Deck 22: Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/33
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Carbonyl Alpha-Substitution Reactions
1
Exhibit 22-3
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s).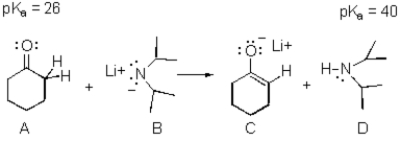
Refer to Exhibit 22-3.The enolate ion in the reaction is:
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s).

Refer to Exhibit 22-3.The enolate ion in the reaction is:
C
2
Exhibit 22-1
Refer to the compounds below to answer the following question(s):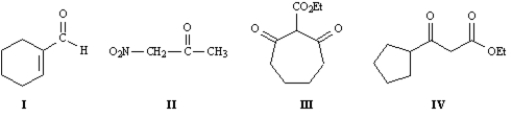
Indicate which hydrogens in Compound II are the most acidic.Explain your answer.
Refer to the compounds below to answer the following question(s):

Indicate which hydrogens in Compound II are the most acidic.Explain your answer.
The methylene hydrogens are the most acidic because they are flanked by two electron-withdrawing groups,−NO2 and C=O.The enolate generated by their removal is highly resonance stabilized;it has three resonance forms. 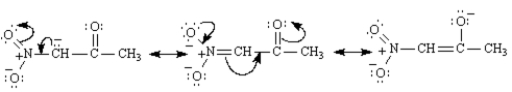 In contrast,the enolate generated by the abstraction of a methyl proton is stabilized by only one electron-withdrawing group and has two resonance forms:
In contrast,the enolate generated by the abstraction of a methyl proton is stabilized by only one electron-withdrawing group and has two resonance forms: 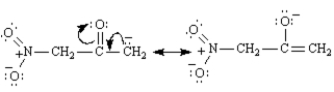
 In contrast,the enolate generated by the abstraction of a methyl proton is stabilized by only one electron-withdrawing group and has two resonance forms:
In contrast,the enolate generated by the abstraction of a methyl proton is stabilized by only one electron-withdrawing group and has two resonance forms: 
3
Exhibit 22-4
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):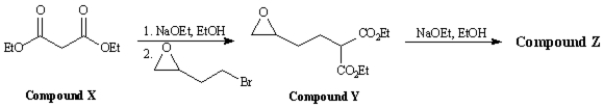
Refer to Exhibit 22-4.Write the complete stepwise mechanism for the conversion of Compound X into Compound Y.Show all electron flow with arrows and draw all intermediate structures.
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 22-4.Write the complete stepwise mechanism for the conversion of Compound X into Compound Y.Show all electron flow with arrows and draw all intermediate structures.
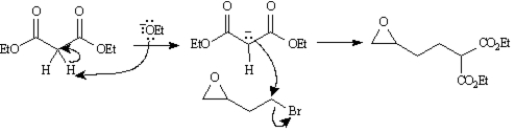
4
Exhibit 22-1
Refer to the compounds below to answer the following question(s):
Refer to Exhibit 22-1.Draw the structures for all enols of Compound I.
Refer to the compounds below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 22-1.Draw the structures for all enols of Compound I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Exhibit 22-5
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):
Refer to Exhibit 22-5.Conversion of B into C involves hydrolysis of the ester followed by decarboxylation.On the structures provided below,show the electron flow for the decarboxylation step.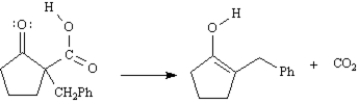
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 22-5.Conversion of B into C involves hydrolysis of the ester followed by decarboxylation.On the structures provided below,show the electron flow for the decarboxylation step.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Exhibit 22-2
Consider the structures below to answer the following question(s).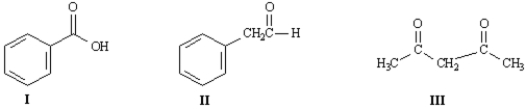
Refer to Exhibit 22-2.Indicate the most acidic hydrogens in each of the molecules.
Consider the structures below to answer the following question(s).

Refer to Exhibit 22-2.Indicate the most acidic hydrogens in each of the molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Exhibit 22-1
Refer to the compounds below to answer the following question(s):
Refer to Exhibit 22-1.Choose the most acidic compound from Compounds I - IV.Explain your choice.
Refer to the compounds below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 22-1.Choose the most acidic compound from Compounds I - IV.Explain your choice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Exhibit 22-1
Refer to the compounds below to answer the following question(s):
Refer to Exhibit 22-1.Indicate all the acidic hydrogens in Compounds I through IV.
Refer to the compounds below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 22-1.Indicate all the acidic hydrogens in Compounds I through IV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Exhibit 22-5
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):
Refer to Exhibit 22-5.The starting material A in this reaction sequence is called _____.
A)a β-keto ester
B)an α-carboethoxy ketone
C)a malonic ester
D)an acetoacetic ester
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 22-5.The starting material A in this reaction sequence is called _____.
A)a β-keto ester
B)an α-carboethoxy ketone
C)a malonic ester
D)an acetoacetic ester

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Exhibit 22-3
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Exhibit 22-3.The weakest acid in the reaction is:
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s).

Refer to Exhibit 22-3.The weakest acid in the reaction is:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Exhibit 22-3
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Exhibit 22-3.On the structures provided above,draw arrows indicating electron flow in the generation of the intermediate C.
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s).

Refer to Exhibit 22-3.On the structures provided above,draw arrows indicating electron flow in the generation of the intermediate C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Exhibit 22-2
Consider the structures below to answer the following question(s).
Rank the molecules above in order of increasing acidity (least acidic to most acidic).
A)III,II,I
B)II,III,I
C)I,II,III
D)II,I,III
Consider the structures below to answer the following question(s).

Rank the molecules above in order of increasing acidity (least acidic to most acidic).
A)III,II,I
B)II,III,I
C)I,II,III
D)II,I,III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Exhibit 22-6
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):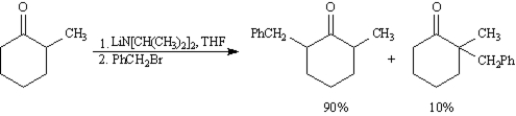
Refer to Exhibit 22-6.Write the complete stepwise mechanism for the reaction above.Show all intermediate structures and all electron flow with arrows.
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 22-6.Write the complete stepwise mechanism for the reaction above.Show all intermediate structures and all electron flow with arrows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Exhibit 22-6
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):
Refer to Exhibit 22-6.Explain the product ratio in this reaction.
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 22-6.Explain the product ratio in this reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Exhibit 22-5
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):
Refer to Exhibit 22-5.Conversion of A into B is a type of reaction termed _____.
A)an acylation
B)an enolation
C)an alkylation
D)a phenylation
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 22-5.Conversion of A into B is a type of reaction termed _____.
A)an acylation
B)an enolation
C)an alkylation
D)a phenylation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Exhibit 22-4
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):
Refer to Exhibit 22-4.Below are the structures and electron flow for the conversion of Compound Y into Compound Z.Draw the structure of Compound Z.(Hint: Compound Z is an alcohol. )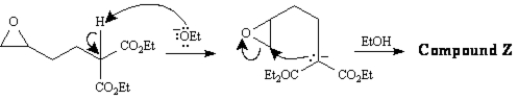
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 22-4.Below are the structures and electron flow for the conversion of Compound Y into Compound Z.Draw the structure of Compound Z.(Hint: Compound Z is an alcohol. )


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Exhibit 22-3
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s).
Refer to Exhibit 22-3.The strongest base in the reaction is:
Consider the reaction below to answer the following question(s).

Refer to Exhibit 22-3.The strongest base in the reaction is:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Exhibit 22-5
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):
Refer to Exhibit 22-5.The initial product formed on decarboxylation is an enol,which rapidly equilibrates to its keto form under the acidic reaction conditions.Write the complete stepwise mechanism for the acid-catalyzed conversion of the enol into its keto form,Compound C.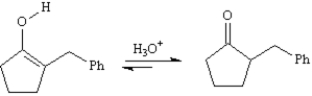
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 22-5.The initial product formed on decarboxylation is an enol,which rapidly equilibrates to its keto form under the acidic reaction conditions.Write the complete stepwise mechanism for the acid-catalyzed conversion of the enol into its keto form,Compound C.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Exhibit 22-4
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):
Refer to Exhibit 22-4.Compound X,diethyl propanedioate,is more commonly known as _____.
A)ethyl acetoacetate
B)acetoacetic ester
C)oxalic ester
D)malonic ester
Consider the reaction sequence below to answer the following question(s):

Refer to Exhibit 22-4.Compound X,diethyl propanedioate,is more commonly known as _____.
A)ethyl acetoacetate
B)acetoacetic ester
C)oxalic ester
D)malonic ester

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Nitroethane [CH3CH2NO2,pKa = 8.6] is a much stronger acid than ethane [CH3CH3,pKa ≈ 60].Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Explain how to use an alkylation reaction to produce: 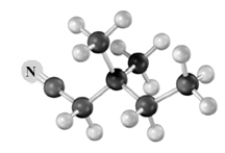 from
from 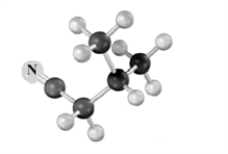 Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled.
Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled.
 from
from  Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled.
Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The alkyl halide that should be used to produce octanoic acid via the malonic ester synthesis is:
A)1-bromooctane
B)1-bromohexane
C)1-bromopentane
D)1-bromodecane
E)1-bromoundecane
A)1-bromooctane
B)1-bromohexane
C)1-bromopentane
D)1-bromodecane
E)1-bromoundecane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Draw the mechanism of the acid-catalyzed chlorination of acetophenone in the presence of a base.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Draw the structure of the major product formed when the substance represented by the following molecular model is treated with: 1.Br2/acetic acid,2.pyridine/heat.Atoms of other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 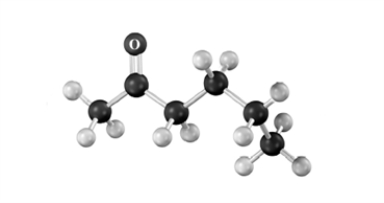


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Explain why the following reaction does not occur to any significant extent respect when the reactant is treated with bromine in the presence of acetic acid.Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled.
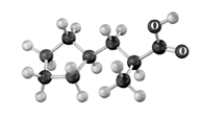
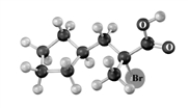 Reactant Product
Reactant Product

 Reactant Product
Reactant Product
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Draw the mechanism of enol formation from acetone in a reaction catalyzed by hydrochloric acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Examine the following generalized structure. 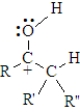 This represents
This represents
A)the acid catalyzed intermediate between an keto and enol tautomer.
B)the base catalyzed intermediate between an keto and enol tautomer.
C)one of the resonance forms of the acid catalyzed intermediate between an keto and enol tautomer.
D)one of the resonance forms of the acid catalyzed intermediate between an keto and enol tautomer..
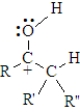 This represents
This representsA)the acid catalyzed intermediate between an keto and enol tautomer.
B)the base catalyzed intermediate between an keto and enol tautomer.
C)one of the resonance forms of the acid catalyzed intermediate between an keto and enol tautomer.
D)one of the resonance forms of the acid catalyzed intermediate between an keto and enol tautomer..

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Draw the general mechanism of the α-substitution reaction between acetone and the electrophilic methyl group.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Write the complete stepwise mechanism for the reaction of cyclopentanone with bromine in acetic acid to give 2-bromocyclopentanone.Show all intermediate structures and all electron flow with arrows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the hydrogen atoms indicated by a number is the most acidic in the structure below? Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 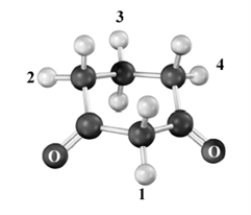
A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

A)1
B)2
C)3
D)4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The following substance is produced using acetoacetic ester synthesis.Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. 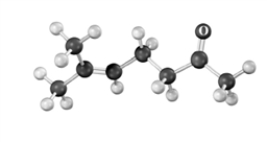 Which of the following regions of an IR spectrum could be used to monitor the progress of the reaction?
Which of the following regions of an IR spectrum could be used to monitor the progress of the reaction?
A)2850 - 29060 cm-1
B)2500 - 3100 cm-1
C)1670 - 1780 cm-1
D)500 - 600 cm-1
E)either c or d
 Which of the following regions of an IR spectrum could be used to monitor the progress of the reaction?
Which of the following regions of an IR spectrum could be used to monitor the progress of the reaction?A)2850 - 29060 cm-1
B)2500 - 3100 cm-1
C)1670 - 1780 cm-1
D)500 - 600 cm-1
E)either c or d

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Using the acetoacetic ester synthesis,to produce 5-methyl-2-heptanone,the alkyl halide that should be used is:
A)1-bromo-2-methylpentane
B)1-bromo-2-methylnonane
C)1-bromo-2-methylbutane
D)1-bromo-2-methyldecane
E)1-bromo-5-methylheptane
A)1-bromo-2-methylpentane
B)1-bromo-2-methylnonane
C)1-bromo-2-methylbutane
D)1-bromo-2-methyldecane
E)1-bromo-5-methylheptane

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is not correct?
A)Tautomers are constitutional isomers.
B)Tautomers rapidly interconvert.
C)The enol form is generally more stable.
D)Tautomerization is catalyzed by both acids and bases.
E)All of the above are correct with respect to tautomers.
A)Tautomers are constitutional isomers.
B)Tautomers rapidly interconvert.
C)The enol form is generally more stable.
D)Tautomerization is catalyzed by both acids and bases.
E)All of the above are correct with respect to tautomers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 33 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



