Deck 29: The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/48
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 29: The Organic Chemistry of Metabolic Pathways
1
Exhibit 29-1
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Coenzyme NAD+ required in the β-oxidation of fatty acids,glycolysis,and the citric acid cycle.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)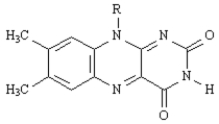
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)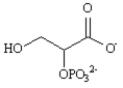
O)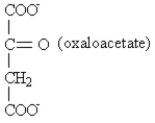
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Coenzyme NAD+ required in the β-oxidation of fatty acids,glycolysis,and the citric acid cycle.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
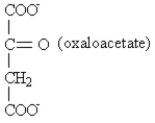
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

2
Exhibit 29-1
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Pyridoxal phosphate,the cofactor in transaminations.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)
O)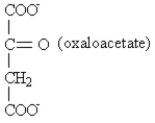
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Pyridoxal phosphate,the cofactor in transaminations.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
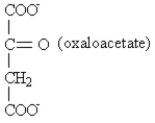
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

3
Exhibit 29-1
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ The pathway by which organisms make glucose from simple precursors.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)
O)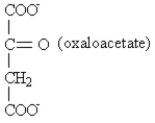
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ The pathway by which organisms make glucose from simple precursors.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
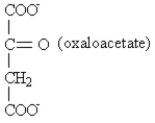
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
gluconeogenesis
4
Exhibit 29-1
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Discoverers of the glycolysis pathway.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)
O)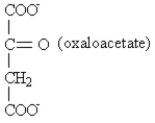
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Discoverers of the glycolysis pathway.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
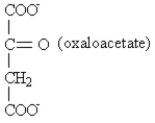
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Exhibit 29-1
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Common fatty acids have an even number of carbons because they are biosynthesized from _____.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)
O)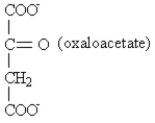
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Common fatty acids have an even number of carbons because they are biosynthesized from _____.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
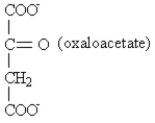
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Exhibit 29-3
Use the data below to answer the following question(s).
Mevalonate is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.This six-carbon compound can be formed from acetyl CoA utilizing two separate pathways.The most significant one involves the intermediate β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA.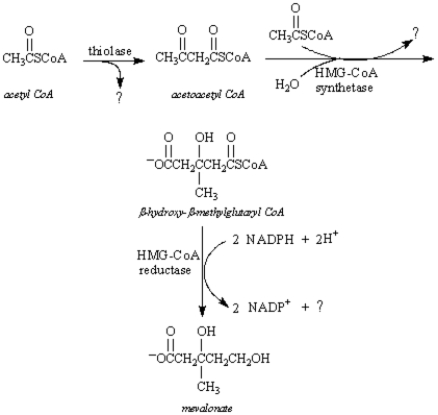
Refer to Exhibit 29-3.In step 2 of the mevalonate biosynthesis,acetoacetyl CoA is converted into β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA.This reaction is analogous to:
A)a Claisen condensation
B)an aldol reaction
C)the malonic ester synthesis
D)a carbonyl reduction reaction
Use the data below to answer the following question(s).
Mevalonate is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.This six-carbon compound can be formed from acetyl CoA utilizing two separate pathways.The most significant one involves the intermediate β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA.

Refer to Exhibit 29-3.In step 2 of the mevalonate biosynthesis,acetoacetyl CoA is converted into β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA.This reaction is analogous to:
A)a Claisen condensation
B)an aldol reaction
C)the malonic ester synthesis
D)a carbonyl reduction reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Exhibit 29-1
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ The product of the citric acid cycle,which is a reactant in the first step.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)
O)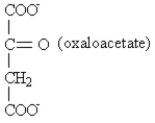
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ The product of the citric acid cycle,which is a reactant in the first step.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
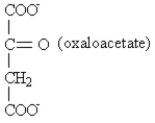
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Exhibit 29-3
Use the data below to answer the following question(s).
Mevalonate is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.This six-carbon compound can be formed from acetyl CoA utilizing two separate pathways.The most significant one involves the intermediate β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA.
Refer to Exhibit 29-3.Propose a mechanism for step 2 of the mevalonate biosynthesis.
Use the data below to answer the following question(s).
Mevalonate is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.This six-carbon compound can be formed from acetyl CoA utilizing two separate pathways.The most significant one involves the intermediate β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA.

Refer to Exhibit 29-3.Propose a mechanism for step 2 of the mevalonate biosynthesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Exhibit 29-2
Use the data below to answer the following question(s):
Under certain metabolic conditions associated with a high rate of fatty acid oxidation,the liver produces considerable quantities of acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate.Acetoacetate continually undergoes spontaneous decarboxylation to yield acetone.The interrelationship of these compounds is shown below.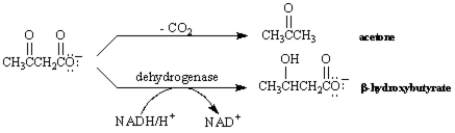
Refer to Exhibit 29-2.The reduction of acetoacetate to β-hydroxybutyrate is analogous to the hydride reductions of ketones studied in Chapter 9.Write the mechanism of this reduction.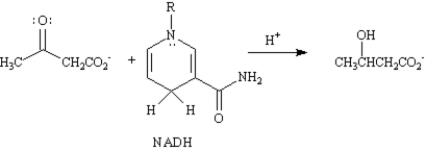
Use the data below to answer the following question(s):
Under certain metabolic conditions associated with a high rate of fatty acid oxidation,the liver produces considerable quantities of acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate.Acetoacetate continually undergoes spontaneous decarboxylation to yield acetone.The interrelationship of these compounds is shown below.

Refer to Exhibit 29-2.The reduction of acetoacetate to β-hydroxybutyrate is analogous to the hydride reductions of ketones studied in Chapter 9.Write the mechanism of this reduction.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Olive oil is comprised of 80% oleic acid,CH3(CH2)7CH=CH(CH2)7COOH.How many molecules of acetyl CoA are produced by catabolism of one molecule of oleic acid and how many passages of the β-oxidation pathway are needed for its complete catabolism?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following statements about catabolism is false?
A)The ultimate products of food catabolism are CO2,H2O,and ATP.
B)The citric acid cycle is a stage of catabolism.
C)Gluconeogenesis is the catabolism of glucose.
D)Transamination is the catabolism of proteins.
A)The ultimate products of food catabolism are CO2,H2O,and ATP.
B)The citric acid cycle is a stage of catabolism.
C)Gluconeogenesis is the catabolism of glucose.
D)Transamination is the catabolism of proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Exhibit 29-1
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ The "energy currency" of the cell.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)
O)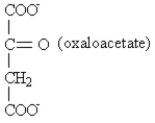
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ The "energy currency" of the cell.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
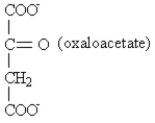
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Exhibit 29-2
Use the data below to answer the following question(s):
Under certain metabolic conditions associated with a high rate of fatty acid oxidation,the liver produces considerable quantities of acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate.Acetoacetate continually undergoes spontaneous decarboxylation to yield acetone.The interrelationship of these compounds is shown below.
Refer to Exhibit 29-2.Write a mechanism for the decarboxylation of acetoacetate to yield acetone.
Use the data below to answer the following question(s):
Under certain metabolic conditions associated with a high rate of fatty acid oxidation,the liver produces considerable quantities of acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate.Acetoacetate continually undergoes spontaneous decarboxylation to yield acetone.The interrelationship of these compounds is shown below.

Refer to Exhibit 29-2.Write a mechanism for the decarboxylation of acetoacetate to yield acetone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is the structure of the α-keto acid formed by transamination of the amino acid isoleucine? 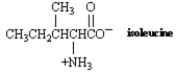


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Exhibit 29-2
Use the data below to answer the following question(s):
Under certain metabolic conditions associated with a high rate of fatty acid oxidation,the liver produces considerable quantities of acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate.Acetoacetate continually undergoes spontaneous decarboxylation to yield acetone.The interrelationship of these compounds is shown below.
Refer to Exhibit 29-2.The reduction of acetoacetate to β-hydroxybutyrate is an example of a:
A)nucleophilic substitution reaction.
B)nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction.
C)nucleophilic addition reaction.
D)nucleophilic exchange reaction.
Use the data below to answer the following question(s):
Under certain metabolic conditions associated with a high rate of fatty acid oxidation,the liver produces considerable quantities of acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate.Acetoacetate continually undergoes spontaneous decarboxylation to yield acetone.The interrelationship of these compounds is shown below.

Refer to Exhibit 29-2.The reduction of acetoacetate to β-hydroxybutyrate is an example of a:
A)nucleophilic substitution reaction.
B)nucleophilic acyl substitution reaction.
C)nucleophilic addition reaction.
D)nucleophilic exchange reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Exhibit 29-1
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Acetyl groups are oxidized to yield carbon dioxide and water.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)
O)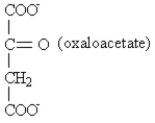
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Acetyl groups are oxidized to yield carbon dioxide and water.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
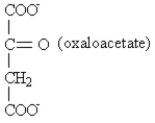
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Exhibit 29-1
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Pathways that synthesize larger biomolecules from smaller ones.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)
O)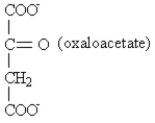
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Pathways that synthesize larger biomolecules from smaller ones.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
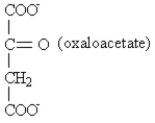
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Exhibit 29-3
Use the data below to answer the following question(s).
Mevalonate is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.This six-carbon compound can be formed from acetyl CoA utilizing two separate pathways.The most significant one involves the intermediate β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA.
Refer to Exhibit 29-3.What is the by-product represented as a question mark (?) in each step of this reaction sequence?
Use the data below to answer the following question(s).
Mevalonate is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.This six-carbon compound can be formed from acetyl CoA utilizing two separate pathways.The most significant one involves the intermediate β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA.

Refer to Exhibit 29-3.What is the by-product represented as a question mark (?) in each step of this reaction sequence?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Exhibit 29-3
Use the data below to answer the following question(s).
Mevalonate is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.This six-carbon compound can be formed from acetyl CoA utilizing two separate pathways.The most significant one involves the intermediate β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA.
Refer to Exhibit 29-3.In step 1 of the mevalonate biosynthesis,acetyl CoA is converted into acetoacetyl CoA.This reaction is analogous to:
A)a Claisen condensation
B)an aldol reaction
C)the malonic ester synthesis
D)a carbonyl reduction reaction
Use the data below to answer the following question(s).
Mevalonate is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.This six-carbon compound can be formed from acetyl CoA utilizing two separate pathways.The most significant one involves the intermediate β-hydroxy-β-methylglutaryl-CoA.

Refer to Exhibit 29-3.In step 1 of the mevalonate biosynthesis,acetyl CoA is converted into acetoacetyl CoA.This reaction is analogous to:
A)a Claisen condensation
B)an aldol reaction
C)the malonic ester synthesis
D)a carbonyl reduction reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Exhibit 29-1
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Uses the energy produced in the citric acid cycle to make ATP.
A)electron-transport chain
B)
C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)
G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)
K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)
O)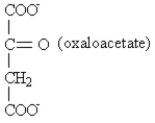
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism
MATCH a term or structure from the list below to each of the following definitions or names.Place the letter of the term or structure in the blank to the left of the definition or name which it describes.
_____ Uses the energy produced in the citric acid cycle to make ATP.
A)electron-transport chain
B)

C)citric acid cycle
D)Embden-Meyerhoff
E)glycolysis
F)

G)Hans Krebs
H)catabolism
I)ATP
J)

K)fatty acid spiral
L)anabolism
M)acetyl CoA
N)

O)
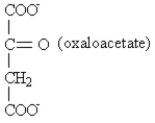
P)gluconeogenesis
Q)metabolism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Phosphoenolpyruvate could undergo hydrolysis to form pyruvate and hydrogen phosphate.This reaction could be represented as shown below.(ΔG°' = -61.9 kJ/mol) 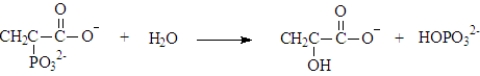 This reaction can be used to phosphorylate ADP.Write the net reaction when this reaction is coupled with ADP phosphorylation and calculate ΔG°' for the reaction.
This reaction can be used to phosphorylate ADP.Write the net reaction when this reaction is coupled with ADP phosphorylation and calculate ΔG°' for the reaction.
 This reaction can be used to phosphorylate ADP.Write the net reaction when this reaction is coupled with ADP phosphorylation and calculate ΔG°' for the reaction.
This reaction can be used to phosphorylate ADP.Write the net reaction when this reaction is coupled with ADP phosphorylation and calculate ΔG°' for the reaction.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Draw the structure of the product formed on the transamination of the following substance.Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 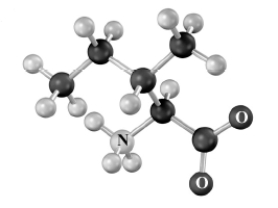


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following does not correctly describe a stage of metabolism in humans?
A)first stage: ester and peptide bond broken
B)first stage: fatty acids and simple sugars degraded in cytoplasm
C)second stage: produces acetyl groups
D)third stage: involves the citric acid cycle
A)first stage: ester and peptide bond broken
B)first stage: fatty acids and simple sugars degraded in cytoplasm
C)second stage: produces acetyl groups
D)third stage: involves the citric acid cycle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In coupled reactions,the net reaction has:
A)ΔG = 0
B)ΔG > 0
C)ΔG < 0
A)ΔG = 0
B)ΔG > 0
C)ΔG < 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What type of high energy bonds are found in ATP and ADP?
A)carboxylic anhydride
B)phosphodiester
C)thioester
D)phosphoanhydride
A)carboxylic anhydride
B)phosphodiester
C)thioester
D)phosphoanhydride

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
During the synthesis of fatty acids,the following substance is formed by two pathways. 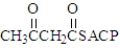 Draw the structure(s) of the starting material(s) for each path?
Draw the structure(s) of the starting material(s) for each path?
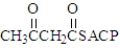 Draw the structure(s) of the starting material(s) for each path?
Draw the structure(s) of the starting material(s) for each path?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Exhibit 29-4
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):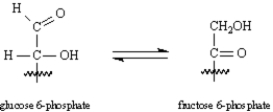
Refer to Exhibit 29-4.Write the mechanism for this isomerization.
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 29-4.Write the mechanism for this isomerization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Phosphoenolpyruvate could undergo hydrolysis to form pyruvate and hydrogen phosphate.This reaction could be represented as shown below.This reaction can be coupled to the phosphorylation of ADP. 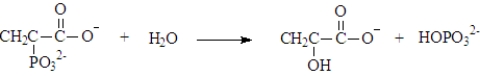 The product exists as tautomers.Draw their structures.
The product exists as tautomers.Draw their structures.
 The product exists as tautomers.Draw their structures.
The product exists as tautomers.Draw their structures.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Exhibit 29-5
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):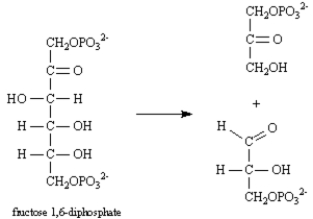
Refer to Exhibit 29-5.This reaction is an example of:
A)an aldol reaction.
B)a Claisen reaction.
C)a reverse Claisen reaction.
D)a retro aldol reaction.
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 29-5.This reaction is an example of:
A)an aldol reaction.
B)a Claisen reaction.
C)a reverse Claisen reaction.
D)a retro aldol reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following does not represent a correct relationship in catabolism?
A)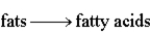
B)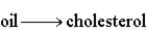
C)
D)
A)
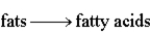
B)
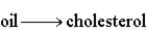
C)

D)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements about anabolism is false?
A)Anabolic reactions "spend" ATP by transferring a phosphate group to another molecule.
B)As a rule,the anabolic pathway by which an organism makes a substance is the exact reverse of the catabolic pathway.
C)Pathways that synthesize larger biomolecules from smaller ones are known as anabolism.
D)Gluconeogenesis is the anabolic pathway by which organisms make glucose from pyruvate.
A)Anabolic reactions "spend" ATP by transferring a phosphate group to another molecule.
B)As a rule,the anabolic pathway by which an organism makes a substance is the exact reverse of the catabolic pathway.
C)Pathways that synthesize larger biomolecules from smaller ones are known as anabolism.
D)Gluconeogenesis is the anabolic pathway by which organisms make glucose from pyruvate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Fatty acids always have an even number of carbon atoms.Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Exhibit 29-5
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):
Refer to Exhibit 29-5.Draw arrows on the structure below showing electron flow in this reaction.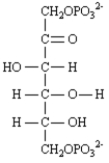
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 29-5.Draw arrows on the structure below showing electron flow in this reaction.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following statements about ATP is false?
A)ADP is synthesized from ATP.
B)ATP is produced in the fourth stage of catabolism,the electron-transport chain.
C)Catabolic reactions "pay off" in ATP.
D)ATP is a phosphoric acid anhydride.
A)ADP is synthesized from ATP.
B)ATP is produced in the fourth stage of catabolism,the electron-transport chain.
C)Catabolic reactions "pay off" in ATP.
D)ATP is a phosphoric acid anhydride.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Exhibit 29-4
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):
Refer to Exhibit 29-4.The isomerization of glucose 6-phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate is an example of:
A)an elimination reaction
B)an oxidation reaction
C)keto-enol tautomerism
D)a conjugate addition reaction
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 29-4.The isomerization of glucose 6-phosphate to fructose 6-phosphate is an example of:
A)an elimination reaction
B)an oxidation reaction
C)keto-enol tautomerism
D)a conjugate addition reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The following reaction occurs in the citric acid cycle. 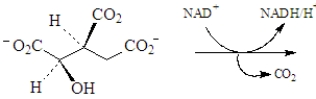 Draw the structure of the product.
Draw the structure of the product.
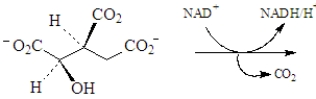 Draw the structure of the product.
Draw the structure of the product.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Draw the structure of the amino acid that is the precursor to the substance shown below.Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 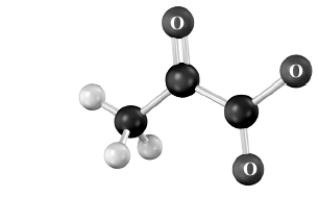


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
During the synthesis of fatty acids,the following sequence occurs.Draw the products presented by the question marks and identify the type of reaction. 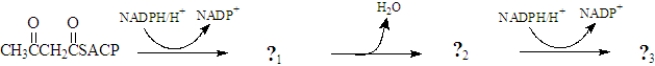
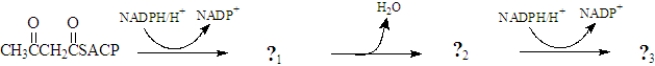

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Exhibit 29-4
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):
Refer to Exhibit 29-4.This reaction proceeds through a common enol structure.Draw the structure of the glucose/fructose enol.
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 29-4.This reaction proceeds through a common enol structure.Draw the structure of the glucose/fructose enol.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Consider the following reaction: 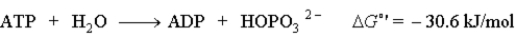 Which of the following reactions per mole could not be driven by the hydrolysis of ATP?
Which of the following reactions per mole could not be driven by the hydrolysis of ATP?
A)Reaction 1: ΔG°' = 12.6 kJ/mol
B)Reaction 1: ΔG°' = 22.5 kJ/mol
C)Reaction 1: ΔG°' = 29.6 kJ/mol
D)Reaction 1: ΔG°' = 40.6 kJ/mol
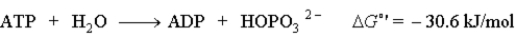 Which of the following reactions per mole could not be driven by the hydrolysis of ATP?
Which of the following reactions per mole could not be driven by the hydrolysis of ATP?A)Reaction 1: ΔG°' = 12.6 kJ/mol
B)Reaction 1: ΔG°' = 22.5 kJ/mol
C)Reaction 1: ΔG°' = 29.6 kJ/mol
D)Reaction 1: ΔG°' = 40.6 kJ/mol

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
During β-oxidation the following reaction occurs.What type of reaction is this? 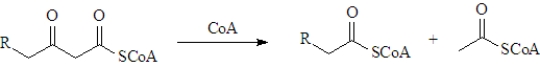
A)Claisen condensation
B)retro-Claisen condensation
C)aldol condensation
D)retro-aldol condensation
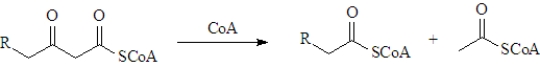
A)Claisen condensation
B)retro-Claisen condensation
C)aldol condensation
D)retro-aldol condensation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consider the following reaction: 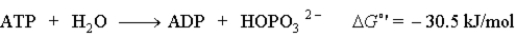 Hydrolysis of which of the following biomolecules could drive the formation of ATP?
Hydrolysis of which of the following biomolecules could drive the formation of ATP?
A)glycerol-1-phosphate ΔG°' = -9.2 kJ/mol
B)glucose-6-phosphate ΔG°' = -13.8 kJ/mol
C)fructose-6-phosphate ΔG°' = -15.8 kJ/mol
D)phosphocreatine ΔG°' = -49.5 kJ/mol
E)All could drive the formation of ATP.
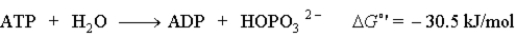 Hydrolysis of which of the following biomolecules could drive the formation of ATP?
Hydrolysis of which of the following biomolecules could drive the formation of ATP?A)glycerol-1-phosphate ΔG°' = -9.2 kJ/mol
B)glucose-6-phosphate ΔG°' = -13.8 kJ/mol
C)fructose-6-phosphate ΔG°' = -15.8 kJ/mol
D)phosphocreatine ΔG°' = -49.5 kJ/mol
E)All could drive the formation of ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In which of the following steps of glycolysis is ATP produced?
A)Steps 1 and 3
B)Steps 7 and 10
C)Steps 1,3 and 10
D)Steps 1,3,and 7
E)Steps 1,3,7,and 10
A)Steps 1 and 3
B)Steps 7 and 10
C)Steps 1,3 and 10
D)Steps 1,3,and 7
E)Steps 1,3,7,and 10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The transformation of FAD to FADH2 accompanies which of the following types of reactions?
A)isomerization
B)double bond formation
C)thioester formation
D)alcohol oxidation
A)isomerization
B)double bond formation
C)thioester formation
D)alcohol oxidation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Which of the following is an anabolic pathway?
A)glycolysis
B)citric acid cycle
C)β-oxidation
D)gluconeogenesis
A)glycolysis
B)citric acid cycle
C)β-oxidation
D)gluconeogenesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Consider the following conversion that occurs in the citric acid cycle.  What formula should be placed at the tail of the arrow?
What formula should be placed at the tail of the arrow?
A)FADH2
B)FAD
C)NAD+
D)NADH
 What formula should be placed at the tail of the arrow?
What formula should be placed at the tail of the arrow?A)FADH2
B)FAD
C)NAD+
D)NADH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
During β-oxidation the following reaction occurs. 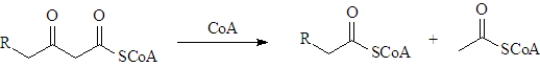 How many times will this reaction occur for the following acid? Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled.
How many times will this reaction occur for the following acid? Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 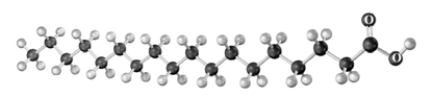
A)8
B)9
C)16
D)18
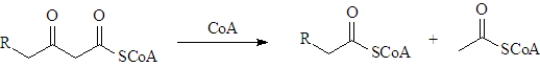 How many times will this reaction occur for the following acid? Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled.
How many times will this reaction occur for the following acid? Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 
A)8
B)9
C)16
D)18

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Which of the following correctly describes glycolysis?
A)produces a net of 4 ATP
B)intermediate path in glucose catabolism
C)produces two equivalents of pyruvate ions
D)involves one dephosphorylation and two phophorylations.
A)produces a net of 4 ATP
B)intermediate path in glucose catabolism
C)produces two equivalents of pyruvate ions
D)involves one dephosphorylation and two phophorylations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 48 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



