between the angles of insolation at the equator and the poles.
D)the latitude of the subsolar point.
E)the distance of the sun from Earth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The Tropic of Cancer refers to
A)0° latitude when the Sun crosses the equator.
B)the location of the subsolar point on or around December 21.
C)the parallel that occurs at 23.5° South.
D)the parallel that is the farthest northern location of the subsolar point during the year.
E)the location of the subsolar point on or around September 22.
A)0° latitude when the Sun crosses the equator.
B)the location of the subsolar point on or around December 21.
C)the parallel that occurs at 23.5° South.
D)the parallel that is the farthest northern location of the subsolar point during the year.
E)the location of the subsolar point on or around September 22.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is not one of the reasons for Earth's seasonality?
A)the moon's rotation around Earth
B)Earth's sphericity
C)Earth's daily rotation on its axis
D)Earth's axial tilt
E)rotation of Earth around the Sun
A)the moon's rotation around Earth
B)Earth's sphericity
C)Earth's daily rotation on its axis
D)Earth's axial tilt
E)rotation of Earth around the Sun

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The Tropic of Capricorn refers to
A)the location of the subsolar point on or around September 22.
B)the parallel that is the farthest northern location of the subsolar point during the year.
C)the parallel that occurs at 66.5° South.
D)the location of the subsolar point on or around December 21.
E)the parallel that occurs at 23.5° South.
A)the location of the subsolar point on or around September 22.
B)the parallel that is the farthest northern location of the subsolar point during the year.
C)the parallel that occurs at 66.5° South.
D)the location of the subsolar point on or around December 21.
E)the parallel that occurs at 23.5° South.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Explain the significance of each of the equinoxes and solstices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following relationships is incorrect?
A)June 21 - subsolar point at 23.5° N
B)December solstice - subsolar point at 23.5° S
C)September equinox - subsolar point at 23.5° S
D)June solstice - subsolar point at 23.5° N
E)March equinox - subsolar point at 0°
A)June 21 - subsolar point at 23.5° N
B)December solstice - subsolar point at 23.5° S
C)September equinox - subsolar point at 23.5° S
D)June solstice - subsolar point at 23.5° N
E)March equinox - subsolar point at 0°

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
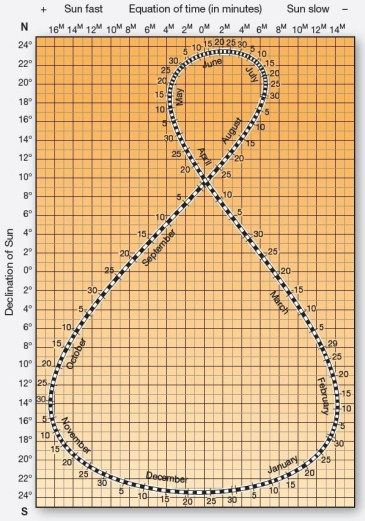 The analemma chart On approximately which dates is the subsolar point 16° S?
The analemma chart On approximately which dates is the subsolar point 16° S?A)September 15 and March 30
B)March 30 and September 15
C)May 5 and August 10
D)April 25 and August 20
E)February 5 and November 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
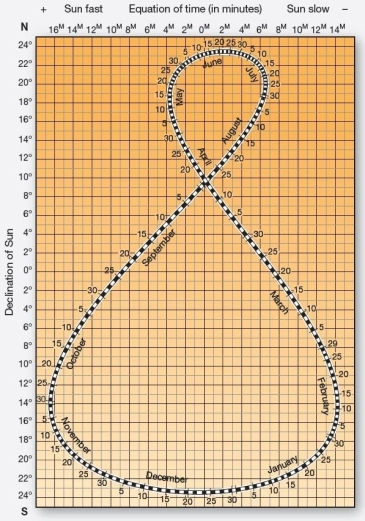 The analemma chart The Sun passes directly overhead at 25° N times a year?
The analemma chart The Sun passes directly overhead at 25° N times a year?A)0
B)1
C)2
D)3
E)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is global net radiation? Describe the latitudinal variations thereof.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The equinox
A)has 12 hours of day and 12 hours of night for all locations.
B)occurs four times during the year.
C)is the longest day of the year at any given place.
D)occurs only in the Southern Hemisphere.
E)is when the subsolar point is at one of the tropics.
A)has 12 hours of day and 12 hours of night for all locations.
B)occurs four times during the year.
C)is the longest day of the year at any given place.
D)occurs only in the Southern Hemisphere.
E)is when the subsolar point is at one of the tropics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Describe Earth's orbit around the sun,discussing the orbital shape and Earth-Sun distance throughout the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Describe the radiation emitted from both the Sun and Earth in terms of the electromagnetic spectrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What primary factors determine the seasons on Earth?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
On the September Equinox
A)the subsolar point is at the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° S).
B)the sun rises at the South Pole and will remain over the horizon for the next six months.
C)the Arctic Circle is completely within the circle of illuminations and experiences 24 hours of daylength.
D)all latitudes on Earth except the equator experiences unequal daylengths.
E)the Northern Hemisphere's spring officially begins.
A)the subsolar point is at the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° S).
B)the sun rises at the South Pole and will remain over the horizon for the next six months.
C)the Arctic Circle is completely within the circle of illuminations and experiences 24 hours of daylength.
D)all latitudes on Earth except the equator experiences unequal daylengths.
E)the Northern Hemisphere's spring officially begins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following is an example of humans influencing solar energy or seasonality?
A)Solar energy drives ecosystem processes that benefit humans.
B)Solar winds affect communication systems on the Earth.
C)Longer summers due to climate change have altered migration patterns of some animals.
D)Seasonal change determines the rhythm of life and food resources.
E)Shorter summers shorten the length of the growing season.
A)Solar energy drives ecosystem processes that benefit humans.
B)Solar winds affect communication systems on the Earth.
C)Longer summers due to climate change have altered migration patterns of some animals.
D)Seasonal change determines the rhythm of life and food resources.
E)Shorter summers shorten the length of the growing season.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What is a light-year? Why is the light-year a useful unit of measurement for astronomical distances?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
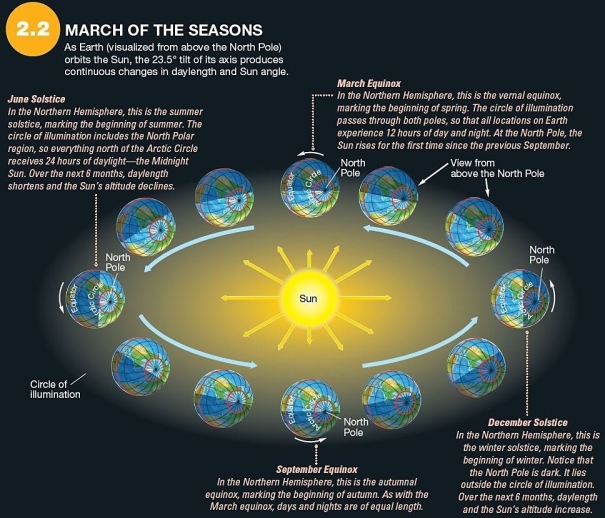 Which is true of the September equinox?
Which is true of the September equinox?A)The subsolar point is at the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° S).
B)There are 24 hours of daylight at the North Pole.
C)The circle of illumination passes through both poles.
D)The Antarctic Circle is completely within the circle of illumination.
E)The Arctic Circle is completely within the circle of illumination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What is the circle of illumination and the importance thereof?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
On June 21,the Sun never sets at Finn's location.Based on this,it can be concluded that Finn is currently
A)above the Arctic Circle.
B)between the Tropic of Cancer and Arctic Circle.
C)above the Antarctic Circle.
D)at the equator.
E)between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle.
A)above the Arctic Circle.
B)between the Tropic of Cancer and Arctic Circle.
C)above the Antarctic Circle.
D)at the equator.
E)between the Tropic of Capricorn and the Antarctic Circle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Describe the causes and consequences of the uneven distribution of insolation,including a discussion of the thermopause,insolation,solar constant,subsolar point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following statements is correct?
A)The Northern Hemisphere's vernal equinox is the Southern Hemisphere's summer equinox.
B)The Northern Hemisphere's vernal equinox is the Southern Hemisphere's autumnal equinox.
C)The Northern Hemisphere's vernal equinox is the Southern Hemisphere's winter solstice.
D)The Northern Hemisphere's vernal equinox is the Southern Hemisphere's vernal equinox.
E)The Northern Hemisphere's vernal equinox is the Southern Hemisphere's summer solstice.
A)The Northern Hemisphere's vernal equinox is the Southern Hemisphere's summer equinox.
B)The Northern Hemisphere's vernal equinox is the Southern Hemisphere's autumnal equinox.
C)The Northern Hemisphere's vernal equinox is the Southern Hemisphere's winter solstice.
D)The Northern Hemisphere's vernal equinox is the Southern Hemisphere's vernal equinox.
E)The Northern Hemisphere's vernal equinox is the Southern Hemisphere's summer solstice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
For observers in the Northern Hemisphere,which of the following is true?
A)Daylength decreases from the winter solstice until the vernal equinox,when it begins to increase.
B)Daylength becomes increasingly longer during the period from the summer solstice until the winter solstice.
C)The longest day of the year occurs on the December solstice.
D)Daylength variations are negligible for all locations throughout the year except above the Arctic Circle.
E)Daylength is longest on the summer solstice and is shortest on the winter solstice.
A)Daylength decreases from the winter solstice until the vernal equinox,when it begins to increase.
B)Daylength becomes increasingly longer during the period from the summer solstice until the winter solstice.
C)The longest day of the year occurs on the December solstice.
D)Daylength variations are negligible for all locations throughout the year except above the Arctic Circle.
E)Daylength is longest on the summer solstice and is shortest on the winter solstice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
One June 21st,the Sun's declination is at
A)the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° S).
B)the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° S).
C)the equator.
D)the Arctic Circle.
E)the Antarctic Circle.
A)the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° S).
B)the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° S).
C)the equator.
D)the Arctic Circle.
E)the Antarctic Circle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What conditions would one expect to find in Quito,Ecuador,located at 0° 15' N,78° 35' S?
A)Equal daylengths throughout the year.
B)The subsolar point directly overhead at noon on June 21st.
C)Long,dark winter nights.
D)24 hours of darkness during the June Solstice.
E)The subsolar point directly overhead at noon on December 21st.
A)Equal daylengths throughout the year.
B)The subsolar point directly overhead at noon on June 21st.
C)Long,dark winter nights.
D)24 hours of darkness during the June Solstice.
E)The subsolar point directly overhead at noon on December 21st.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 83 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



