Deck 13: Weathering, Karst Landscapes, and Mass Movement
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/89
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Weathering, Karst Landscapes, and Mass Movement
1
Because the climate of a region slowly changes and tectonic adjustments slowly occur,the landscape
A)is constantly at a threshold condition.
B)is continuously adjusting to new conditions that develop.
C)is usually in a state of stable equilibrium.
D)is constantly at a threshold,continuously adjusting,and in a state of dynamic equilibrium.
E)is continuously adjusting,and in a state of dynamic equilibrium,but not constantly at a threshold.
A)is constantly at a threshold condition.
B)is continuously adjusting to new conditions that develop.
C)is usually in a state of stable equilibrium.
D)is constantly at a threshold,continuously adjusting,and in a state of dynamic equilibrium.
E)is continuously adjusting,and in a state of dynamic equilibrium,but not constantly at a threshold.
E
2
The process that breaks down rock at the Earth's surface through disintegration of rocks into mineral particles or dissolving it into water is known as
A)erosion.
B)mass movement.
C)landmass denudation.
D)deposition.
E)weathering.
A)erosion.
B)mass movement.
C)landmass denudation.
D)deposition.
E)weathering.
E
3
The concave lower portion of a typical slope is called a
A)waning slope.
B)waxing slope.
C)debris slope.
D)free face.
E)pediment.
A)waning slope.
B)waxing slope.
C)debris slope.
D)free face.
E)pediment.
A
4
The maximum incline at which sediments on a slope can remain at rest before pulled downward by gravity is known as the
A)catchment.
B)angle of repose.
C)free face.
D)regolith.
E)slope.
A)catchment.
B)angle of repose.
C)free face.
D)regolith.
E)slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is not a denudation process?
A)chemical weathering
B)erosion
C)orogeny
D)mass movement
E)physical weathering
A)chemical weathering
B)erosion
C)orogeny
D)mass movement
E)physical weathering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Inclined surfaces that form the boundaries of landforms are known as
A)catchments.
B)slopes.
C)free face.
D)regoliths.
E)viewsheds.
A)catchments.
B)slopes.
C)free face.
D)regoliths.
E)viewsheds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A slope is if its strength exceed denudation processes and if its materials are weaker than denudation processes.
A)stable;unstable
B)unstable;stable
C)in equilibrium;in disequilibrium
D)in disequilibrium;in equilibrium
E)inertial;gravitational
A)stable;unstable
B)unstable;stable
C)in equilibrium;in disequilibrium
D)in disequilibrium;in equilibrium
E)inertial;gravitational

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following is not exogenic in nature?
A)weathering
B)erosion
C)denudation
D)tectonic uplift
E)mass movement
A)weathering
B)erosion
C)denudation
D)tectonic uplift
E)mass movement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The science that specifically studies the origin,evolution,form,and spatial distribution of landforms is
A)geology.
B)geography.
C)geomorphology.
D)environmental chemistry.
E)hydrology.
A)geology.
B)geography.
C)geomorphology.
D)environmental chemistry.
E)hydrology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The angle of repose represent a balance between the driving force and resisting force.Which of the following is the driving force?
A)friction
B)shear
C)gravity
D)inertia
E)cohesion
A)friction
B)shear
C)gravity
D)inertia
E)cohesion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The uplift of mountains is caused by
A)endogenic processes.
B)aggradation.
C)denudation.
D)exogenic forces.
E)mass movement.
A)endogenic processes.
B)aggradation.
C)denudation.
D)exogenic forces.
E)mass movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
All processes that cause reduction and rearrangement of landforms are included in the term
A)mass movement.
B)erosion.
C)weathering.
D)denudation.
E)evisceration.
A)mass movement.
B)erosion.
C)weathering.
D)denudation.
E)evisceration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The dynamic equilibrium model refers to
A)a balancing act between tectonic uplift and rates of denudation by weathering and erosion in a given landscape.
B)a hypothesis involving the cyclic or evolutionary development of a landscape.
C)a sequential development of landforms.
D)the idea that landscapes show great variations over time,but the forces of denudation and orogeny always balance.
E)a hypothesis suggestion that landscapes form from catastrophic events followed by long periods of stability.
A)a balancing act between tectonic uplift and rates of denudation by weathering and erosion in a given landscape.
B)a hypothesis involving the cyclic or evolutionary development of a landscape.
C)a sequential development of landforms.
D)the idea that landscapes show great variations over time,but the forces of denudation and orogeny always balance.
E)a hypothesis suggestion that landscapes form from catastrophic events followed by long periods of stability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
After a threshold is crossed,the landscape
A)remains unstable thereafter.
B)adjusts to a new equilibrium condition.
C)looks identical to the landscape that existed prior to the crossing of the threshold.
D)returns to the conditions that existed prior to the crossing the threshold.
E)is stable as before because landscapes do not cross thresholds.
A)remains unstable thereafter.
B)adjusts to a new equilibrium condition.
C)looks identical to the landscape that existed prior to the crossing of the threshold.
D)returns to the conditions that existed prior to the crossing the threshold.
E)is stable as before because landscapes do not cross thresholds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The principle that landscape formation is balance between endogenic and exogenic processes is called
A)the dynamic equilibrium model.
B)uniformitarianism.
C)catastrophism.
D)steady state theory.
E)tipping point model.
A)the dynamic equilibrium model.
B)uniformitarianism.
C)catastrophism.
D)steady state theory.
E)tipping point model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If material is to move downslope,it must overcome the force of
A)friction.
B)the cohesion of particles to each other.
C)inertial resistance of the material.
D)both friction and inertial resistance.
E)friction,cohesion of particles,and inertial resistance.
A)friction.
B)the cohesion of particles to each other.
C)inertial resistance of the material.
D)both friction and inertial resistance.
E)friction,cohesion of particles,and inertial resistance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
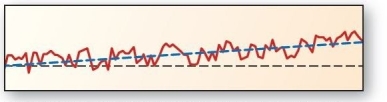 Landscape formation is a balancing act between tectonic uplift and denudation.This figure depicts which of the following?
Landscape formation is a balancing act between tectonic uplift and denudation.This figure depicts which of the following?A)steady-state equilibrium
B)dynamic equilibrium
C)dynamic equilibrium with threshold
D)denudation,only
E)tectonic uplift,only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The convex upper portion of a typical slope is called a
A)waning slope.
B)debris slope.
C)waxing slope.
D)free face.
E)capstone.
A)waning slope.
B)debris slope.
C)waxing slope.
D)free face.
E)capstone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
is a steep scarp or cliff whose presence indicates an outcrop of resistant rock.
A)Waning slope
B)Waxing slope
C)Debris slope
D)Free face
E)Regolith
A)Waning slope
B)Waxing slope
C)Debris slope
D)Free face
E)Regolith

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
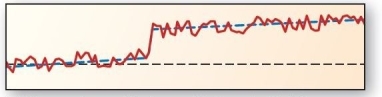 Landscape formation is a balancing act between tectonic uplift and denudation.This figure depicts which of the following?
Landscape formation is a balancing act between tectonic uplift and denudation.This figure depicts which of the following?A)steady-state equilibrium
B)dynamic equilibrium
C)dynamic equilibrium with threshold
D)denudation,only
E)tectonic uplift,only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
occurs as rock surfaces heated by the Sun during the day expand slightly,and then contract with nighttime cooling.
A)Exfoliation
B)Thermal expansion
C)Frost wedging
D)Salt-crystal growth
E)Hydrolysis
A)Exfoliation
B)Thermal expansion
C)Frost wedging
D)Salt-crystal growth
E)Hydrolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Factors influencing the weathering process include
A)the climate of an area only.
B)rock composition and structure only.
C)organic processes only.
D)subsurface water only.
E)rock composition and structure,climate,organic processes,and subsurface water.
A)the climate of an area only.
B)rock composition and structure only.
C)organic processes only.
D)subsurface water only.
E)rock composition and structure,climate,organic processes,and subsurface water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The fact that water expands as much as 9% of its volume as it freezes is the basis of
A)oxidization.
B)exfoliation.
C)salt crystal growth.
D)frost wedging.
E)hydrolysis
A)oxidization.
B)exfoliation.
C)salt crystal growth.
D)frost wedging.
E)hydrolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Exfoliation occurs because
A)water combines with minerals and increases their size,thereby causing surrounding minerals to expand.
B)water freezes in joints and expands.
C)overlying rock is removed,thereby allowing the underlying rock mass to expand and fracture.
D)evaporated water leaves behind previously dissolved mineral to form crystals,which accumulate and grow over time,exerting pressure on the rock.
E)rock minerals react with carbonic acids in rain,causing weathering to occur.
A)water combines with minerals and increases their size,thereby causing surrounding minerals to expand.
B)water freezes in joints and expands.
C)overlying rock is removed,thereby allowing the underlying rock mass to expand and fracture.
D)evaporated water leaves behind previously dissolved mineral to form crystals,which accumulate and grow over time,exerting pressure on the rock.
E)rock minerals react with carbonic acids in rain,causing weathering to occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When pressure is removed from overlying rock,the pressure of deep burial is relieved,initiating pressure-release jointing.The joints then separate into curved slabs.This is known as
A)exfoliation.
B)frost wedging.
C)salt crystal growth.
D)spheroidal weathering.
E)crystallization.
A)exfoliation.
B)frost wedging.
C)salt crystal growth.
D)spheroidal weathering.
E)crystallization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The consolidated or unconsolidated materials from which soils develop is known as
A)joints.
B)regolith.
C)parent material.
D)outcrop.
E)free face.
A)joints.
B)regolith.
C)parent material.
D)outcrop.
E)free face.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Frost wedging is an example of weathering processes.
A)only chemical
B)only physical
C)only biological
D)both biological and chemical
E)both biological and physical
A)only chemical
B)only physical
C)only biological
D)both biological and chemical
E)both biological and physical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Chemical weathering that softens and rounds the sharp edges and corners of jointed rock is known as
A)spheroidal weathering.
B)exfoliation.
C)hydration.
D)hydrolysis.
E)thermal expansion.
A)spheroidal weathering.
B)exfoliation.
C)hydration.
D)hydrolysis.
E)thermal expansion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In which climates would rocks experience the highest amounts of chemical decomposition and decay?
A)cold and wet
B)cold and dry
C)hot and wet
D)hot and dry
E)cool and moist
A)cold and wet
B)cold and dry
C)hot and wet
D)hot and dry
E)cool and moist

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is not a type of physical weathering process?
A)exfoliation
B)hydrolysis
C)salt crystal growth
D)frost wedging
E)thermal expansion
A)exfoliation
B)hydrolysis
C)salt crystal growth
D)frost wedging
E)thermal expansion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Chemical weathering is greatest under conditions of
A)higher rainfall and temperatures.
B)lower rainfall and temperatures.
C)higher rainfall,but lower temperatures.
D)lower rainfall,but higher temperatures.
E)near absence of rainfall,but higher temperatures.
A)higher rainfall and temperatures.
B)lower rainfall and temperatures.
C)higher rainfall,but lower temperatures.
D)lower rainfall,but higher temperatures.
E)near absence of rainfall,but higher temperatures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When rock is broken down and disintegrated without any chemical alterations,the process in operation is
A)physical weathering.
B)chemical weathering.
C)hydrolysis.
D)carbonation.
E)erosion.
A)physical weathering.
B)chemical weathering.
C)hydrolysis.
D)carbonation.
E)erosion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Exfoliation is most common in
A)foliated metamorphic rocks.
B)sedimentary rocks high in CaCO3.
C)mafic extrusive igneous rocks.
D)clastic sedimentary rocks.
E)high silica intrusive igneous rocks.
A)foliated metamorphic rocks.
B)sedimentary rocks high in CaCO3.
C)mafic extrusive igneous rocks.
D)clastic sedimentary rocks.
E)high silica intrusive igneous rocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
When rock is broken down and disintegrated in the presence of water and with chemical alterations to the rock,the process in operation is
A)physical weathering.
B)chemical weathering.
C)mass movement.
D)scarification.
E)biological weathering.
A)physical weathering.
B)chemical weathering.
C)mass movement.
D)scarification.
E)biological weathering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Other than the rock itself,the most important chemical substance needed for the majority of weathering processes is
A)oxygen.
B)nitrogen.
C)water.
D)carbon dioxide.
E)potassium.
A)oxygen.
B)nitrogen.
C)water.
D)carbon dioxide.
E)potassium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Salt-crystal growth (salt weathering)is prevalent in which climate type?
A)mesothermal
B)tropical
C)arid
D)polar
E)microthermal
A)mesothermal
B)tropical
C)arid
D)polar
E)microthermal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
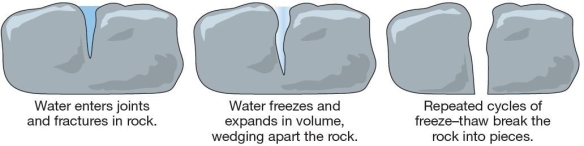 The weathering process responsible for breaking this granite slab is likely
The weathering process responsible for breaking this granite slab is likelyA)exfoliation.
B)carbonation.
C)frost wedging.
D)salt-crystal growth.
E)hydrolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
 Tafoni,or honeycomb weathering,in sandstone along the Pacific Coast in Salt Point State Park,California Pitted rock surfaces known as tafoni,or honeycomb weathering,result from weathering.
Tafoni,or honeycomb weathering,in sandstone along the Pacific Coast in Salt Point State Park,California Pitted rock surfaces known as tafoni,or honeycomb weathering,result from weathering.A)exfoliation
B)carbonation
C)frost wedging
D)salt-crystal growth
E)thermal expansion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When the upper surface of consolidated rock undergoes constant weathering,it creates broken-up rock called
A)bedrock.
B)regolith.
C)parent material.
D)outcrop.
E)angle of repose.
A)bedrock.
B)regolith.
C)parent material.
D)outcrop.
E)angle of repose.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Salt-crystal growth (salt weathering)is an example of weathering processes.
A)only chemical
B)only physical
C)only biological
D)both biological and physical
E)both biological and chemical
A)only chemical
B)only physical
C)only biological
D)both biological and physical
E)both biological and chemical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The downslope movement of a body of material made up of soil,sediment,or rock propelled by the force of gravity is known as
A)lahar.
B)downslope flow.
C)mass movement.
D)slide.
E)weathering.
A)lahar.
B)downslope flow.
C)mass movement.
D)slide.
E)weathering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A sinkhole that develops over a period of hours or days and forms from a collapse through the roof of an underground cavern is known as a
A)solution sinkhole.
B)collapse sinkhole.
C)doline.
D)karst valley.
E)karst tower.
A)solution sinkhole.
B)collapse sinkhole.
C)doline.
D)karst valley.
E)karst tower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
 These rounded granite outcrops are the result of which weathering process?
These rounded granite outcrops are the result of which weathering process?A)oxidation
B)hydration
C)spheroidal weathering
D)carbonation
E)thermal expansion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Extensive landscapes formed by the dissolution of limestone and other carbonate rock and characterized by pitted,bumpy surface topography,poor surface drainage,and well developed solutions channels are known as
A)plains.
B)basins.
C)karst topography.
D)high tablelands.
E)badlands.
A)plains.
B)basins.
C)karst topography.
D)high tablelands.
E)badlands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Continuing dissolution and collapse may lead the coalescing of sinkholes to form a
A)disappearing stream.
B)rise.
C)doline.
D)drip curtain.
E)karst valley.
A)disappearing stream.
B)rise.
C)doline.
D)drip curtain.
E)karst valley.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The weathering of limestone can create circular depressions known as
A)uvalas.
B)stalactites.
C)sinkholes.
D)caverns.
E)disappearing streams.
A)uvalas.
B)stalactites.
C)sinkholes.
D)caverns.
E)disappearing streams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When rainwater attacks formations of limestone,the minerals dissolve and wash away with the mildly acid rainwater.This is an example of
A)oxidation.
B)crystallization.
C)frost action.
D)carbonation.
E)hydration.
A)oxidation.
B)crystallization.
C)frost action.
D)carbonation.
E)hydration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Cones and cockpit karst develop in
A)cold,midlatitude climates.
B)arid regions.
C)wet tropical areas.
D)polar regions.
E)Mediterranean climates.
A)cold,midlatitude climates.
B)arid regions.
C)wet tropical areas.
D)polar regions.
E)Mediterranean climates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following are examples of dripstones?
A)stalactites
B)sinkholes
C)disappearing streams
D)caverns
E)rockfall
A)stalactites
B)sinkholes
C)disappearing streams
D)caverns
E)rockfall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Hydrolysis involves
A)the chemical reaction of water.
B)the addition of water with little chemical change.
C)frost action.
D)salt crystal growth from evaporation.
E)pressure-release jointing.
A)the chemical reaction of water.
B)the addition of water with little chemical change.
C)frost action.
D)salt crystal growth from evaporation.
E)pressure-release jointing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The scientific study of caves is known as
A)dendrochronology.
B)glaciology.
C)speleology.
D)volcanology.
E)physiography.
A)dendrochronology.
B)glaciology.
C)speleology.
D)volcanology.
E)physiography.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Rocks of the same composition and structure found in the same area may have weathered at uneven rates due to a variety of factors.This is known as
A)angle of repose.
B)jointing.
C)inertial resistance.
D)denudation.
E)differential weathering.
A)angle of repose.
B)jointing.
C)inertial resistance.
D)denudation.
E)differential weathering.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Carbonation,in terms of chemical weathering,occurs when
A)carbon dioxide combines with hydrogen to form hydrocarbons that can weather rock and other materials.
B)carbon dioxide gas in water is dissolved under high pressure.
C)water vapor dissolves carbon dioxide,yielding precipitation that contains carbonic acid.
D)carbon dioxide interacts with calcium hydroxide and hydrates calcium silicates.
E)any chemical reaction involving carbon dioxide occurs in the soil.
A)carbon dioxide combines with hydrogen to form hydrocarbons that can weather rock and other materials.
B)carbon dioxide gas in water is dissolved under high pressure.
C)water vapor dissolves carbon dioxide,yielding precipitation that contains carbonic acid.
D)carbon dioxide interacts with calcium hydroxide and hydrates calcium silicates.
E)any chemical reaction involving carbon dioxide occurs in the soil.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Hydration involves
A)the chemical reaction of water.
B)the addition of water with little chemical change.
C)frost action.
D)salt crystal growth from evaporation.
E)pressure-release jointing.
A)the chemical reaction of water.
B)the addition of water with little chemical change.
C)frost action.
D)salt crystal growth from evaporation.
E)pressure-release jointing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Any large cave formed by chemical processes is a
A)cavern.
B)doline.
C)karst valley.
D)collapse sinkhole.
E)stalagmite.
A)cavern.
B)doline.
C)karst valley.
D)collapse sinkhole.
E)stalagmite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
 The yellow-red stains that occur on some rock surfaces are the result of which is a form of weathering.
The yellow-red stains that occur on some rock surfaces are the result of which is a form of weathering.A)hydration;physical
B)hydration;chemical
C)solution;chemical
D)oxidation;physical
E)oxidation;chemical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Plants are important to the development of karst primarily because
A)openings adjacent to their roots serve as microchannels that allow water to enter the rock.
B)the decay of large roots below the surface produces cavities which eventually enlarge to form caves.
C)they supply organic acids that enhance the dissolution process.
D)they provide the calcium carbonate necessary for karst topography to form.
E)they lessen the impact of raindrops on the surface so the water can more rapidly flow into stream channels.
A)openings adjacent to their roots serve as microchannels that allow water to enter the rock.
B)the decay of large roots below the surface produces cavities which eventually enlarge to form caves.
C)they supply organic acids that enhance the dissolution process.
D)they provide the calcium carbonate necessary for karst topography to form.
E)they lessen the impact of raindrops on the surface so the water can more rapidly flow into stream channels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Rust,formed by the reaction of iron and oxygen in the presence of water,is an example of
A)hydration.
B)frost wedging.
C)carbonation.
D)oxidation.
E)hydrolysis.
A)hydration.
B)frost wedging.
C)carbonation.
D)oxidation.
E)hydrolysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
may form at the bottom of cockpits and may even be an important cause of cockpit karst topography.
A)River floodplains
B)Sinkholes
C)Stalactites
D)Grabens
E)Dripstones
A)River floodplains
B)Sinkholes
C)Stalactites
D)Grabens
E)Dripstones

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Which of the following is not necessary for well-developed karst to develop?
A)high proportion of calcium carbonate in the rock
B)joints in rock of otherwise low permeability
C)vegetation
D)arid conditions
E)a zone of air between the ground surface and water table
A)high proportion of calcium carbonate in the rock
B)joints in rock of otherwise low permeability
C)vegetation
D)arid conditions
E)a zone of air between the ground surface and water table

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which of the following can lead to the slope failure that causes mass movement?
A)saturation from rainfall only
B)oversteepening of the slope only
C)earthquakes only
D)volcanic eruptions only
E)saturation,oversteepening of slopes,earthquakes,and volcanic eruptions.
A)saturation from rainfall only
B)oversteepening of the slope only
C)earthquakes only
D)volcanic eruptions only
E)saturation,oversteepening of slopes,earthquakes,and volcanic eruptions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
 On May 5,2014,700 homes in northeastern Afghanistan were buried causing hundreds of fatalities after prolonged rainfall on fine-grained soils led to a
On May 5,2014,700 homes in northeastern Afghanistan were buried causing hundreds of fatalities after prolonged rainfall on fine-grained soils led to aA)solifluction.
B)creep.
C)scarification.
D)rockfall.
E)landslide.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A slow persistent mass movement of surface soil is called
A)a debris avalanche.
B)soil creep.
C)a soil slide.
D)a rockfall.
E)slump.
A)a debris avalanche.
B)soil creep.
C)a soil slide.
D)a rockfall.
E)slump.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A rotational slide (slump)involves
A)movement of surface material along a concave surface.
B)movement of surface material along a planar surface.
C)unconsolidated flow of material.
D)a slurry of unconsolidated materials moving downslope.
E)detachment and rapid downward movement of a volume by gravity.
A)movement of surface material along a concave surface.
B)movement of surface material along a planar surface.
C)unconsolidated flow of material.
D)a slurry of unconsolidated materials moving downslope.
E)detachment and rapid downward movement of a volume by gravity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
 The photograph is an example of a
The photograph is an example of aA)talus slope.
B)debris avalanche.
C)mudflow.
D)landslide.
E)creep.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
In polar and alpine regions,thawing and saturation of the upper layer of soil,resulting in a slow downslope movement called
A)transitional slide.
B)mudflow.
C)solifluction.
D)lahar.
E)slump.
A)transitional slide.
B)mudflow.
C)solifluction.
D)lahar.
E)slump.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is not a class of mass movement?
A)fall
B)slide
C)slip
D)flow
E)creep
A)fall
B)slide
C)slip
D)flow
E)creep

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Human-induced mass movements produce a category of processes known as
A)debris flows.
B)denudation.
C)scarification.
D)translational slides.
E)lahar.
A)debris flows.
B)denudation.
C)scarification.
D)translational slides.
E)lahar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
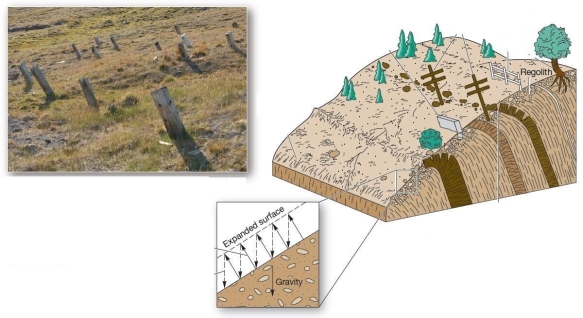 The mass movement process responsible of the curved growing pattern in the trees and the downslope leaning of the utility posts and fences is
The mass movement process responsible of the curved growing pattern in the trees and the downslope leaning of the utility posts and fences isA)debris avalanche.
B)soil creep.
C)landslide.
D)rockfall.
E)slump.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The type of mass movement in which material moves in a unit along a zone of weakness is
A)fall.
B)flow.
C)scarification.
D)weathering.
E)slides.
A)fall.
B)flow.
C)scarification.
D)weathering.
E)slides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following human activities can contribute to mass movement?
A)a road cut only
B)surface mining only
C)residential development only
D)commercial development only
E)any human disturbance of a slope,including road cuts,surface mining,and development
A)a road cut only
B)surface mining only
C)residential development only
D)commercial development only
E)any human disturbance of a slope,including road cuts,surface mining,and development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Discuss the dynamic equilibrium model and the concept of geomorphic threshold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A translational slide involves
A)movement of surface material along a concave surface.
B)movement of surface material along a planar surface.
C)unconsolidated flow of material.
D)a slurry of unconsolidated materials moving downslope.
E)detachment and rapid downward movement of a volume by gravity.
A)movement of surface material along a concave surface.
B)movement of surface material along a planar surface.
C)unconsolidated flow of material.
D)a slurry of unconsolidated materials moving downslope.
E)detachment and rapid downward movement of a volume by gravity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Describe the forces acting on a slope,and also the various physical aspects of a slope,such as waxing slope and debris slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The presence of talus slopes indicates the occurrence of
A)planar slides.
B)mudflow.
C)creep.
D)rockfall.
E)slump.
A)planar slides.
B)mudflow.
C)creep.
D)rockfall.
E)slump.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Flows involve
A)movement of surface material along a concave surface.
B)movement of surface material along a planar surface.
C)unconsolidated flow of material.
D)a slurry of unconsolidated materials moving downslope.
E)detachment and rapid downward movement of a volume by gravity.
A)movement of surface material along a concave surface.
B)movement of surface material along a planar surface.
C)unconsolidated flow of material.
D)a slurry of unconsolidated materials moving downslope.
E)detachment and rapid downward movement of a volume by gravity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
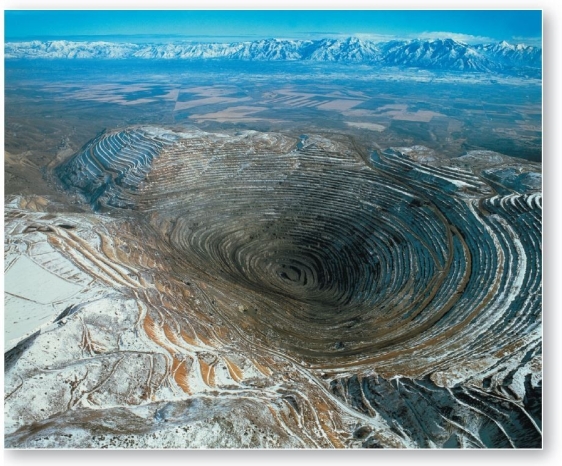 The Bingham Canyon Mine outside Salt Lake City,Utah,2014 The photograph shows an example of which mass movement process?
The Bingham Canyon Mine outside Salt Lake City,Utah,2014 The photograph shows an example of which mass movement process?A)debris flows
B)creep
C)landslide
D)scarification
E)solifluction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A is a type of debris flow associated with volcanic activity.
A)slump
B)creep
C)rockfall
D)landslide
E)lahar
A)slump
B)creep
C)rockfall
D)landslide
E)lahar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A mass of falling and tumbling rock,debris,and soil traveling at a high velocity owing to the presence of ice or water is a
A)rockfall.
B)mudflow.
C)debris avalanche.
D)landslide.
E)lahar.
A)rockfall.
B)mudflow.
C)debris avalanche.
D)landslide.
E)lahar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A is a mixture of water and loosely consolidated sediment,such as gravels,boulders,and coarse rock fragments,moving downslope.
A)debris flow
B)creep
C)rockfall
D)landslide
E)slump
A)debris flow
B)creep
C)rockfall
D)landslide
E)slump

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 89 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



