Deck 2: Observing and Explaining the Economy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/108
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Observing and Explaining the Economy
1
Which of the following is not an economic issue?
A) Why is college tuition so high?
B) Why has health-care spending increased faster than the rest of the economy?
C) How can one earn $1 million without working at all?
D) How can one reduce the currently high levels of unemployment in Europe?
E) Why are there so many types of dog food?
A) Why is college tuition so high?
B) Why has health-care spending increased faster than the rest of the economy?
C) How can one earn $1 million without working at all?
D) How can one reduce the currently high levels of unemployment in Europe?
E) Why are there so many types of dog food?
How can one earn $1 million without working at all?
2
It has been documented that beer consumption rises when the unemployment rate rises. To conclude that this correlation means that increased unemployment causes increased beer consumption is to mistake correlation for causality.
True
3
The table shows the price of motor fuel (mainly gasoline) and the overall price level (the consumer price index) in five-year intervals over the period 1970 through 1990. 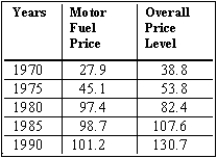

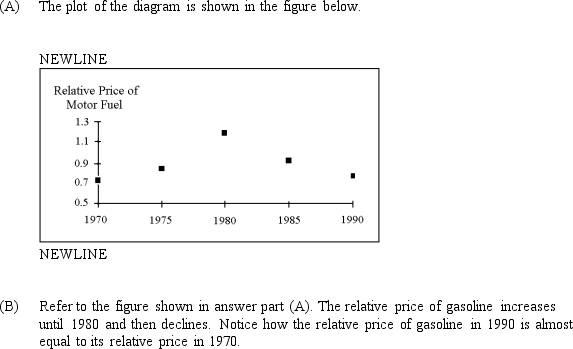
4
Explaining why the total amount of miles traveled in vehicles have risen in recent years is one example of what economists do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Two variables are correlated if
A) they both move up or down at about the same time.
B) an increase in one variable only causes another variable to increase.
C) a fall in one variable only causes another variable to fall.
D) changes in one have no effect on the other.
E) changes in one variable do not cause changes in the other.
A) they both move up or down at about the same time.
B) an increase in one variable only causes another variable to increase.
C) a fall in one variable only causes another variable to fall.
D) changes in one have no effect on the other.
E) changes in one variable do not cause changes in the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If the price of gasoline decreases but not as much as the decrease in the average price of other goods and services, then the relative price of gasoline
A) cannot be determined.
B) decreases.
C) remains the same.
D) increases.
E) increases or decreases, depending on the price of automobiles.
A) cannot be determined.
B) decreases.
C) remains the same.
D) increases.
E) increases or decreases, depending on the price of automobiles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
All of the following are examples of an economic variable except
A) the amount of income tax that a household has to pay.
B) a person's income.
C) the price of gasoline.
D) an integer 24.
E) the number of unemployed people.
A) the amount of income tax that a household has to pay.
B) a person's income.
C) the price of gasoline.
D) an integer 24.
E) the number of unemployed people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The relative price of an iPad is
A) the actual price that a consumer pays for the iPad.
B) the actual price that the seller received for the iPad.
C) the actual price of the iPad compared with its suggested retail price.
D) the price of the iPad compared with the average price of all goods and services.
E) zero if it is a used iPad.
A) the actual price that a consumer pays for the iPad.
B) the actual price that the seller received for the iPad.
C) the actual price of the iPad compared with its suggested retail price.
D) the price of the iPad compared with the average price of all goods and services.
E) zero if it is a used iPad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
All of the following are what economists commonly do except
A) describing economic events.
B) explaining why economic events occur.
C) making predictions for some economic events.
D) eliminating scarcity in resources.
E) making recommendations for economic policy.
A) describing economic events.
B) explaining why economic events occur.
C) making predictions for some economic events.
D) eliminating scarcity in resources.
E) making recommendations for economic policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Causation
A) occurs when there is no correlation.
B) occurs when two variables are correlated.
C) means one event brings about another event.
D) means one event is observed to occur along with another.
E) means one event occurs subsequently to another event.
A) occurs when there is no correlation.
B) occurs when two variables are correlated.
C) means one event brings about another event.
D) means one event is observed to occur along with another.
E) means one event occurs subsequently to another event.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If we observe that an increase in the amount of vehicle miles traveled rises after the price of gasoline rises, then we can conclude that
A) the amount of vehicle miles traveled and the price of gasoline are positively correlated.
B) the amount of vehicle miles traveled and the price of gasoline are negatively correlated.
C) the amount of vehicle miles traveled causes the price of gasoline to go up.
D) the price of gasoline causes the amount of vehicle miles traveled to go up.
E) a negative causation occurs between the amount of vehicle miles traveled and the price of gasoline
A) the amount of vehicle miles traveled and the price of gasoline are positively correlated.
B) the amount of vehicle miles traveled and the price of gasoline are negatively correlated.
C) the amount of vehicle miles traveled causes the price of gasoline to go up.
D) the price of gasoline causes the amount of vehicle miles traveled to go up.
E) a negative causation occurs between the amount of vehicle miles traveled and the price of gasoline

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If two variables are correlated, then it must be true that one of the variables causes the other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
To see whether the price of gasoline has risen compared to the prices of other goods and services, one would calculate
A) gasoline spending divided by spending on all other goods and services.
B) gasoline spending divided by total consumer spending.
C) the trend in the price of gasoline.
D) the price of gasoline divided by the overall price level.
E) the price of gasoline divided by the rate of inflation.
A) gasoline spending divided by spending on all other goods and services.
B) gasoline spending divided by total consumer spending.
C) the trend in the price of gasoline.
D) the price of gasoline divided by the overall price level.
E) the price of gasoline divided by the rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Controlled experiments are
A) seldom used in economics because economists do not like to repeat experiments.
B) often used because controlling other factors is relatively easy in economics.
C) not used as widely in economics as in other disciplines.
D) often used in economics.
E) performed by the government to collect economic data.
A) seldom used in economics because economists do not like to repeat experiments.
B) often used because controlling other factors is relatively easy in economics.
C) not used as widely in economics as in other disciplines.
D) often used in economics.
E) performed by the government to collect economic data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
In order to determine a causation between a change in the price of iPads and the amount of iPads purchased by customers, an economist must show that
A) there is no correlation between the price of iPads and the quantity of iPads purchased.
B) the change in the quantity of iPads purchased occurs after the change in the price of iPads.
C) the change in the price of iPads occurs along with the change in the quantity of iPads purchased.
D) the changes in the price and quantity of iPads purchased always move in the same direction.
E) the change in the price of iPads brings about the change in the quantity of iPads purchased.
A) there is no correlation between the price of iPads and the quantity of iPads purchased.
B) the change in the quantity of iPads purchased occurs after the change in the price of iPads.
C) the change in the price of iPads occurs along with the change in the quantity of iPads purchased.
D) the changes in the price and quantity of iPads purchased always move in the same direction.
E) the change in the price of iPads brings about the change in the quantity of iPads purchased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The relative price of gasoline has increased since 2000 because we have paid more dollars for each gallon of gasoline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Economic data always give an accurate picture of what affects consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An economic variable is any economic measure that
A) has different values because of researchers' different perspectives.
B) has no market value.
C) has a fixed value over time.
D) has no effect on the economy.
E) can vary over a range of values.
A) has different values because of researchers' different perspectives.
B) has no market value.
C) has a fixed value over time.
D) has no effect on the economy.
E) can vary over a range of values.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
To determine causality in many sciences, researchers
A) check for correlation.
B) use scatter diagrams.
C) perform controlled experiments.
D) plot the variables against time or location.
E) use only a small amount of data.
A) check for correlation.
B) use scatter diagrams.
C) perform controlled experiments.
D) plot the variables against time or location.
E) use only a small amount of data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Experimental economics
A) is the dominant method in economics.
B) does not exist.
C) uses laboratory experiments to analyze economic behavior.
D) is the method used when comparing the economic experience of other countries.
E) is the method used by the government to collect economic data.
A) is the dominant method in economics.
B) does not exist.
C) uses laboratory experiments to analyze economic behavior.
D) is the method used when comparing the economic experience of other countries.
E) is the method used by the government to collect economic data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A microeconomic model must be much smaller in size than a macroeconomic model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Explain why it is more difficult to determine causality in economics than in other sciences such as physics, chemistry, and biology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is considered a macroeconomic question?
A) How can one particular firm maximize profits?
B) What is the impact of competition on the profits of a business?
C) How can economic policy fight inflation?
D) How does a family allocate income among various available goods and services?
E) What factors determine the wage rate in a certain industry?
A) How can one particular firm maximize profits?
B) What is the impact of competition on the profits of a business?
C) How can economic policy fight inflation?
D) How does a family allocate income among various available goods and services?
E) What factors determine the wage rate in a certain industry?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Economic models
A) are different from the phenomena they attempt to explain.
B) are new phenomena because they are by-products of experimental economics.
C) are not complicated because the behavior they describe is not complicated.
D) are complicated because human behavior is complicated.
E) would not be needed if controlled experiments were used more often.
A) are different from the phenomena they attempt to explain.
B) are new phenomena because they are by-products of experimental economics.
C) are not complicated because the behavior they describe is not complicated.
D) are complicated because human behavior is complicated.
E) would not be needed if controlled experiments were used more often.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Two variables are negatively correlated if
A) the value of one variable decreases as the value of the other variable decreases.
B) the value of one variable increases as the value of the other variable decreases.
C) a fall in one variable only causes another variable to fall.
D) changes in one have no effect on the other.
E) the value of one variable remains constant as the value of another variable changes.
A) the value of one variable decreases as the value of the other variable decreases.
B) the value of one variable increases as the value of the other variable decreases.
C) a fall in one variable only causes another variable to fall.
D) changes in one have no effect on the other.
E) the value of one variable remains constant as the value of another variable changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A model gives the most realistic description of the real world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Economic models differ from those in the physical sciences because
A) they are usually more difficult than models in the physical sciences.
B) economics has nothing to do with anything physical.
C) they are less difficult than those in the physical sciences.
D) they attempt to explain human behavior.
E) economics relies on controlled experiments.
A) they are usually more difficult than models in the physical sciences.
B) economics has nothing to do with anything physical.
C) they are less difficult than those in the physical sciences.
D) they attempt to explain human behavior.
E) economics relies on controlled experiments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Exhibit 2-2 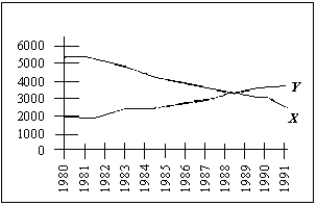
If the quantity demanded of coffee increases when the price of coffee declines, then these two ____ are ____.
A) variables; negatively related
B) constants; positively related
C) variables; positively related
D) constants; negatively related
E) variables; not related

If the quantity demanded of coffee increases when the price of coffee declines, then these two ____ are ____.
A) variables; negatively related
B) constants; positively related
C) variables; positively related
D) constants; negatively related
E) variables; not related

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Macroeconomics is concerned primarily with
A) the economy as a whole.
B) the operation of a particular firm.
C) individual consumer behavior.
D) the labor market.
E) a detailed examination of how price and output decisions are made in specific markets.
A) the economy as a whole.
B) the operation of a particular firm.
C) individual consumer behavior.
D) the labor market.
E) a detailed examination of how price and output decisions are made in specific markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Macroeconomics deals with large industries such as the health-care industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Exhibit 2-2 
Exhibit 2-2 shows the relationship between X and Y between 1980 and 1991. Suppose this correlation between X and Y continues to hold for the next 10 years. If Y declines over the period 1993 through 1998, we would expect
A) X to fall over the same period because X and Y are negatively correlated.
B) X to increase over the same period because X and Y are positively correlated.
C) X to increase over the same period because X and Y are negatively correlated.
D) the correlation to be unknown because we do not know the units of measurement for X and Y and thus cannot say anything about how X and Y are related.
E) X to fall over the same period because X and Y are positively correlated.

Exhibit 2-2 shows the relationship between X and Y between 1980 and 1991. Suppose this correlation between X and Y continues to hold for the next 10 years. If Y declines over the period 1993 through 1998, we would expect
A) X to fall over the same period because X and Y are negatively correlated.
B) X to increase over the same period because X and Y are positively correlated.
C) X to increase over the same period because X and Y are negatively correlated.
D) the correlation to be unknown because we do not know the units of measurement for X and Y and thus cannot say anything about how X and Y are related.
E) X to fall over the same period because X and Y are positively correlated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An economic model is a tool used to help us understand the real world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Economics has always been a good example of an experimental science.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Exhibit 2-1 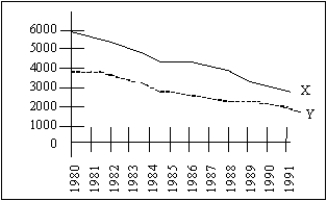
Exhibit 2-1 shows movements of two variables, X and Y, from 1980 through 1991. From this diagram the most one can conclude is that
A) X and Y are positively correlated with each other.
B) X and Y are negatively correlated with each other.
C) X and Y are positively correlated with each other and either X causes Y or Y causes X.
D) we cannot say anything about how X and Y are related because we do not know the units of measurement for X and Y.
E) X and Y are not correlated with each other.

Exhibit 2-1 shows movements of two variables, X and Y, from 1980 through 1991. From this diagram the most one can conclude is that
A) X and Y are positively correlated with each other.
B) X and Y are negatively correlated with each other.
C) X and Y are positively correlated with each other and either X causes Y or Y causes X.
D) we cannot say anything about how X and Y are related because we do not know the units of measurement for X and Y.
E) X and Y are not correlated with each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
When economists explain the relationship between the price of hotdogs and the number that consumers will buy, the ceteris paribus assumption implies that
A) the price of hotdogs is constant.
B) the quantity of hotdogs purchased is constant.
C) both the price and quantity of hotdogs purchased are constant.
D) factors other than the price and quantity of hotdogs purchased are constant.
E) everything in the world does not change.
A) the price of hotdogs is constant.
B) the quantity of hotdogs purchased is constant.
C) both the price and quantity of hotdogs purchased are constant.
D) factors other than the price and quantity of hotdogs purchased are constant.
E) everything in the world does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following is more of a microeconomic concept than a macroeconomic concept?
A) Concern over simultaneous high rates of inflation and unemployment
B) Price determination in the resource market
C) The rate of economic growth
D) Concern over an entire economy's balance of payments
E) How the composition of output is determined in an economy
A) Concern over simultaneous high rates of inflation and unemployment
B) Price determination in the resource market
C) The rate of economic growth
D) Concern over an entire economy's balance of payments
E) How the composition of output is determined in an economy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Economic models
A) are not complicated because the behavior they describe is not complicated.
B) require either algebra or graphs.
C) are complicated because human behavior is complicated.
D) are simplifications of the phenomena they attempt to explain.
E) need to be the same as the phenomena they describe.
A) are not complicated because the behavior they describe is not complicated.
B) require either algebra or graphs.
C) are complicated because human behavior is complicated.
D) are simplifications of the phenomena they attempt to explain.
E) need to be the same as the phenomena they describe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An economic model is the same as a theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Economic models need to resemble, as much as possible, the phenomena being explained.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What is the difference between correlation and causality?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Explain how economic models are similar to and different from models used in other sciences. What are the consequences of these differences?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A model is valid if
A) it is based on human behavior.
B) it is new.
C) it has been around for many years.
D) observations can be explained by it.
E) it incorporates asymmetric information.
A) it is based on human behavior.
B) it is new.
C) it has been around for many years.
D) observations can be explained by it.
E) it incorporates asymmetric information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The ceteris paribus assumption is always used whenever an economist analyzes the relationship of two variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A market economy in which the government plays some role is called
A) capitalism.
B) socialism.
C) communism.
D) a laissez faire system.
E) a mixed economy.
A) capitalism.
B) socialism.
C) communism.
D) a laissez faire system.
E) a mixed economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Economics was originally called
A) political engineering.
B) political economy.
C) economic physics.
D) social engineering.
E) social physics.
A) political engineering.
B) political economy.
C) economic physics.
D) social engineering.
E) social physics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the difference between microeconomics and macroeconomics?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The ceteris paribus assumption is used in economics
A) because economic theory is an accurate reflection of the real world.
B) to isolate the important variables when formulating a theory.
C) primarily to identify unstable equilibrium situations.
D) to make the theory more complicated
E) to distinguish economics from other disciplines.
A) because economic theory is an accurate reflection of the real world.
B) to isolate the important variables when formulating a theory.
C) primarily to identify unstable equilibrium situations.
D) to make the theory more complicated
E) to distinguish economics from other disciplines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Economists develop new models only when new economic data become available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Economists are likely to evaluate the impacts of rising gasoline prices through the use of
A) outdated models with new applications.
B) models that are not relevant to the health-care industry.
C) existing models that are useful for explaining observations.
D) models that are useful only for exposition in economics textbooks.
E) new models with old data.
A) outdated models with new applications.
B) models that are not relevant to the health-care industry.
C) existing models that are useful for explaining observations.
D) models that are useful only for exposition in economics textbooks.
E) new models with old data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Exhibit 2-3 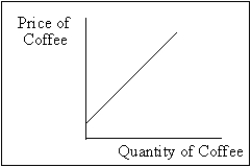
In Exhibit 2-3, an example of a constant would be
A) the quantity of coffee supplied.
B) the price that corresponds to any quantity of coffee supplied.
C) the price of coffee.
D) the slope of the line.
E) both the price and quantity of coffee.

In Exhibit 2-3, an example of a constant would be
A) the quantity of coffee supplied.
B) the price that corresponds to any quantity of coffee supplied.
C) the price of coffee.
D) the slope of the line.
E) both the price and quantity of coffee.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The ceteris paribus, or everything else held constant, assumption is used in economics primarily to identify unstable equilibrium situations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A major reason for the development of new models is
A) because of asymmetric information.
B) that new observations cannot be explained by existing models.
C) that old economic laws are often repealed.
D) that human behavior is no longer important.
E) that new models are always easier to understand.
A) because of asymmetric information.
B) that new observations cannot be explained by existing models.
C) that old economic laws are often repealed.
D) that human behavior is no longer important.
E) that new models are always easier to understand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Exhibit 2-3 
In Exhibit 2-3, an example of a variable would be the
A) price of coffee.
B) intercept.
C) relationship that shows by how many units the supply of coffee will change for any unit change in the price of coffee.
D) slope of the line.
E) price at which the supply of coffee is zero.

In Exhibit 2-3, an example of a variable would be the
A) price of coffee.
B) intercept.
C) relationship that shows by how many units the supply of coffee will change for any unit change in the price of coffee.
D) slope of the line.
E) price at which the supply of coffee is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Explain how new models or theories are developed in economics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Exhibit 2-3 
Exhibit 2-3 shows two variables that are
A) constant.
B) positively related.
C) negatively related.
D) not related.
E) both positively and negatively related.

Exhibit 2-3 shows two variables that are
A) constant.
B) positively related.
C) negatively related.
D) not related.
E) both positively and negatively related.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A hypothesis is
A) an alternative to using models.
B) a testable statement used to explain observations.
C) an untestable explanation used to explain observations.
D) a fact.
E) the same as a theory.
A) an alternative to using models.
B) a testable statement used to explain observations.
C) an untestable explanation used to explain observations.
D) a fact.
E) the same as a theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The figure below shows the relationship of the quantity demanded for coffee beans to the price of coffee beans at a local coffee shop. 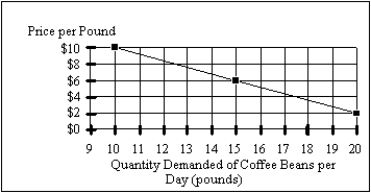


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Ceteris paribus means
A) that rational self-interest is being assumed.
B) "all variables are independent."
C) that no other assumptions are being made.
D) "other things being equal."
E) "all relationships are inverse."
A) that rational self-interest is being assumed.
B) "all variables are independent."
C) that no other assumptions are being made.
D) "other things being equal."
E) "all relationships are inverse."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In describing the relationship between X and Y, the ceteris paribus assumption implies that
A) the value of X does not change.
B) the value of Y does not change.
C) the values of both X and Y do not change.
D) all other factors that may affect X and Y are constant.
E) nothing in the world can change.
A) the value of X does not change.
B) the value of Y does not change.
C) the values of both X and Y do not change.
D) all other factors that may affect X and Y are constant.
E) nothing in the world can change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Those who support a laissez faire system
A) argue for a French-style economy.
B) argue for a market economy.
C) support government intervention.
D) argue for a command economy.
E) argue for a mixed economy.
A) argue for a French-style economy.
B) argue for a market economy.
C) support government intervention.
D) argue for a command economy.
E) argue for a mixed economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Positive economics
A) will usually indicate which economic policy is best.
B) is concerned with what ought to be.
C) is the same as normative economics.
D) is strictly quantitative and so has little to say to those with philosophical goals to achieve in policymaking.
E) produces verifiable statements.
A) will usually indicate which economic policy is best.
B) is concerned with what ought to be.
C) is the same as normative economics.
D) is strictly quantitative and so has little to say to those with philosophical goals to achieve in policymaking.
E) produces verifiable statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Whether to have more or less government involvement in the overall economy is essentially a
A) normative issue.
B) positive issue.
C) political issue, and therefore the techniques of economic analysis are not applicable.
D) positive or normative issue; it could be either.
E) both normative and positive issues.
A) normative issue.
B) positive issue.
C) political issue, and therefore the techniques of economic analysis are not applicable.
D) positive or normative issue; it could be either.
E) both normative and positive issues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Economics is the only science concerned with politically controversial subjects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
All microeconomic issues are normative in nature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Karl Marx argued that capitalism would eventually collapse and give rise to a new economic system, which is called
A) a political system.
B) socialism.
C) a market system.
D) a laissez faire system.
E) a mixed economy.
A) a political system.
B) socialism.
C) a market system.
D) a laissez faire system.
E) a mixed economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The category of economics that contains statements about what ought to be is known as
A) objective economics.
B) positive economics.
C) normative economics.
D) microeconomics.
E) macroeconomics.
A) objective economics.
B) positive economics.
C) normative economics.
D) microeconomics.
E) macroeconomics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Positive economics is the
A) study of the desirable attributes of economic relationships.
B) scientific study of "what is" among economic relationships.
C) scientific study of how people behave positively.
D) study of how economic policy should improve the welfare of individuals.
E) study of how people and institutions should behave.
A) study of the desirable attributes of economic relationships.
B) scientific study of "what is" among economic relationships.
C) scientific study of how people behave positively.
D) study of how economic policy should improve the welfare of individuals.
E) study of how people and institutions should behave.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A newspaper editorial explaining what should be done to reduce the budget deficit is an example of
A) everything else held constant.
B) microeconomics.
C) functional economics.
D) positive economics.
E) normative economics.
A) everything else held constant.
B) microeconomics.
C) functional economics.
D) positive economics.
E) normative economics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A system in which the government essentially owns and controls all production is called
A) capitalism.
B) socialism.
C) a market system.
D) a laissez faire system.
E) a mixed economy.
A) capitalism.
B) socialism.
C) a market system.
D) a laissez faire system.
E) a mixed economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
"Inflation is a more serious problem than unemployment." This statement is an example of
A) a normative statement.
B) the fallacy of composition.
C) a positive statement.
D) microeconomics.
E) macroeconomics.
A) a normative statement.
B) the fallacy of composition.
C) a positive statement.
D) microeconomics.
E) macroeconomics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A mixed system is an economy with only private industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
"Inflation is currently 4 percent in the United States." This statement is an example of
A) a positive statement.
B) a normative statement.
C) the fallacy of composition.
D) macroeconomics.
E) microeconomics.
A) a positive statement.
B) a normative statement.
C) the fallacy of composition.
D) macroeconomics.
E) microeconomics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In modern market economies, the role of government is small.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A positive statement is necessarily a subjective statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A laissez faire system is an economy with many government regulations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following statements is true?
A) Normative economics deals with what is.
B) Normative economics expresses someone's opinion.
C) Positive economics is subjective.
D) Positive economics deals with what ought to be.
E) Normative economics tries to refrain from opinions.
A) Normative economics deals with what is.
B) Normative economics expresses someone's opinion.
C) Positive economics is subjective.
D) Positive economics deals with what ought to be.
E) Normative economics tries to refrain from opinions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
To argue that economics is the only science not used objectively is
A) true because only economics engages in politically controversial issues.
B) false because other sciences besides economics engage in politically controversial issues.
C) true because all other sciences use controlled experiments.
D) false because one's reasoning is either correct or incorrect.
E) false because none of the other sciences use controlled experiments.
A) true because only economics engages in politically controversial issues.
B) false because other sciences besides economics engage in politically controversial issues.
C) true because all other sciences use controlled experiments.
D) false because one's reasoning is either correct or incorrect.
E) false because none of the other sciences use controlled experiments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following is a normative statement?
A) "Income inequality in the United States has increased."
B) "The Federal Reserve has observed that the rate of inflation has been increasing."
C) "The government should increase the minimum wage to help low-income groups."
D) "Real wages in many cities have decreased over time."
E) "The relative price of gasoline has remained low in the past 30 years."
A) "Income inequality in the United States has increased."
B) "The Federal Reserve has observed that the rate of inflation has been increasing."
C) "The government should increase the minimum wage to help low-income groups."
D) "Real wages in many cities have decreased over time."
E) "The relative price of gasoline has remained low in the past 30 years."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
To argue that economics is a partisan policy tool means that
A) economics is being used without political considerations.
B) part of the policy is based on economic analysis.
C) economics is not always used objectively.
D) economics is used objectively.
E) economic analysis is always misleading.
A) economics is being used without political considerations.
B) part of the policy is based on economic analysis.
C) economics is not always used objectively.
D) economics is used objectively.
E) economic analysis is always misleading.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Economics
A) can only be used objectively.
B) cannot be practiced as a science unless it uses controlled experiments.
C) is always practiced as a science.
D) is not always used objectively.
E) can never be used objectively.
A) can only be used objectively.
B) cannot be practiced as a science unless it uses controlled experiments.
C) is always practiced as a science.
D) is not always used objectively.
E) can never be used objectively.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 108 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



