Deck 14: River Systems
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/99
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: River Systems
1
Stream drainage patterns are determined by which of the following?
A)regional steepness and relief only
B)variations in rock resistance only
C)climate only
D)landscape characteristics only
E)climate,regional steepness and relief,landscape characteristics,and variations in rock resistance.
A)regional steepness and relief only
B)variations in rock resistance only
C)climate only
D)landscape characteristics only
E)climate,regional steepness and relief,landscape characteristics,and variations in rock resistance.
E
2
Processes that are related expressly to streams and rivers are termed
A)fluvial.
B)geomorphic.
C)lentic.
D)lotic.
E)riverine.
A)fluvial.
B)geomorphic.
C)lentic.
D)lotic.
E)riverine.
A
3
Overland flow can concentrate in small grooves called ,which can enlarge to form .
A)striations;potholes
B)potholes;striations
C)rills;gullies
D)gullies;rills
E)striations;gullies
A)striations;potholes
B)potholes;striations
C)rills;gullies
D)gullies;rills
E)striations;gullies
C
4
A basin in which water leaves via evapotranspiration or subsurface gravitational flow instead of reaching the ocean is said to have
A)disappearing streams.
B)hydraulic action.
C)base flow.
D)deranged patterns.
E)internal drainage.
A)disappearing streams.
B)hydraulic action.
C)base flow.
D)deranged patterns.
E)internal drainage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The general term for channelized water flow,regardless of size,is
A)river.
B)gully.
C)stream.
D)rill.
E)interfluve.
A)river.
B)gully.
C)stream.
D)rill.
E)interfluve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The area of land from which all water in it drains into the same place is known as a(n)
A)interfluve.
B)watershed.
C)drainage divide.
D)fluvial unit.
E)hydrologic unit.
A)interfluve.
B)watershed.
C)drainage divide.
D)fluvial unit.
E)hydrologic unit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
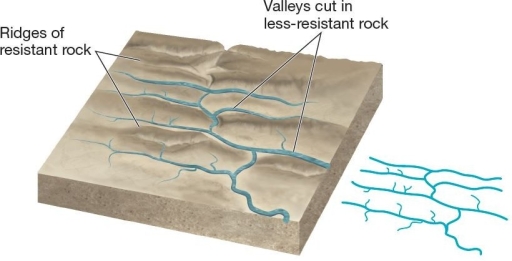 This drainage pattern is characteristic of dipping or folded topography.
This drainage pattern is characteristic of dipping or folded topography.A)annular
B)trellis
C)radial
D)rectangular
E)dendritic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Rectangular drainage patterns form primarily as a result of
A)differential resistance to erosion.
B)topographic uplift.
C)flow through anticlinal and synclinal topography.
D)flow through a faulted and jointed landscape.
E)hard,resistant rock that prevents erosion.
A)differential resistance to erosion.
B)topographic uplift.
C)flow through anticlinal and synclinal topography.
D)flow through a faulted and jointed landscape.
E)hard,resistant rock that prevents erosion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Drainage density is determined by
A)dividing the number of streams in a basin by the basin area.
B)dividing the actual path length of a stream by the shortest path length of the stream.
C)averaging the discharge values across a drainage basin.
D)dividing the total length of all stream channels in the basin by the area of the basin.
E)averaging the channel depth of the streams in a drainage basin.
A)dividing the number of streams in a basin by the basin area.
B)dividing the actual path length of a stream by the shortest path length of the stream.
C)averaging the discharge values across a drainage basin.
D)dividing the total length of all stream channels in the basin by the area of the basin.
E)averaging the channel depth of the streams in a drainage basin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A drainage divide that separates drainage basins that empty into different bodies of water surrounding a continent is known as
A)a catchment.
B)a delta.
C)a continental divide.
D)an interfluve.
E)a rill.
A)a catchment.
B)a delta.
C)a continental divide.
D)an interfluve.
E)a rill.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the drainage density of a 100 mi2 drainage basin with 25 miles of stream,running through three rivers?
A)3
B)33.333
C)4 mi./mi.2
D)0.25 mi./mi.2
E)0.15 km/km2
A)3
B)33.333
C)4 mi./mi.2
D)0.25 mi./mi.2
E)0.15 km/km2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In stream formation,surface water initially moves down slope in a thin film called
A)river.
B)gully.
C)sheetflow.
D)rill.
E)interfluve.
A)river.
B)gully.
C)sheetflow.
D)rill.
E)interfluve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Drainage basins are
A)open systems.
B)closed systems.
C)equilibrium systems.
D)open systems in terms of energy,closed systems in terms of matter.
E)closed systems in terms of energy,open systems in terms of matter.
A)open systems.
B)closed systems.
C)equilibrium systems.
D)open systems in terms of energy,closed systems in terms of matter.
E)closed systems in terms of energy,open systems in terms of matter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Watersheds are defined by
A)continental divides.
B)drainage divides.
C)stream orders.
D)fluvial units.
E)stream size and density.
A)continental divides.
B)drainage divides.
C)stream orders.
D)fluvial units.
E)stream size and density.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The science of water and its global circulation,distribution,and properties is known as
A)geomorphology.
B)climatology.
C)lithology.
D)fluviology.
E)hydrology.
A)geomorphology.
B)climatology.
C)lithology.
D)fluviology.
E)hydrology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The area of high ground that separates one valley from another and directs sheetflow is known as .
A)the maximum contour elevation
B)a drainage divide
C)an interfluve
D)the continental divide
E)rill
A)the maximum contour elevation
B)a drainage divide
C)an interfluve
D)the continental divide
E)rill

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
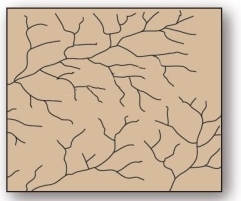 This tree-like drainage pattern efficiently moves water and sediment through its system due to minimization of the total length of each branch.
This tree-like drainage pattern efficiently moves water and sediment through its system due to minimization of the total length of each branch.A)dendritic
B)trellis
C)radial
D)deranged
E)rectangular

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
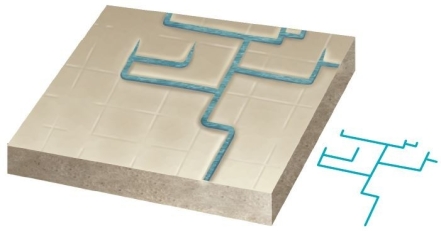 Faulted and jointed landscapes direct stream courses in patterns of right-angle turns forming this drainage pattern.
Faulted and jointed landscapes direct stream courses in patterns of right-angle turns forming this drainage pattern.A)radial
B)rectangular
C)trellis
D)dendritic
E)deranged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
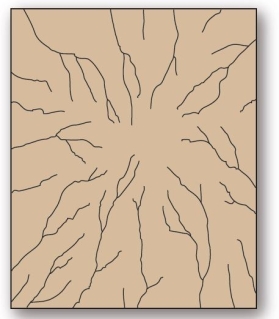 This drainage pattern results when streams flow off a central peak or dome.
This drainage pattern results when streams flow off a central peak or dome.A)annular
B)trellis
C)radial
D)rectangular
E)deranged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
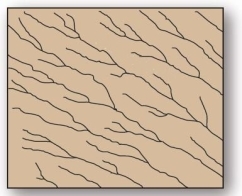 This drainage pattern is associated with steep slopes.
This drainage pattern is associated with steep slopes.A)parallel
B)dendritic
C)trellis
D)deranged
E)radial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
streams have some groundwater input,but only flow for certain periods during a year.
A)Perennial
B)Intermittent
C)Ephemeral
D)Temporary
E)Exotic
A)Perennial
B)Intermittent
C)Ephemeral
D)Temporary
E)Exotic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Hydraulic action is highest
A)near the surface in the middle of streams.
B)in areas with low discharge.
C)where flow is turbulent.
D)within deep and wide channels.
E)along slow moving currents.
A)near the surface in the middle of streams.
B)in areas with low discharge.
C)where flow is turbulent.
D)within deep and wide channels.
E)along slow moving currents.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If a stream originates in a humid region,but subsequently flows through an arid region,discharge is likely highest
A)upstream.
B)downstream.
C)midstream.
D)at an estuary or confluence with another stream.
E)along tributaries.
A)upstream.
B)downstream.
C)midstream.
D)at an estuary or confluence with another stream.
E)along tributaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Erosion in which boulders and gravel moving along the channel break apart and as rocks and sediment grind and carve streambeds is known as
A)sheetflow.
B)saltation.
C)weathering.
D)abrasion.
E)hydraulic action.
A)sheetflow.
B)saltation.
C)weathering.
D)abrasion.
E)hydraulic action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A drainage system that maintains its original course and pattern as it erodes into underlying horizontal beds of different structure than that in which the system evolved is called a(n)
A)deranged pattern.
B)discordant stream.
C)annular pattern.
D)yazoo stream.
E)superposed stream.
A)deranged pattern.
B)discordant stream.
C)annular pattern.
D)yazoo stream.
E)superposed stream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
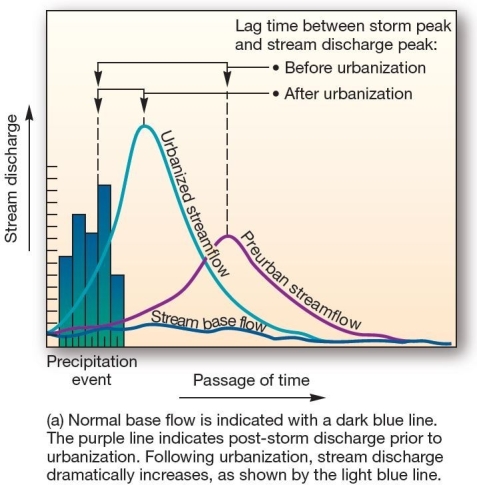 This graph,showing the effects of urbanization on streamflow over time,is an example of a
This graph,showing the effects of urbanization on streamflow over time,is an example of aA)water budget.
B)hydrograph.
C)climograph.
D)hydrological cycle.
E)cladogram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Turbulent flow is likely to be least in
A)channels with tree trunks and other obstacles.
B)shallow streams with boulders.
C)streams with high friction.
D)deep,lowland rivers.
E)along the rocky banks of a stream.
A)channels with tree trunks and other obstacles.
B)shallow streams with boulders.
C)streams with high friction.
D)deep,lowland rivers.
E)along the rocky banks of a stream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In most river basins in humid regions,discharge is highest
A)upstream.
B)downstream.
C)midstream.
D)at the headwaters.
E)along tributaries.
A)upstream.
B)downstream.
C)midstream.
D)at the headwaters.
E)along tributaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
streams flow year-round,fed by snowmelt,rainfall,groundwater,or a combination thereof.
A)Perennial
B)Intermittent
C)Ephemeral
D)Permanent
E)Temporary
A)Perennial
B)Intermittent
C)Ephemeral
D)Permanent
E)Temporary

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The river with the greatest discharge is the
A)Ganges.
B)Mississippi.
C)Orinoco.
D)Yangtze.
E)Amazon.
A)Ganges.
B)Mississippi.
C)Orinoco.
D)Yangtze.
E)Amazon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Erosion performed by flowing water alone is known as
A)sheetflow.
B)saltation.
C)weathering.
D)abrasion.
E)hydraulic action.
A)sheetflow.
B)saltation.
C)weathering.
D)abrasion.
E)hydraulic action.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is used to measure streamflow?
A)current meter
B)barometer and sling psychrometer
C)statistical methods of probability
D)reservoirs
E)evaporimeters
A)current meter
B)barometer and sling psychrometer
C)statistical methods of probability
D)reservoirs
E)evaporimeters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following landforms is incorrectly matched with a drainage pattern?
A)volcano - radial
B)folded mountain belt - trellis
C)faulted and jointed - rectangular
D)glaciated - deranged
E)topographically disrupted areas - parallel
A)volcano - radial
B)folded mountain belt - trellis
C)faulted and jointed - rectangular
D)glaciated - deranged
E)topographically disrupted areas - parallel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A stream's volume of flow per unit of time is its
A)speed.
B)velocity.
C)discharge.
D)flow rate.
E)base load.
A)speed.
B)velocity.
C)discharge.
D)flow rate.
E)base load.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
streams are not connected to groundwater systems and only flow after precipitation events.
A)Perennial
B)Intermittent
C)Ephemeral
D)Temporary
E)Exotic
A)Perennial
B)Intermittent
C)Ephemeral
D)Temporary
E)Exotic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following lists of processes are in the correct sequence as to their occurrence in nature?
A)deposition,erosion,transport,weathering
B)weathering,erosion,deposition,transport
C)weathering,deposition,erosion,transport
D)weathering,erosion,transport,deposition
E)transport,deposition,erosion,weathering
A)deposition,erosion,transport,weathering
B)weathering,erosion,deposition,transport
C)weathering,deposition,erosion,transport
D)weathering,erosion,transport,deposition
E)transport,deposition,erosion,weathering

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a given section of channel,the greatest flow velocities are usually
A)near the surface,near the center.
B)along the shallowest portions of the stream.
C)along either bank.
D)near the bottom of the stream channel.
E)in areas with large obstacles,such as tree trunks and boulders.
A)near the surface,near the center.
B)along the shallowest portions of the stream.
C)along either bank.
D)near the bottom of the stream channel.
E)in areas with large obstacles,such as tree trunks and boulders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
With no clear geometry and no true stream valley,this drainage pattern occurs in areas such as glaciated shield regions.
A)deranged
B)radial
C)parallel
D)dendritic
E)trellis
A)deranged
B)radial
C)parallel
D)dendritic
E)trellis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
As the discharge of a stream increases,which of the following also happens?
A)Stream channels narrow,become shallower,and lose velocity.
B)The rate of flow decreases.
C)Channel width increases but channel depth decreases.
D)Width,depth,and/or velocity increase.
E)Erosion and sediment transport are greatly reduced.
A)Stream channels narrow,become shallower,and lose velocity.
B)The rate of flow decreases.
C)Channel width increases but channel depth decreases.
D)Width,depth,and/or velocity increase.
E)Erosion and sediment transport are greatly reduced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
streams begin in moist regions and flow downstream into arid landscapes with high evapotranspiration.
A)Perennial
B)Intermittent
C)Ephemeral
D)Temporary
E)Exotic
A)Perennial
B)Intermittent
C)Ephemeral
D)Temporary
E)Exotic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The sediment load consisting of fine-grained clastic particles held aloft in the stream is the
A)bed load.
B)suspended load.
C)dissolved load.
D)flow load.
E)saltation.
A)bed load.
B)suspended load.
C)dissolved load.
D)flow load.
E)saltation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The main process contributing material in solution in sediment load is
A)physical weathering.
B)chemical weathering.
C)biological weathering.
D)erosion.
E)deposition.
A)physical weathering.
B)chemical weathering.
C)biological weathering.
D)erosion.
E)deposition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The sediment load consisting of coarse material too large to remain in suspension,moving along the channel bottom via traction and saltation is the
A)bed load.
B)suspended load.
C)dissolved load.
D)flow load.
E)free load.
A)bed load.
B)suspended load.
C)dissolved load.
D)flow load.
E)free load.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A(n)stream is one in which the channel slope has adjusted so that stream velocity is just enough to transport the sediment load.
A)graded
B)ungraded
C)equilibrium
D)disequilibrium
E)channel
A)graded
B)ungraded
C)equilibrium
D)disequilibrium
E)channel

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The total possible load a stream can transport is its ,whereas a stream's ability to move particles of specific size is its .
A)capacity;competence
B)competence;capacity
C)discharge;competence
D)bed load;sediment load
E)saltation;traction
A)capacity;competence
B)competence;capacity
C)discharge;competence
D)bed load;sediment load
E)saltation;traction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Bed load is moved by
A)saltation only.
B)traction only.
C)suspension only.
D)saltation,traction,and suspension.
E)both saltation and traction,but not suspension.
A)saltation only.
B)traction only.
C)suspension only.
D)saltation,traction,and suspension.
E)both saltation and traction,but not suspension.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The suspended load of a stream consists of particles that are
A)rolled along the stream bed.
B)held aloft in the stream flow.
C)dragged along the stream bed.
D)dissolved in solution.
E)bounced along the stream bed.
A)rolled along the stream bed.
B)held aloft in the stream flow.
C)dragged along the stream bed.
D)dissolved in solution.
E)bounced along the stream bed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The ultimate base level is
A)a drainage divide.
B)a dam.
C)sea level.
D)dependent on the geological substrate.
E)any hard,resistant rock in a channel.
A)a drainage divide.
B)a dam.
C)sea level.
D)dependent on the geological substrate.
E)any hard,resistant rock in a channel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Stream transport involves all of the following except
A)saltation.
B)bed load.
C)traction.
D)sheetflow.
E)suspended load.
A)saltation.
B)bed load.
C)traction.
D)sheetflow.
E)suspended load.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A(n)is a stream which maintains an equilibrium between the processes of erosion and deposition and,therefore degradation and aggradation.
A)graded stream
B)oxbow
C)anabranching river
D)meandering stream
E)rill
A)graded stream
B)oxbow
C)anabranching river
D)meandering stream
E)rill

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the load exceeds a stream's capacity,sediment accumulates in the bed in a process called
A)downcutting.
B)degradation.
C)aggradation.
D)saltation.
E)traction
A)downcutting.
B)degradation.
C)aggradation.
D)saltation.
E)traction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The process whereby streams lengthen their channels upstream is called
A)headwater erosion.
B)channel incision.
C)stream piracy.
D)saltation.
E)traction.
A)headwater erosion.
B)channel incision.
C)stream piracy.
D)saltation.
E)traction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following may act as a local base level?
A)a lake that a river flows into
B)a drainage divide
C)the upper surface of a waterfall
D)an interfluve
E)the headwaters
A)a lake that a river flows into
B)a drainage divide
C)the upper surface of a waterfall
D)an interfluve
E)the headwaters

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which of the following is correct of the longitudinal profile of most rivers?
A)It always changes at a constant rate from the headwater region to the sea.
B)It is convex in shape.
C)It is concave in shape.
D)It is gentle upstream and steep downstream.
E)It is highest at the mouth and lowest at the headwaters.
A)It always changes at a constant rate from the headwater region to the sea.
B)It is convex in shape.
C)It is concave in shape.
D)It is gentle upstream and steep downstream.
E)It is highest at the mouth and lowest at the headwaters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The sediment load that travels in solution is
A)bed load.
B)suspended load.
C)dissolved load.
D)flow load.
E)saltation.
A)bed load.
B)suspended load.
C)dissolved load.
D)flow load.
E)saltation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
An interruption in a stream's graded profile of equilibrium is called a
A)gradation.
B)longitudinal interruption.
C)base level.
D)cutbank.
E)nickpoint.
A)gradation.
B)longitudinal interruption.
C)base level.
D)cutbank.
E)nickpoint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Stream piracy refers to
A)the legal process by which a state secures rights to the waters of a river basin.
B)the merging of two streams flowing in the same valley.
C)capturing the headwater regions of another stream by an eroding rill in another system.
D)the illegal withdrawal of water from a river.
E)upstream erosion leading the to the lengthening of the channel.
A)the legal process by which a state secures rights to the waters of a river basin.
B)the merging of two streams flowing in the same valley.
C)capturing the headwater regions of another stream by an eroding rill in another system.
D)the illegal withdrawal of water from a river.
E)upstream erosion leading the to the lengthening of the channel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Base level refers to
A)the amount of discharge in a particular reach of a stream.
B)a level below which a stream cannot erode its valley.
C)an evolutionary cycle of landscape development from fluvial action.
D)the average height of a stream channel.
E)the stream gradient.
A)the amount of discharge in a particular reach of a stream.
B)a level below which a stream cannot erode its valley.
C)an evolutionary cycle of landscape development from fluvial action.
D)the average height of a stream channel.
E)the stream gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A graphic depiction of a streams gradient from its headwaters to mouth is called a(n)
A)altimeter.
B)Keeling curve.
C)hydrograph.
D)climograph.
E)longitudinal profile.
A)altimeter.
B)Keeling curve.
C)hydrograph.
D)climograph.
E)longitudinal profile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The drop in stream elevation per unit distance is known as
A)discharge.
B)base level.
C)gradient.
D)aspect.
E)slope.
A)discharge.
B)base level.
C)gradient.
D)aspect.
E)slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Excess sediment may result in which of the following channel patterns?
A)V-shaped valleys
B)braided stream
C)meandering stream
D)straight,steep-walled channels
E)deeply entrenched U-shaped valleys
A)V-shaped valleys
B)braided stream
C)meandering stream
D)straight,steep-walled channels
E)deeply entrenched U-shaped valleys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Maximum velocity in a meandering stream is
A)near the bottom.
B)at the inner portion of the meander curve.
C)at the center and near the surface.
D)at the outer portion of the meander curve.
E)at the point bar.
A)near the bottom.
B)at the inner portion of the meander curve.
C)at the center and near the surface.
D)at the outer portion of the meander curve.
E)at the point bar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is incorrect regarding floodplains?
A)They are formed by recurrent flooding in the area adjacent to the stream.
B)Natural levees on either side of a stream are formed during times when the stream is at flood stage and overflows the bank.
C)They are generally low-lying areas.
D)Residual deposits from abandoned channels often result in meander scars in floodplains.
E)They are characterized by rapids and low waterfalls.
A)They are formed by recurrent flooding in the area adjacent to the stream.
B)Natural levees on either side of a stream are formed during times when the stream is at flood stage and overflows the bank.
C)They are generally low-lying areas.
D)Residual deposits from abandoned channels often result in meander scars in floodplains.
E)They are characterized by rapids and low waterfalls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Which of the following is incorrectly matched?
A)cutbank - at outer portion of a stream meander
B)point bar - area of substantial erosion
C)aggradation - sediment accumulation in the stream channel
D)braided stream - maze of interconnected channels
E)undercut bank - area of erosion
A)cutbank - at outer portion of a stream meander
B)point bar - area of substantial erosion
C)aggradation - sediment accumulation in the stream channel
D)braided stream - maze of interconnected channels
E)undercut bank - area of erosion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Maximum velocity in a straight channel is found
A)near the bottom.
B)near the inside of a meander.
C)at the center and near the surface,corresponding with the deepest parts of the stream channel.
D)at the center and near the surface,corresponding with the shallowest parts of the stream channel.
E)near either of the river banks.
A)near the bottom.
B)near the inside of a meander.
C)at the center and near the surface,corresponding with the deepest parts of the stream channel.
D)at the center and near the surface,corresponding with the shallowest parts of the stream channel.
E)near either of the river banks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The portion of each meandering curve subject to the fastest water velocity undergoes the greatest erosive action.This action forms a steep
A)meander scar.
B)oxbow.
C)cutback.
D)point bar.
E)uppercut bank.
A)meander scar.
B)oxbow.
C)cutback.
D)point bar.
E)uppercut bank.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The portion of each meandering curve subject to the slowest water velocity undergoes aggradation.This results in a(n)
A)meander scar.
B)oxbow.
C)cutback.
D)neck.
E)point bar.
A)meander scar.
B)oxbow.
C)cutback.
D)neck.
E)point bar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Channels with gradual slopes often develop a sinuous form called a(n)pattern.
A)braided stream
B)anabranching
C)meandering stream
D)straight
E)exotic
A)braided stream
B)anabranching
C)meandering stream
D)straight
E)exotic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
As they migrate,meandering streams erode their out outside banks,often forming a narrow neck of land that eventually erodes through and forms a and the stream becomes .
A)meander scar;narrower
B)cutoff;straighter
C)cutback;more sinuous
D)point bar;wider
E)neck;longer
A)meander scar;narrower
B)cutoff;straighter
C)cutback;more sinuous
D)point bar;wider
E)neck;longer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Natural levees are created during
A)floods.
B)normal flow conditions.
C)low flow conditions.
D)degradation.
E)erosional events.
A)floods.
B)normal flow conditions.
C)low flow conditions.
D)degradation.
E)erosional events.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Entrenchment of a channel occurs because
A)a decrease in stream gradient occurs.
B)a change in the bed load size-distribution occurs.
C)the river flows from consolidated rock into a region composed of loose sediments.
D)rejuvenation occurs due to uplift.
E)isostatic downwarping of the crust occurs.
A)a decrease in stream gradient occurs.
B)a change in the bed load size-distribution occurs.
C)the river flows from consolidated rock into a region composed of loose sediments.
D)rejuvenation occurs due to uplift.
E)isostatic downwarping of the crust occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
is the general term for unconsolidated clay,silt,sand,gravel,and mineral fragments deposited by running water.
A)Alluvium
B)Deposition
C)Aggradation
D)Degradation
E)Fluvium
A)Alluvium
B)Deposition
C)Aggradation
D)Degradation
E)Fluvium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A maze of interconnected channels formed on a river with a high sediment load is known as a(n)stream.
A)braided
B)anabranching
C)meandering
D)straight
E)exotic
A)braided
B)anabranching
C)meandering
D)straight
E)exotic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A(n)is a meander that becomes isolated from the rest of the river.
A)oxbow lake
B)undercut bank
C)point bar
D)cutoff
E)cutbank
A)oxbow lake
B)undercut bank
C)point bar
D)cutoff
E)cutbank

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A yazoo tributary stream cannot join with the main river in an area because
A)the yazoo flows in a different valley.
B)a small structural ridge separates the rivers.
C)a natural levee on the main river prevents joining.
D)a man-made flow control structure keeps the rivers separate.
E)a large topographic barrier,such as a mesa,separates them.
A)the yazoo flows in a different valley.
B)a small structural ridge separates the rivers.
C)a natural levee on the main river prevents joining.
D)a man-made flow control structure keeps the rivers separate.
E)a large topographic barrier,such as a mesa,separates them.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
As a stream's velocity decreases,which of the following sizes of sediments will be deposited last?
A)gravel
B)sand
C)silt
D)loam
E)clay
A)gravel
B)sand
C)silt
D)loam
E)clay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A stream that downcuts at the same rate as tectonic uplift,thereby maintaining its course is called a(n)
A)meandering stream.
B)anabranching river.
C)antecedent stream.
D)rejuvenated river.
E)graded stream.
A)meandering stream.
B)anabranching river.
C)antecedent stream.
D)rejuvenated river.
E)graded stream.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The entrenchment of a river into its own floodplain can produce
A)backswamps.
B)alluvial terraces.
C)natural levees.
D)river deltas.
E)yazoo streams.
A)backswamps.
B)alluvial terraces.
C)natural levees.
D)river deltas.
E)yazoo streams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The process whereby streams deepen their channel is known as
A)headwater erosion.
B)channel incision.
C)stream piracy.
D)saltation.
E)traction.
A)headwater erosion.
B)channel incision.
C)stream piracy.
D)saltation.
E)traction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Coarser particles generally settle out _,while finer particles settle out .
A)closer to the mouth;closer to the headwaters
B)along cutbanks;at point bars
C)at point bars;along cutbanks
D)closer to the mouth;not at all
E)closer to the headwaters;closer to the mouth
A)closer to the mouth;closer to the headwaters
B)along cutbanks;at point bars
C)at point bars;along cutbanks
D)closer to the mouth;not at all
E)closer to the headwaters;closer to the mouth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



