Deck 15: Aeolian Processes and Arid Landscapes
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/60
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 15: Aeolian Processes and Arid Landscapes
1
Desert pavement refers to
A)specially constructed roadbeds in dry and hot regions.
B)surfaces of concentrated pebbles and gravels.
C)deposits of silt and clay.
D)sand-covered surfaces.
E)any rock shaped by eolian erosion.
A)specially constructed roadbeds in dry and hot regions.
B)surfaces of concentrated pebbles and gravels.
C)deposits of silt and clay.
D)sand-covered surfaces.
E)any rock shaped by eolian erosion.
B
2
Arid and semiarid climates cover about of Earth's surface.
A)three-fourths
B)a quarter
C)two-thirds
D)one-half
E)one-third
A)three-fourths
B)a quarter
C)two-thirds
D)one-half
E)one-third
E
3
The term "eolian" refers to
A)stream-related processes.
B)glacial processes in areas outside the polar regions.
C)erosion,transportation,and deposition by the wind.
D)weathering and mass movement in humid regions.
E)coastal erosion and deposition.
A)stream-related processes.
B)glacial processes in areas outside the polar regions.
C)erosion,transportation,and deposition by the wind.
D)weathering and mass movement in humid regions.
E)coastal erosion and deposition.
C
4
The transport of small sand particles (0.07 to 0.20 mm)along the ground in a bouncing and skipping action is known as
A)deflation.
B)abrasion.
C)saltation.
D)surface creep.
E)traction.
A)deflation.
B)abrasion.
C)saltation.
D)surface creep.
E)traction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following terms is not a correct reference to a desert pavement?
A)gibber plain
B)lag gravels
C)sand seas
D)reg desert
E)gobi
A)gibber plain
B)lag gravels
C)sand seas
D)reg desert
E)gobi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Saltation accounts for about % of sediment transport by wind.
A)15
B)35
C)50
D)65
E)80
A)15
B)35
C)50
D)65
E)80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The smallest features shaped by individual saltating grains are
A)ripples.
B)dunes.
C)sand seas.
D)reg deserts.
E)ventifacts.
A)ripples.
B)dunes.
C)sand seas.
D)reg deserts.
E)ventifacts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The sliding and rolling along the ground of particles larger than 0.5 mm is known as
A)deflation.
B)abrasion.
C)saltation.
D)surface creep.
E)traction.
A)deflation.
B)abrasion.
C)saltation.
D)surface creep.
E)traction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The sediment-accumulation hypothesis of desert pavement formation states
A)wind removes fine particles leaving large pebbles,gravels,and rocks,which become consolidated.
B)wind delivers fine particles that settle and wash downward as cycles of swelling and shrinking cause gravels to migrate upward.
C)water removes fine particles leaving large pebbles,gravels,and rocks,which become consolidated.
D)water delivers fine particles that settle and wash downward as cycles of swelling and shrinking cause gravels to migrate upward.
E)both wind and water remove fine particles leaving large pebbles,gravels,and rocks,which become consolidated.
A)wind removes fine particles leaving large pebbles,gravels,and rocks,which become consolidated.
B)wind delivers fine particles that settle and wash downward as cycles of swelling and shrinking cause gravels to migrate upward.
C)water removes fine particles leaving large pebbles,gravels,and rocks,which become consolidated.
D)water delivers fine particles that settle and wash downward as cycles of swelling and shrinking cause gravels to migrate upward.
E)both wind and water remove fine particles leaving large pebbles,gravels,and rocks,which become consolidated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An extensive area of sand and sand dunes is known as a(n)
A)reg desert.
B)erg desert,or sand sea.
C)lag desert.
D)desert pavement.
E)gibber plain.
A)reg desert.
B)erg desert,or sand sea.
C)lag desert.
D)desert pavement.
E)gibber plain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
 The term used to describe rocks that are pitted,fluted,or polished from eolian erosion is
The term used to describe rocks that are pitted,fluted,or polished from eolian erosion isA)desert pavement.
B)pumice.
C)ventifacts.
D)deflation hollows.
E)dunes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A depression created by deflation is known as a
A)playa.
B)bolson.
C)blowout.
D)structural basin.
E)haboob.
A)playa.
B)bolson.
C)blowout.
D)structural basin.
E)haboob.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The deflation hypothesis of desert pavement formation states
A)wind removes fine particles leaving large pebbles,gravels,and rocks,which become consolidated.
B)wind delivers fine particles that settle and wash downward as cycles of swelling and shrinking cause gravels to migrate upward.
C)water removes fine particles leaving large pebbles,gravels,and rocks,which become consolidated.
D)water delivers fine particles that settle and wash downward as cycles of swelling and shrinking cause gravels to migrate upward.
E)both wind and water deliver fine particles that settle and wash downward as cycles of swelling and shrinking cause gravels to migrate upward.
A)wind removes fine particles leaving large pebbles,gravels,and rocks,which become consolidated.
B)wind delivers fine particles that settle and wash downward as cycles of swelling and shrinking cause gravels to migrate upward.
C)water removes fine particles leaving large pebbles,gravels,and rocks,which become consolidated.
D)water delivers fine particles that settle and wash downward as cycles of swelling and shrinking cause gravels to migrate upward.
E)both wind and water deliver fine particles that settle and wash downward as cycles of swelling and shrinking cause gravels to migrate upward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The grinding and shaping of rock surfaces by the "sand blasting" action of particles captured in the air is termed
A)deflation.
B)abrasion.
C)saltation.
D)deposition.
E)traction.
A)deflation.
B)abrasion.
C)saltation.
D)deposition.
E)traction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
For purposes of discussing eolian processes,the wind acts like a
A)solid.
B)gas.
C)plasma.
D)fluid.
E)degenerate matter.
A)solid.
B)gas.
C)plasma.
D)fluid.
E)degenerate matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The removal and lifting of individual loose particles by the wind is termed
A)deflation.
B)abrasion.
C)saltation.
D)deposition.
E)traction.
A)deflation.
B)abrasion.
C)saltation.
D)deposition.
E)traction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Large depressions,such as the Qattâra depression,formed as a result of
A)deflation.
B)orogeny.
C)subduction.
D)converging plates.
E)tectonic forces.
A)deflation.
B)orogeny.
C)subduction.
D)converging plates.
E)tectonic forces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
 a()Ground view
a()Ground view  b()Aerial view
b()Aerial viewDust storms engulf Phoenix,Arizona,in 2013 (ground view)and 2016 (aerial view).
Dust storms,such as one from Arizona in 2013,are caused by downbursts associated with thunderstorms.Such storms are termed
A)playas.
B)deflation.
C)blowout depression.
D)ventifacts.
E)haboobs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
 Elongated,streamlined ridges aligned parallel to the most effective wind direction are called
Elongated,streamlined ridges aligned parallel to the most effective wind direction are calledA)ventifacts.
B)yardangs.
C)desert pavements.
D)alluvial rock structures.
E)terraces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The ability of the wind to move materials
A)exceeds that of other transporting agents,such as water and ice.
B)is small compared to other transporting agents,such as water and ice.
C)is greater than that of water because of the higher density of air compared to water.
D)increases with decreased wind speed.
E)is equal to other transporting agents,such as water and ice.
A)exceeds that of other transporting agents,such as water and ice.
B)is small compared to other transporting agents,such as water and ice.
C)is greater than that of water because of the higher density of air compared to water.
D)increases with decreased wind speed.
E)is equal to other transporting agents,such as water and ice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
 dunes form with their tips pointing downwind,usually in areas with limited sand supply and little to no vegetation.
dunes form with their tips pointing downwind,usually in areas with limited sand supply and little to no vegetation.A)Linear
B)Barchan
C)Longitudinal
D)Transverse
E)Parabolic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The loess deposits in Europe and North America are thought to be derived mainly from
A)alluvium,i.e.stream deposited materials.
B)ocean sediments.
C)windblown desert sediments.
D)glacial and periglacial sources.
E)deeply entrenched river channels.
A)alluvium,i.e.stream deposited materials.
B)ocean sediments.
C)windblown desert sediments.
D)glacial and periglacial sources.
E)deeply entrenched river channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The leading cause of decline in Lake Urmia is
A)drought.
B)climate change.
C)urbanization.
D)hydroelectric production.
E)water withdrawal.
A)drought.
B)climate change.
C)urbanization.
D)hydroelectric production.
E)water withdrawal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
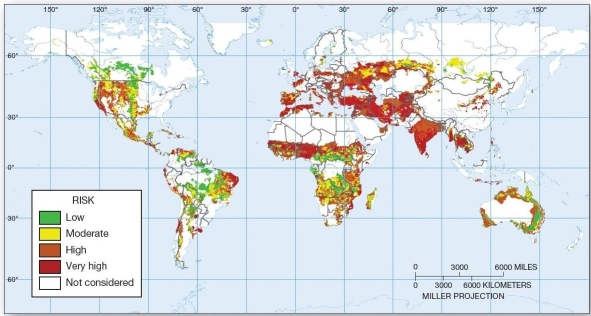 Areas at risk of desertification Which of the following areas is at highest (very high)risk of desertification?
Areas at risk of desertification Which of the following areas is at highest (very high)risk of desertification?A)the U.S.Great Plains
B)the Sahel
C)central Canada
D)eastern China
E)central Australia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Ephemeral channels that form in dryland climates in response to infrequent precipitation events are known as
A)arroyos.
B)hollows.
C)yardangs.
D)ventifacts.
E)alluvial fans.
A)arroyos.
B)hollows.
C)yardangs.
D)ventifacts.
E)alluvial fans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is not a general shape upon which scientists classify dunes?
A)rectilinear
B)crescentic
C)linear
D)star
E)parabolic
A)rectilinear
B)crescentic
C)linear
D)star
E)parabolic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Active dunes cover approximately % of Earth's deserts.
A)10
B)27
C)45
D)63
E)80
A)10
B)27
C)45
D)63
E)80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
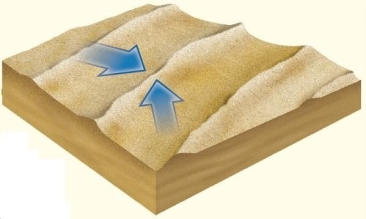 dunes form parallel to the prevailing wind,often extending for hundreds of kilometers in length.
dunes form parallel to the prevailing wind,often extending for hundreds of kilometers in length.A)Linear
B)Barchan
C)Longitudinal
D)Transverse
E)Star

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which side of a dune typically has a slope angle equal to that of the angle of repose for sand?
A)windward
B)leeward
C)stoss
D)top
E)bottom
A)windward
B)leeward
C)stoss
D)top
E)bottom

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Windblown dust that accumulates into homogeneous deposits is known as
A)gobi.
B)deflation hollows.
C)yardangs.
D)desert pavement.
E)loess.
A)gobi.
B)deflation hollows.
C)yardangs.
D)desert pavement.
E)loess.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Relative to dune movement and form,a dune's slipface forms on which side?
A)leeward side
B)windward side
C)freedune side
D)direction opposite of dune movement
E)It is not associated with a particular side.
A)leeward side
B)windward side
C)freedune side
D)direction opposite of dune movement
E)It is not associated with a particular side.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Factors that influence dry climates include all the following except
A)seasonal influence of the ITCZ.
B)dry,subsiding air associated with subtropical high pressure systems.
C)location in the rain shadow of mountains.
D)cool,stabilizing ocean currents along the western margins of continents.
E)location in continental interiors.
A)seasonal influence of the ITCZ.
B)dry,subsiding air associated with subtropical high pressure systems.
C)location in the rain shadow of mountains.
D)cool,stabilizing ocean currents along the western margins of continents.
E)location in continental interiors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The vast loess deposits in China are thought to be derived mainly from
A)alluvium,i.e.stream deposited materials.
B)ocean sediments.
C)windblown desert sediments.
D)glacial and periglacial sources.
E)deeply entrenched river channels.
A)alluvium,i.e.stream deposited materials.
B)ocean sediments.
C)windblown desert sediments.
D)glacial and periglacial sources.
E)deeply entrenched river channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is correct regarding loess deposits?
A)They are principally composed of sands and gravels.
B)They are formed of fine-grained clays,silts and fine.
C)They are found only in the United States.
D)They form only following glacial activity.
E)They are poor agricultural soils.
A)They are principally composed of sands and gravels.
B)They are formed of fine-grained clays,silts and fine.
C)They are found only in the United States.
D)They form only following glacial activity.
E)They are poor agricultural soils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Cone-shaped deposits of sediment often found at mouth of canyons in arid and semiarid climates are called
A)deposition.
B)deltas.
C)alluvial fans.
D)clastics.
E)arroyos.
A)deposition.
B)deltas.
C)alluvial fans.
D)clastics.
E)arroyos.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
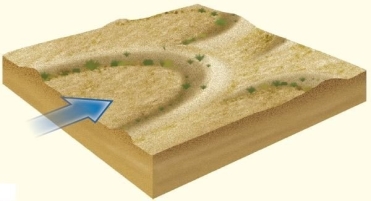 In vegetated dune landscapes,dunes form with their tips pointing upwind.
In vegetated dune landscapes,dunes form with their tips pointing upwind.A)Linear
B)Barchan
C)Longitudinal
D)Transverse
E)Parabolic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The Aral Sea,once one of the four largest lakes in the world,has steadily decreased since the 1960s on account of
A)diversion of incoming rivers for irrigation.
B)climate change.
C)urbanization.
D)hydroelectric production.
E)deforestation and resulting sedimentation.
A)diversion of incoming rivers for irrigation.
B)climate change.
C)urbanization.
D)hydroelectric production.
E)deforestation and resulting sedimentation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is not considered a cause of desertification?
A)poor agricultural practices
B)climate change
C)poor soil-moisture management
D)salinization
E)afforestation
A)poor agricultural practices
B)climate change
C)poor soil-moisture management
D)salinization
E)afforestation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The general term for the land degradation in arid and semiarid regions characterized by expansions of deserts is
A)desertification.
B)woody plant encroachment.
C)eolian process.
D)deflation.
E)saltation.
A)desertification.
B)woody plant encroachment.
C)eolian process.
D)deflation.
E)saltation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
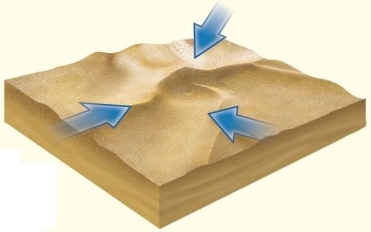 dunes are the largest in size and have multiple slipfaces produced by winds from varying directions.
dunes are the largest in size and have multiple slipfaces produced by winds from varying directions.A)Linear
B)Barchan
C)Longitudinal
D)Transverse
E)Star

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What are the two competing hypotheses describing the formation of desert pavement?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
are flat-topped landforms with steep slopes resulting from differential weathering.
A)Mesas
B)Inselbergs
C)Badlands
D)Arroyos
E)Alluvial fans
A)Mesas
B)Inselbergs
C)Badlands
D)Arroyos
E)Alluvial fans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A forms when individual alluvial fans coalesce.
A)star dune
B)playa
C)yardang
D)desert pavement
E)bajada
A)star dune
B)playa
C)yardang
D)desert pavement
E)bajada

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Describe the eolian processes of deflation and abrasion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
 Weathering of sandstone alcoves used for ancient cliff dwellings An alcove in sandstone,such as that in the Cliff House at Mesa Verde,is indicative of which weathering process?
Weathering of sandstone alcoves used for ancient cliff dwellings An alcove in sandstone,such as that in the Cliff House at Mesa Verde,is indicative of which weathering process?A)exfoliation
B)carbonation
C)root wedging
D)salt-crystal growth
E)hydrolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is loess? How do the loess deposits of North America and Europe vary from those in China?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
are isolated remnants of resistant rock and products of long-term weathering and erosion.
A)Mesas
B)Inselbergs
C)Badlands
D)Arroyos
E)Alluvial fans
A)Mesas
B)Inselbergs
C)Badlands
D)Arroyos
E)Alluvial fans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Dryland rugged terrain of slopes dissected by rills and gullies are known as
A)qanats.
B)arroyos.
C)badlands.
D)bajadas.
E)playas.
A)qanats.
B)arroyos.
C)badlands.
D)bajadas.
E)playas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A is a dry bed of an ephemeral lake a dryland region.
A)star dune
B)playa.
C)yardang
D)desert pavement
E)bajada
A)star dune
B)playa.
C)yardang
D)desert pavement
E)bajada

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Rocks of the same composition and structure found in the same area may have weathered at uneven rates due to a variety of factors.This is known as .
A)angle of repose
B)jointing
C)inertial resistance
D)denudation
E)differential weathering
A)angle of repose
B)jointing
C)inertial resistance
D)denudation
E)differential weathering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The Basin and Range Province in the western United States is an example of a landscape.
A)tensional
B)reverse
C)horst and graben
D)compressional
E)Great Plains
A)tensional
B)reverse
C)horst and graben
D)compressional
E)Great Plains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A large region identifiable by several topographic or geological traits is known as a(n)
A)topographic region.
B)ecoregion.
C)physiographic province.
D)biome.
E)alluvial terrace.
A)topographic region.
B)ecoregion.
C)physiographic province.
D)biome.
E)alluvial terrace.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What are the mechanisms by which air moves dust and sand?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Dune migration on the Navajo Nation in the U.S.Southwest is an example of
A)desertification.
B)woody plant encroachment.
C)eolian transport.
D)deflation.
E)saltation.
A)desertification.
B)woody plant encroachment.
C)eolian transport.
D)deflation.
E)saltation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Describe the formation of alluvial fans and bajadas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The coarsest materials,such as gravel,of an alluvial fan are found
A)near the mouth of the canyon.
B)at the edge of the fan.
C)throughout the whole fan.
D)within a playa.
E)at the base of the fan.
A)near the mouth of the canyon.
B)at the edge of the fan.
C)throughout the whole fan.
D)within a playa.
E)at the base of the fan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Alluvial fans are formed as flowing water as it leaves a constricted channel.
A)gains velocity
B)changes direction
C)down cuts
D)loses velocity
E)expands.
A)gains velocity
B)changes direction
C)down cuts
D)loses velocity
E)expands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is desertification? What causes it? What areas are at risk of desertification?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Explain the formation of sand dunes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
are steep-sided landforms resulting from the weathering and mass wasting of mesas.
A)Volcanic necks
B)Badlands
C)Dikes
D)Plugs
E)Buttes
A)Volcanic necks
B)Badlands
C)Dikes
D)Plugs
E)Buttes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 60 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



