
Biological Science 6th Edition by Scott Freeman,Kim Quillin,Lizabeth Allison,Michael Black,Greg Podgorski,Emily Taylor,Jeff Carmichael
Edition 6ISBN: 978-0134243061
Biological Science 6th Edition by Scott Freeman,Kim Quillin,Lizabeth Allison,Michael Black,Greg Podgorski,Emily Taylor,Jeff Carmichael
Edition 6ISBN: 978-0134243061 Exercise 5
When Sutton and Boveri published the chromosome theory of inheritance, research on meiosis had not yet established that paternal and maternal homologs of different chromosomes assort independently. Then, in 1913, Elinor Carothers published a paper about a grasshopper species with an unusual karyotype: One chromosome had no homolog (meaning no pairing partner at meiosis I); another chromosome had homologs that could be distinguished under the light microscope. If chromosomes assort independently, how often should Carothers have observed each of the four products of meiosis shown in the following figure? 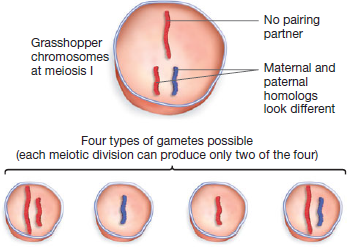
A) Only the gametes with one of each type of chromosome would occur.
B) The four types of gametes should be observed to occur at equal frequencies.
C) The chromosome with no pairing partner would disintegrate, so only gametes with one copy of the other chromosome would be observed.
D) Gametes with one of each type of chromosome would occur twice as often as gametes with just one chromosome.

A) Only the gametes with one of each type of chromosome would occur.
B) The four types of gametes should be observed to occur at equal frequencies.
C) The chromosome with no pairing partner would disintegrate, so only gametes with one copy of the other chromosome would be observed.
D) Gametes with one of each type of chromosome would occur twice as often as gametes with just one chromosome.
Explanation
Independent assortment of the genes take...
Biological Science 6th Edition by Scott Freeman,Kim Quillin,Lizabeth Allison,Michael Black,Greg Podgorski,Emily Taylor,Jeff Carmichael
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



