Deck 11: The Dynamic Planet
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/119
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: The Dynamic Planet
1
Which of the following is an endogenic process?
A)weathering
B)stream deposition
C)volcanism
D)glacial erosion
E)wind erosion
A)weathering
B)stream deposition
C)volcanism
D)glacial erosion
E)wind erosion
C
2
Scientists have direct evidence of the Earth's structure to
A)the inner core.
B)the upper mantle (~250 km (155 mi)).
C)about 12 km (7.6 mi)from the surface.
D)15 km (9.3 mi)from the surface,based on the deepest well shaft.
E)the Gutenberg discontinuity.
A)the inner core.
B)the upper mantle (~250 km (155 mi)).
C)about 12 km (7.6 mi)from the surface.
D)15 km (9.3 mi)from the surface,based on the deepest well shaft.
E)the Gutenberg discontinuity.
C
3
The scientific study of rock strata (layers)is known as and based on the principle of .
A)stratigraphy;superposition
B)geomorphology;uniformitarianism
C)Paleontology;catastrophism
D)Paleogeography;plate tectonics
E)sedimentology;deposition
A)stratigraphy;superposition
B)geomorphology;uniformitarianism
C)Paleontology;catastrophism
D)Paleogeography;plate tectonics
E)sedimentology;deposition
A
4
Which of the following is incorrectly matched?
A)plate tectonics - endogenic processes
B)volcanism - endogenic processes
C)radioactive decay heat - exogenic process
D)weathering - exogenic process
E)erosion - exogenic process
A)plate tectonics - endogenic processes
B)volcanism - endogenic processes
C)radioactive decay heat - exogenic process
D)weathering - exogenic process
E)erosion - exogenic process

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is an example of an age-relationship based on relative dating?
A)The Tonto Group in the Grand Canyon formed during the Paleozoic era.
B)The Grand Canyon's Vishnu Schist is from the Precambrian.
C)The Coconino Sandstone of the Grand Canyon is younger than the Hermit Shale.
D)Clovis points have been dated at 11,000 years old in North America.
E)Fossil records show flowering plants developed during the Cretaceous.
A)The Tonto Group in the Grand Canyon formed during the Paleozoic era.
B)The Grand Canyon's Vishnu Schist is from the Precambrian.
C)The Coconino Sandstone of the Grand Canyon is younger than the Hermit Shale.
D)Clovis points have been dated at 11,000 years old in North America.
E)Fossil records show flowering plants developed during the Cretaceous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Boundaries between intervals of the geological time scale are determined by
A)dividing the time range of the interval by the number desired subdivisions,thereby creating equal intervals between the divisions.
B)major events in the Earth's history,such as major extinctions.
C)using a quantile method whereby the number of years in each subdivision is determined by dividing the number of years by the desired number of classes.
D)climatic periods based on paleoclimatological reconstructions.
E)historical misunderstandings based on the principle of uniformitarianism;they remain as relicts of this bygone scientific period.
A)dividing the time range of the interval by the number desired subdivisions,thereby creating equal intervals between the divisions.
B)major events in the Earth's history,such as major extinctions.
C)using a quantile method whereby the number of years in each subdivision is determined by dividing the number of years by the desired number of classes.
D)climatic periods based on paleoclimatological reconstructions.
E)historical misunderstandings based on the principle of uniformitarianism;they remain as relicts of this bygone scientific period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is an exogenic process?
A)earthquakes
B)volcanism
C)flows of heat and materials in the mantle
D)weathering
E)radioactive decay
A)earthquakes
B)volcanism
C)flows of heat and materials in the mantle
D)weathering
E)radioactive decay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The subfield of geography and geology concerned with the study of the origins,evolutions,form,and spatial distribution of the Earth's landforms is
A)geophysics.
B)lithology.
C)geomorphology.
D)pedology.
E)edaphology.
A)geophysics.
B)lithology.
C)geomorphology.
D)pedology.
E)edaphology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When geologists conclude that the Grand Canyon sequence of rocks was formed through hundreds of millions of years of deposition,mountain building,and erosion,they are basing this conclusion on the principle of which states that .
A)catastrophism;most rock formations were created as a result of supernatural processes
B)catastrophism;a single,large flood was responsible for the creation of the rock sequence
C)uniformitarianism;all geologic processes take immense amounts of time to occur and always occur at the same rate
D)uniformitarianism;the geologic processes that operated in the past are the same as those that operate today,and they occurred in accordance with the same laws of nature that are operating today
E)stasis;the Grand Canyon today is as it has always been,never changing
A)catastrophism;most rock formations were created as a result of supernatural processes
B)catastrophism;a single,large flood was responsible for the creation of the rock sequence
C)uniformitarianism;all geologic processes take immense amounts of time to occur and always occur at the same rate
D)uniformitarianism;the geologic processes that operated in the past are the same as those that operate today,and they occurred in accordance with the same laws of nature that are operating today
E)stasis;the Grand Canyon today is as it has always been,never changing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The most recent epoch in the geologic time scale is the ,though numerous scientists agree we have entered a new epoch called the .
A)Pleistocene;Holocene
B)Pliocene;Pleistocene
C)Miocene;Pliocene
D)Oligocene;Miocene
E)Holocene;Anthropocene
A)Pleistocene;Holocene
B)Pliocene;Pleistocene
C)Miocene;Pliocene
D)Oligocene;Miocene
E)Holocene;Anthropocene

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following is an example of the principle of uniformitarianism?
A)It is not possible to know how Earth processes have changed over time;therefore,it is not possible to deduce how Earth's ancient landforms evolved.
B)The processes by which streams carve valleys at present are the same as those that carved valleys 500 million years ago.
C)Catastrophic events,such as major landslides,earthquakes,and volcanic episodes,are the primary drivers of geomorphological change.
D)The Earth's geological history is mostly uniform and homogenous,existing now as it mostly always has with the exception of minor recent changes.
E)Prior to written history,knowledge of Earth history is largely unknowable.
A)It is not possible to know how Earth processes have changed over time;therefore,it is not possible to deduce how Earth's ancient landforms evolved.
B)The processes by which streams carve valleys at present are the same as those that carved valleys 500 million years ago.
C)Catastrophic events,such as major landslides,earthquakes,and volcanic episodes,are the primary drivers of geomorphological change.
D)The Earth's geological history is mostly uniform and homogenous,existing now as it mostly always has with the exception of minor recent changes.
E)Prior to written history,knowledge of Earth history is largely unknowable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
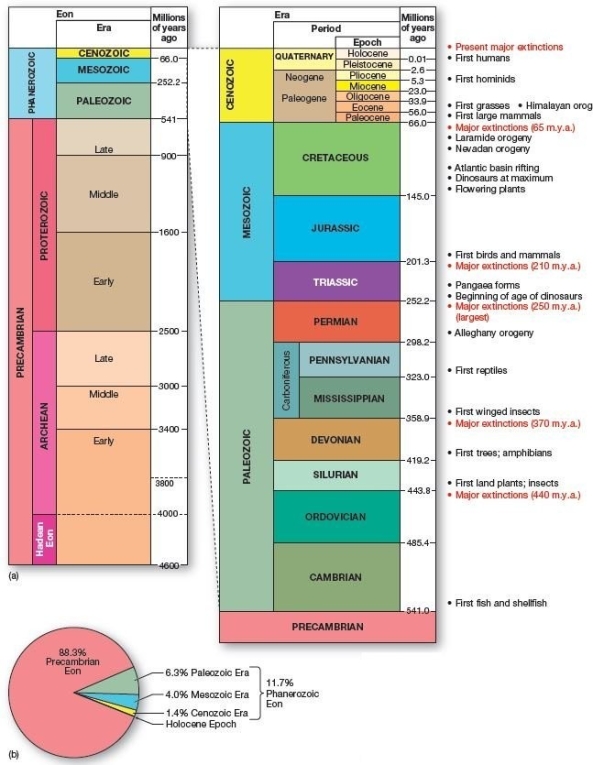 Geologic time scale showing highlights of Earth's history.(a)Dates appear in m.y.a.(millions of years ago). The Precambrian Eon encompasses what percentage of Earth's total history?
Geologic time scale showing highlights of Earth's history.(a)Dates appear in m.y.a.(millions of years ago). The Precambrian Eon encompasses what percentage of Earth's total history?A)0.04 %
B)5%
C)54.1%
D)72.4%
E)88.3%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In terms of dating of specific rocks,structures,or landscapes,relative age refers to
A)the age of geological features based on radiometric dating techniques.
B)the approximate age of geological features based on the period or epoch in which they occurred.For instance,noting a feature is from the Cretaceous.
C)the inability to ascertain exact age through isotopic methods and the necessity to provide a date range for such features.
D)the age of one feature with respect to another within a sequence of events and deduced from the positions of rock strata above and below one another.
E)an educated guess of the rocks age based on its crystalline structure.
A)the age of geological features based on radiometric dating techniques.
B)the approximate age of geological features based on the period or epoch in which they occurred.For instance,noting a feature is from the Cretaceous.
C)the inability to ascertain exact age through isotopic methods and the necessity to provide a date range for such features.
D)the age of one feature with respect to another within a sequence of events and deduced from the positions of rock strata above and below one another.
E)an educated guess of the rocks age based on its crystalline structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following is correct in regards to the geologic time scale?
A)An epoch is composed of one or more periods.
B)The largest defined unit is an eon or,according to some,a supereon.
C)An era is the smallest unit of geologic time.
D)Every period is composed of 2 epochs.
E)Boundaries between geologic time spans are based on equal interval divisions.
A)An epoch is composed of one or more periods.
B)The largest defined unit is an eon or,according to some,a supereon.
C)An era is the smallest unit of geologic time.
D)Every period is composed of 2 epochs.
E)Boundaries between geologic time spans are based on equal interval divisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Uniformitarianism assumes that
A)Earth is quite young and is shaped by dramatic events.
B)catastrophic episodes have regularly occurred.
C)the same physical processes we see today are a key to understanding the processes that have been operating throughout geologic time.
D)mountains,plains,and canyons formed by catastrophic events.
E)much of Earth history is ultimately unknowable and we must therefore only concentrate on those parts that have been documented by written historical accounts.
A)Earth is quite young and is shaped by dramatic events.
B)catastrophic episodes have regularly occurred.
C)the same physical processes we see today are a key to understanding the processes that have been operating throughout geologic time.
D)mountains,plains,and canyons formed by catastrophic events.
E)much of Earth history is ultimately unknowable and we must therefore only concentrate on those parts that have been documented by written historical accounts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following is not an example of an age-relationship based on absolute dating?
A)The oldest known rocks on Earth are 3.96 billion years old.
B)The Vishnu schist at the bottom of the Grand Canyon is 2 billion years old.
C)The dinosaurs became extinct 65 million years ago.
D)The Coconino formation in the Grand Canyon is older than the Kaibab formation.
E)Fossil records show flowering plants developed during the Cretaceous.
A)The oldest known rocks on Earth are 3.96 billion years old.
B)The Vishnu schist at the bottom of the Grand Canyon is 2 billion years old.
C)The dinosaurs became extinct 65 million years ago.
D)The Coconino formation in the Grand Canyon is older than the Kaibab formation.
E)Fossil records show flowering plants developed during the Cretaceous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
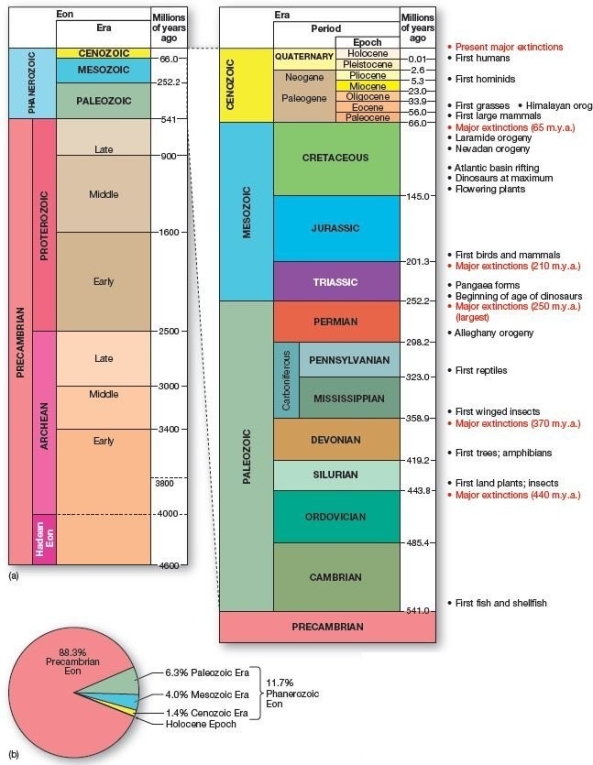 Geologic time scale showing highlights of Earth's history.(a)Dates appear in m.y.a.(millions of years ago). Which of the following is correct regarding the geologic time scale?
Geologic time scale showing highlights of Earth's history.(a)Dates appear in m.y.a.(millions of years ago). Which of the following is correct regarding the geologic time scale?A)The Jurassic period occurred during the Paleozoic era.
B)Over 87 percent of Earth's history has elapsed during the more recent Cenozoic,Mesozoic,and Paleozoic eras.
C)The bulk of Earth's history has occurred during the Precambrian eon.
D)Modern humans live in the Tertiary period.
E)Flowering plants emerged in the Precambrian.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In terms of dating of specific rocks,structures,or landscapes,absolute age refers to
A)the age of geological features based on radiometric dating techniques.
B)the approximate age of geological features based on the period or epoch in which they occurred.For instance,noting a feature is from the Cretaceous.
C)a range of numeric values in which features were likely formed and based on several lines of evidence,such as paleoclimatic and paleobotanical reconstructions.
D)the age of one feature with respect to another within a sequence of events and deduced from the positions of rock strata above and below one another.
E)historical records from the earliest modern humans that recorded when the rocks and structures were formed.
A)the age of geological features based on radiometric dating techniques.
B)the approximate age of geological features based on the period or epoch in which they occurred.For instance,noting a feature is from the Cretaceous.
C)a range of numeric values in which features were likely formed and based on several lines of evidence,such as paleoclimatic and paleobotanical reconstructions.
D)the age of one feature with respect to another within a sequence of events and deduced from the positions of rock strata above and below one another.
E)historical records from the earliest modern humans that recorded when the rocks and structures were formed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which is the correct order of geologic time spans,from largest to smallest?
A)eon - era - period - epoch
B)epoch - period - era - eon
C)era -eon -epoch - period
D)epoch - era - period - eon
E)eon - epoch - period - era
A)eon - era - period - epoch
B)epoch - period - era - eon
C)era -eon -epoch - period
D)epoch - era - period - eon
E)eon - epoch - period - era

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The principle that the same physical processes currently active in the environment were operating throughout Earth's history is known as
A)uniformitarianism.
B)catastrophism.
C)parallelism.
D)stasis.
E)ubiquity.
A)uniformitarianism.
B)catastrophism.
C)parallelism.
D)stasis.
E)ubiquity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following gives the correct sequence of layers in Earth,from the surface to the center?
A)crust,inner core,mantle,outer core
B)inner core,outer core,mantle,crust
C)mantle,crust,inner core,outer core
D)crust,mantle,outer core,inner core
E)outer core,inner core,crust,mantle
A)crust,inner core,mantle,outer core
B)inner core,outer core,mantle,crust
C)mantle,crust,inner core,outer core
D)crust,mantle,outer core,inner core
E)outer core,inner core,crust,mantle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The fact that Earth's interior is sorted into layers indicates that
A)the process of formation from a nebula (by the slamming together of material and planetesimals that stuck together on impact)produces nice,neat layers.
B)Earth was once in a molten state,during which materials became sorted based on density.
C)the rotation of the early Earth acted like a centrifuge which separated materials based on weight.
D)the planet was formed due to successive bombardments of cosmic debris.
E)nothing can be inferred about such a perplexing level of organization.
A)the process of formation from a nebula (by the slamming together of material and planetesimals that stuck together on impact)produces nice,neat layers.
B)Earth was once in a molten state,during which materials became sorted based on density.
C)the rotation of the early Earth acted like a centrifuge which separated materials based on weight.
D)the planet was formed due to successive bombardments of cosmic debris.
E)nothing can be inferred about such a perplexing level of organization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The is liquid and is responsible for producing Earth's magnetic field.
A)inner core
B)outer core
C)lower mantle
D)asthenosphere
E)Mohorovičić discontinuity
A)inner core
B)outer core
C)lower mantle
D)asthenosphere
E)Mohorovičić discontinuity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The heat from is the energy that drives plate tectonics.
A)tidal motion
B)incoming solar radiation
C)Earth's extremely hot interior
D)conducted surface thermal radiation
E)friction along plate boundaries
A)tidal motion
B)incoming solar radiation
C)Earth's extremely hot interior
D)conducted surface thermal radiation
E)friction along plate boundaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following statements about Earth's core is not correct?
A)It is composed primarily of iron.
B)The inner core is believed to be liquid and the outer core solid.
C)Scientists think the inner core formed before the outer core.
D)A third of the Earth's entire mass,but only a sixth of its volume lies in its core.
E)The inner core,despite being well above melting temperature,remains solid due to tremendous pressure of overlying materials.
A)It is composed primarily of iron.
B)The inner core is believed to be liquid and the outer core solid.
C)Scientists think the inner core formed before the outer core.
D)A third of the Earth's entire mass,but only a sixth of its volume lies in its core.
E)The inner core,despite being well above melting temperature,remains solid due to tremendous pressure of overlying materials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The transition zone from the upper mantle to the crust is known as the discontinuity.
A)Gutenberg
B)Mohorovičić
C)asthenosphere
D)lithosphere
E)crustal
A)Gutenberg
B)Mohorovičić
C)asthenosphere
D)lithosphere
E)crustal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The dominant element in oceanic crust are
A)silica and aluminum.
B)silica and magnesium.
C)magnesium and aluminum.
D)potassium and iron.
E)calcium and iron.
A)silica and aluminum.
B)silica and magnesium.
C)magnesium and aluminum.
D)potassium and iron.
E)calcium and iron.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Earth's interior is layered because
A)centrifugal force separated out the materials based on weight as the Earth solidified.
B)materials became sorted based on density as the Earth solidified.
C)materials became sorted based on electromagnetic fields as the Earth solidified.
D)the planet was formed due to successive bombardments of cosmic debris.
E)successive subduction events at convergent plate boundaries forcing earthen materials downward.
A)centrifugal force separated out the materials based on weight as the Earth solidified.
B)materials became sorted based on density as the Earth solidified.
C)materials became sorted based on electromagnetic fields as the Earth solidified.
D)the planet was formed due to successive bombardments of cosmic debris.
E)successive subduction events at convergent plate boundaries forcing earthen materials downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The percentage of oxygen in the Earth's crust is ,whereas that in the atmosphere is .
A)10%;72%
B)5%;50%
C)27%;27%
D)1.5%;86%
E)46%;21%
A)10%;72%
B)5%;50%
C)27%;27%
D)1.5%;86%
E)46%;21%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following is correct?
A)Continental crust is less dense than oceanic crust and dominated by silica and magnesium.
B)Continental crust is denser than oceanic crust and dominated by silica and aluminum.
C)Oceanic crust is less dense than continental crust and dominated by silica and aluminum.
D)Oceanic crust is denser than continental crust and dominated by silica and magnesium.
E)The density of continental and oceanic crust is roughly even,though the density varies in both time and space.
A)Continental crust is less dense than oceanic crust and dominated by silica and magnesium.
B)Continental crust is denser than oceanic crust and dominated by silica and aluminum.
C)Oceanic crust is less dense than continental crust and dominated by silica and aluminum.
D)Oceanic crust is denser than continental crust and dominated by silica and magnesium.
E)The density of continental and oceanic crust is roughly even,though the density varies in both time and space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Knowledge of Earth's interior is mostly derived from
A)direct sampling of the interior using deep-test wells.
B)work in Earth's deepest caverns and caves.
C)indirect evidence involving the analysis of seismic waves.
D)historic and prehistoric records.
E)analysis of exposed materials from geologic uplifting events and volcanic eruptions.
A)direct sampling of the interior using deep-test wells.
B)work in Earth's deepest caverns and caves.
C)indirect evidence involving the analysis of seismic waves.
D)historic and prehistoric records.
E)analysis of exposed materials from geologic uplifting events and volcanic eruptions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The uneven transition zone from the outer core to the mantle is known as the discontinuity.
A)Gutenberg
B)Mohorovičić
C)asthenosphere
D)lithosphere
E)crustal
A)Gutenberg
B)Mohorovičić
C)asthenosphere
D)lithosphere
E)crustal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following can occur when seismic waves encounter a layer in Earth's interior?
A)reflection and/or refraction,only
B)absorption,only
C)change in speed,only
D)reflection,refraction,absorption,and change in speed
E)seismic waves cannot penetrate below the crust of Earth
A)reflection and/or refraction,only
B)absorption,only
C)change in speed,only
D)reflection,refraction,absorption,and change in speed
E)seismic waves cannot penetrate below the crust of Earth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If one were to consider the average thickness of oceanic and continental crust under mountain,the thickness ranges from approximately
A)5 km to 70 km (3 mi.to 43 mi. ).
B)70 km to 250 km (43 mi.to 155 mi. ).
C)250 km to 1000 km (155 mi.to 621 mi. ).
D)1000 km to 2000 km (621 to 1243 mi. ).
E)2000 km to 2900 km (1243 mi to 1802 mi. ).
A)5 km to 70 km (3 mi.to 43 mi. ).
B)70 km to 250 km (43 mi.to 155 mi. ).
C)250 km to 1000 km (155 mi.to 621 mi. ).
D)1000 km to 2000 km (621 to 1243 mi. ).
E)2000 km to 2900 km (1243 mi to 1802 mi. ).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Together,the lower and upper mantles represent about of Earth's total volume.
A)10%
B)25%
C)43%
D)65%
E)80%
A)10%
B)25%
C)43%
D)65%
E)80%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The dominant elements in continental crust are
A)silica and aluminum.
B)silica and magnesium.
C)magnesium and aluminum.
D)potassium and iron.
E)calcium and iron
A)silica and aluminum.
B)silica and magnesium.
C)magnesium and aluminum.
D)potassium and iron.
E)calcium and iron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The three most abundant elements in Earth's crust are
A)potassium,sodium,and iron.
B)magnesium,potassium,and oxygen.
C)iron,aluminum,and calcium.
D)oxygen,silicon,and aluminum.
E)magnesium,iron,and calcium
A)potassium,sodium,and iron.
B)magnesium,potassium,and oxygen.
C)iron,aluminum,and calcium.
D)oxygen,silicon,and aluminum.
E)magnesium,iron,and calcium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The majority of the Earth's volume is within the
A)crust.
B)inner core.
C)mantle.
D)outer core.
E)Mohorovičić discontinuity.
A)crust.
B)inner core.
C)mantle.
D)outer core.
E)Mohorovičić discontinuity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The temperature of Earth's interior
A)increases with depth so the hottest temperatures are found within Earth's core.
B)decreases with depth so the hottest temperatures are found within Earth's crust.
C)decreases in the crust,increases in the mantle,decreases in the outer core,and increases in the inner core.
D)increases in the crust,decreases in the mantle,increases in the outer core,and decreases in the inner core.
E)is variable throughout and dependent on the location of and distance from hot spots.
A)increases with depth so the hottest temperatures are found within Earth's core.
B)decreases with depth so the hottest temperatures are found within Earth's crust.
C)decreases in the crust,increases in the mantle,decreases in the outer core,and increases in the inner core.
D)increases in the crust,decreases in the mantle,increases in the outer core,and decreases in the inner core.
E)is variable throughout and dependent on the location of and distance from hot spots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Of the elements in the Earth's crust,makes up the most of the Earth's crust by weight.
A)silicon (Si)
B)aluminum (Al)
C)oxygen (O)
D)iron (Fe)
E)calcium (Ca)
A)silicon (Si)
B)aluminum (Al)
C)oxygen (O)
D)iron (Fe)
E)calcium (Ca)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What type of rock forms from the solidification of molten material?
A)sedimentary
B)metamorphic
C)igneous
D)clastic
E)foliated
A)sedimentary
B)metamorphic
C)igneous
D)clastic
E)foliated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The major rocks of Earth's crust are classified into principal types based on
A)element composition.
B)mineral composition.
C)the manner in which they formed.
D)relative and absolute locations.
E)age and structure.
A)element composition.
B)mineral composition.
C)the manner in which they formed.
D)relative and absolute locations.
E)age and structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
At least 90% of Earth's magnetic field is generated by the
A)inner core.
B)outer core.
C)lower mantle.
D)asthenosphere.
E)Mohorovičić discontinuity.
A)inner core.
B)outer core.
C)lower mantle.
D)asthenosphere.
E)Mohorovičić discontinuity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which rock type makes up approximately 90% of the Earth's crust?
A)sedimentary
B)metamorphic
C)igneous
D)clastic
E)foliated
A)sedimentary
B)metamorphic
C)igneous
D)clastic
E)foliated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The rigid crust and uppermost mantle are known collectively as the
A)asthenosphere.
B)lithosphere.
C)Moho.
D)Gutenberg discontinuity.
E)rigid layer.
A)asthenosphere.
B)lithosphere.
C)Moho.
D)Gutenberg discontinuity.
E)rigid layer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Molten rock beneath the Earth's surface is known as ,whereas molten rock on the Earth's surface is called _ .
A)lava;magma
B)intrusive;extrusive
C)magma;lava
D)extrusive;intrusive
E)lava;extrusive
A)lava;magma
B)intrusive;extrusive
C)magma;lava
D)extrusive;intrusive
E)lava;extrusive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
During the past 4 million years,geomagnetic reversals have occurred.
A)9
B)25
C)50
D)100
E)1,000
A)9
B)25
C)50
D)100
E)1,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Obsidian is an igneous rock with a glassy appearance and minimal crystal growth.What accounts for this?
A)Obsidian is an intrusive igneous rock that cooled slowly beneath the Earth's surface,resulting in little crystal growth.
B)Obsidian is an extrusive igneous rock that cooled slowly on the Earth surface,resulting in little crystal growth.
C)Obsidian is an extrusive igneous rock that cooled very slowly on the Earth surface,resulting in little crystal growth.
D)Obsidian is an intrusive igneous rock that cooled rapidly beneath the Earth's surface,result in little crystal growth.
E)Obsidian has a chemical composition that lends itself to a glassy appearance and minimal crystal growth.
A)Obsidian is an intrusive igneous rock that cooled slowly beneath the Earth's surface,resulting in little crystal growth.
B)Obsidian is an extrusive igneous rock that cooled slowly on the Earth surface,resulting in little crystal growth.
C)Obsidian is an extrusive igneous rock that cooled very slowly on the Earth surface,resulting in little crystal growth.
D)Obsidian is an intrusive igneous rock that cooled rapidly beneath the Earth's surface,result in little crystal growth.
E)Obsidian has a chemical composition that lends itself to a glassy appearance and minimal crystal growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Approximately 95% of the Earth's crust is made up of
A)oxides.
B)phosphates.
C)silicates.
D)carbonates.
E)sulfates.
A)oxides.
B)phosphates.
C)silicates.
D)carbonates.
E)sulfates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The three basic rock types are
A)conglomerates,clastics,and evaporative.
B)intrusive,extrusive,and plutonic.
C)laterite,schist,and basalt.
D)sedimentary,metamorphic,and igneous.
E)felsic,mafic,and ultramafic.
A)conglomerates,clastics,and evaporative.
B)intrusive,extrusive,and plutonic.
C)laterite,schist,and basalt.
D)sedimentary,metamorphic,and igneous.
E)felsic,mafic,and ultramafic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Earth's magnetic poles
A)are fixed.
B)are migrating approximately 60 km (37 mi. )per year.
C)are perfectly aligned with Earth's axis.
D)are misaligned from Earth's axis by 23.5 degrees.
E)are no different than Earth's geographic poles.
A)are fixed.
B)are migrating approximately 60 km (37 mi. )per year.
C)are perfectly aligned with Earth's axis.
D)are misaligned from Earth's axis by 23.5 degrees.
E)are no different than Earth's geographic poles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The plastic layer in the mantle from about 70 to 250 km (43 to 155 mi. )in depth is known as the
A)asthenosphere.
B)lithosphere.
C)Moho.
D)Gutenberg discontinuity.
E)plastic layer.
A)asthenosphere.
B)lithosphere.
C)Moho.
D)Gutenberg discontinuity.
E)plastic layer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A(n)is an assemblage of minerals bound together,a mass composed of a single mineral,a mass of undifferentiated materials,or a mass of solid organic material.
A)compound
B)mineral
C)molecule
D)rock
E)element
A)compound
B)mineral
C)molecule
D)rock
E)element

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The continuous alteration of Earth materials from one rock type to another is known as the
A)geologic cycle.
B)rock cycle.
C)hydrologic cycle.
D)tectonic cycle.
E)biogeochemical cycle.
A)geologic cycle.
B)rock cycle.
C)hydrologic cycle.
D)tectonic cycle.
E)biogeochemical cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following is not a criterion to be classified as a mineral?
A)inorganic
B)anthropogenic
C)solid
D)definable chemical composition
E)crystalline structure
A)inorganic
B)anthropogenic
C)solid
D)definable chemical composition
E)crystalline structure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
An element or combination of elements that forms an inorganic,natural compound is called a
A)tectonic rock.
B)granite.
C)mineral.
D)molecule.
E)compound.
A)tectonic rock.
B)granite.
C)mineral.
D)molecule.
E)compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Coarser grained igneous rocks tend to be because .
A)intrusive;the faster cooling of magma allows more time for crystals to form
B)extrusive;the faster cooling of lava allows more time for crystals to form
C)extrusive;the slower cooling of lava allows more time for crystals to form
D)either intrusive or extrusive;the slower cooling of magma and lava allows more time for crystals to form
E)intrusive;slower cooling of magma allows more time for crystals to form
A)intrusive;the faster cooling of magma allows more time for crystals to form
B)extrusive;the faster cooling of lava allows more time for crystals to form
C)extrusive;the slower cooling of lava allows more time for crystals to form
D)either intrusive or extrusive;the slower cooling of magma and lava allows more time for crystals to form
E)intrusive;slower cooling of magma allows more time for crystals to form

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Geomagnetic reversals
A)are rapid events in which the magnetic field "blinks" off and on again.
B)cause in mass species extinctions due to increased cosmic radiation.
C)are predictable events,occurring at set intervals of 100,000 years.
D)are caused by rapid tectonic movement.
E)involve slow diminishments to low intensity and a rapid regaining of full strength.
A)are rapid events in which the magnetic field "blinks" off and on again.
B)cause in mass species extinctions due to increased cosmic radiation.
C)are predictable events,occurring at set intervals of 100,000 years.
D)are caused by rapid tectonic movement.
E)involve slow diminishments to low intensity and a rapid regaining of full strength.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Felsic igneous rocks,such as granite and rhyolite,
A)have dark coloration.
B)are high in magnesium and iron content.
C)have a high melting temperature.
D)are high in silicate minerals.
E)have a higher density than mafic igneous rocks.
A)have dark coloration.
B)are high in magnesium and iron content.
C)have a high melting temperature.
D)are high in silicate minerals.
E)have a higher density than mafic igneous rocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Finer grained igneous rocks tend to be because _ .
A)intrusive;the faster cooling of magma limits time for crystals to form
B)extrusive;the faster cooling of lava limits time for crystals to form
C)extrusive;the slower cooling of lava limits time for crystals to form
D)either intrusive or extrusive;the faster cooling of magma and lava limits time for crystals to form
E)intrusive;slower cooling of magma limits time for crystals to form
A)intrusive;the faster cooling of magma limits time for crystals to form
B)extrusive;the faster cooling of lava limits time for crystals to form
C)extrusive;the slower cooling of lava limits time for crystals to form
D)either intrusive or extrusive;the faster cooling of magma and lava limits time for crystals to form
E)intrusive;slower cooling of magma limits time for crystals to form

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The occurrence of contact metamorphism would be direct evidence for
A)cementation of sedimentary rock.
B)the local intrusion of magma.
C)regional plate collision.
D)lithification of clastics.
E)rapid cooling of lave above ground.
A)cementation of sedimentary rock.
B)the local intrusion of magma.
C)regional plate collision.
D)lithification of clastics.
E)rapid cooling of lave above ground.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Metamorphism that occurs over broad areas when the pressure and associated heat of overlaying rocks or other tectonic forces cause the rocks to undergo deformation is known as
A)contact metamorphism.
B)regional metamorphism.
C)intrusive metamorphism.
D)extrusive metamorphism.
E)clastic metamorphism.
A)contact metamorphism.
B)regional metamorphism.
C)intrusive metamorphism.
D)extrusive metamorphism.
E)clastic metamorphism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A rock transformed from any other rock through extreme heat and or pressure is referred to as
A)sedimentary.
B)metamorphic.
C)igneous.
D)ancient.
E)clastic.
A)sedimentary.
B)metamorphic.
C)igneous.
D)ancient.
E)clastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The continuous alteration of Earth materials from one rock type to another is known as the
A)geologic cycle.
B)rock cycle.
C)hydrologic cycle.
D)tectonic cycle.
E)biogeochemical cycle.
A)geologic cycle.
B)rock cycle.
C)hydrologic cycle.
D)tectonic cycle.
E)biogeochemical cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A batholith forms from
A)intrusive igneous rock.
B)extrusive igneous rock.
C)metamorphic rock.
D)sediment accumulation in a depression.
E)clastic sedimentation.
A)intrusive igneous rock.
B)extrusive igneous rock.
C)metamorphic rock.
D)sediment accumulation in a depression.
E)clastic sedimentation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Which of the following lists,in proper sequential order,the steps leading to the formation of clastic sedimentary rock?
A)erosion,transportation,deposition,lithification
B)erosion,deposition,transportation,lithification
C)erosion,transportation,deposition,metamorphism
D)precipitation,settling,compaction,lithification
E)sedimentation,precipitation,lithification,erosion
A)erosion,transportation,deposition,lithification
B)erosion,deposition,transportation,lithification
C)erosion,transportation,deposition,metamorphism
D)precipitation,settling,compaction,lithification
E)sedimentation,precipitation,lithification,erosion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Metamorphism that occurs when rocks are exposed to the pressure and extreme temperature associated with intruding magma is known as
A)contact metamorphism.
B)regional metamorphism.
C)intrusive metamorphism.
D)extrusive metamorphism.
E)clastic metamorphism.
A)contact metamorphism.
B)regional metamorphism.
C)intrusive metamorphism.
D)extrusive metamorphism.
E)clastic metamorphism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Lens-shaped bodies of igneous rock formed as magma intruded between rock layers and forced the overlying strata upward in the shape of a dome.These are known as
A)dikes.
B)laccoliths.
C)sills.
D)batholiths.
E)volcanic necks.
A)dikes.
B)laccoliths.
C)sills.
D)batholiths.
E)volcanic necks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following is an example of an intrusive,igneous rock formation?
A)volcano
B)pluton
C)dome
D)lava flow
E)sandstone
A)volcano
B)pluton
C)dome
D)lava flow
E)sandstone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What type of rock is derived from the bits and pieces of former rocks?
A)sedimentary
B)metamorphic
C)igneous
D)hydrothermal
E)mafic
A)sedimentary
B)metamorphic
C)igneous
D)hydrothermal
E)mafic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A is a solidified column of magma that formed in a volcanic vent.
A)dike
B)laccolith
C)sill
D)batholith
E)volcanic neck
A)dike
B)laccolith
C)sill
D)batholith
E)volcanic neck

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The drives the exogenic processes of the rock cycle.
A)atmospheric circulation
B)rock cycle
C)hydrologic cycle
D)tectonic cycle
E)biogeographical cycle
A)atmospheric circulation
B)rock cycle
C)hydrologic cycle
D)tectonic cycle
E)biogeographical cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Small plutons that form parallel to layers of rock that they intrude into are known as
A)dikes.
B)laccoliths.
C)sills.
D)batholiths.
E)volcanic necks
A)dikes.
B)laccoliths.
C)sills.
D)batholiths.
E)volcanic necks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which of the following is not a process that can cause metamorphism?
A)heating
B)solidification of magma
C)pressure
D)compression and shear
E)heating and pressure together
A)heating
B)solidification of magma
C)pressure
D)compression and shear
E)heating and pressure together

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Limestone formed from the shells of marine organisms is an example of sedimentary rock.
A)clastic
B)biochemical
C)extrusive
D)inorganic
E)contact
A)clastic
B)biochemical
C)extrusive
D)inorganic
E)contact

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Travertine,formed from the CaCO3 that has been precipitated from groundwater,is an example of sedimentary rock.
A)clastic
B)contact
C)organic
D)chemical
E)intrusive
A)clastic
B)contact
C)organic
D)chemical
E)intrusive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Mafic igneous rocks,such as gabbro and basalt,
A)are derived from magnesium and iron.
B)have light coloration.
C)are high in silicate minerals.
D)have a low melting temperature.
E)have a low density compared to felsic igneous rocks.
A)are derived from magnesium and iron.
B)have light coloration.
C)are high in silicate minerals.
D)have a low melting temperature.
E)have a low density compared to felsic igneous rocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If you were driving down the highway and saw mountains composed of layered strata,you could be confident that you were looking at
A)sedimentary rocks.
B)extrusive igneous rocks.
C)a shield volcano.
D)batholiths or laccoliths.
E)intrusive igneous rocks.
A)sedimentary rocks.
B)extrusive igneous rocks.
C)a shield volcano.
D)batholiths or laccoliths.
E)intrusive igneous rocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Sedimentary rock formed from the combined processes of weathering,erosion,transportation,deposition,lithification,and compaction of rock fragments of other rocks are
A)clastic.
B)biochemical.
C)organic.
D)chemical.
E)basaltic.
A)clastic.
B)biochemical.
C)organic.
D)chemical.
E)basaltic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Sedimentary rock formed from dissolved minerals that precipitate out of water solution and build up to form rock are
A)clastic.
B)inorganic.
C)organic.
D)chemical.
E)igneous.
A)clastic.
B)inorganic.
C)organic.
D)chemical.
E)igneous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 119 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



