
Environmental Economics 6th Edition by Martha k Field,Barry Field
Edition 6ISBN: 978-0073511481
Environmental Economics 6th Edition by Martha k Field,Barry Field
Edition 6ISBN: 978-0073511481 Exercise 2
What is the difference between a residual and a pollutant? Illustrate this in the context of a common airborne emission such as sulfur dioxide (SO₂ ); with noise; with junked automobiles; with an unsightly building.
Explanation
Residual:
Two major functions of an economy, production and consumption, produce residuals or leftover waste products. Waste materials, products, and energy generated from any production process are called production residuals.Similarly, leftover waste products after the consumption activity is over are termed as consumption residuals.Pollutants:
Pollutants are generally forms of residuals, which alter or lower the ambient quality level after being introduced to the natural environment.Differences between a residual and a pollutant
Differences between residuals and pollutants are given below:
•All pollutants are residuals but all residuals are not pollutants, this is because all residuals do not damage environmental quality.
•Some proportion of residuals generated from production and consumption processes becomes pollutants when introduced to the environment.
•Some proportion of residuals can be re-used, but pollutants cannot be reused as it is already introduced to natural environment.
•All residuals may not have harmful effects on the environmental quality, but all pollutants do alter the environmental quality and have negative impact on natural environment.Airborne emission:
Sulfur dioxide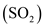 when emitted from tailpipe of automobile would be a residual, and it would be a pollutant when SO₂ is exposed to the environment and thereby altering the ambient quality.Similarly, the noise and junked automobiles are residuals, and they would become a pollutant once they damage the quality of environment.Unsighted buildings could either be a residual or a pollutant based on the aesthetic sense.
when emitted from tailpipe of automobile would be a residual, and it would be a pollutant when SO₂ is exposed to the environment and thereby altering the ambient quality.Similarly, the noise and junked automobiles are residuals, and they would become a pollutant once they damage the quality of environment.Unsighted buildings could either be a residual or a pollutant based on the aesthetic sense.
Two major functions of an economy, production and consumption, produce residuals or leftover waste products. Waste materials, products, and energy generated from any production process are called production residuals.Similarly, leftover waste products after the consumption activity is over are termed as consumption residuals.Pollutants:
Pollutants are generally forms of residuals, which alter or lower the ambient quality level after being introduced to the natural environment.Differences between a residual and a pollutant
Differences between residuals and pollutants are given below:
•All pollutants are residuals but all residuals are not pollutants, this is because all residuals do not damage environmental quality.
•Some proportion of residuals generated from production and consumption processes becomes pollutants when introduced to the environment.
•Some proportion of residuals can be re-used, but pollutants cannot be reused as it is already introduced to natural environment.
•All residuals may not have harmful effects on the environmental quality, but all pollutants do alter the environmental quality and have negative impact on natural environment.Airborne emission:
Sulfur dioxide
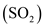 when emitted from tailpipe of automobile would be a residual, and it would be a pollutant when SO₂ is exposed to the environment and thereby altering the ambient quality.Similarly, the noise and junked automobiles are residuals, and they would become a pollutant once they damage the quality of environment.Unsighted buildings could either be a residual or a pollutant based on the aesthetic sense.
when emitted from tailpipe of automobile would be a residual, and it would be a pollutant when SO₂ is exposed to the environment and thereby altering the ambient quality.Similarly, the noise and junked automobiles are residuals, and they would become a pollutant once they damage the quality of environment.Unsighted buildings could either be a residual or a pollutant based on the aesthetic sense.Environmental Economics 6th Edition by Martha k Field,Barry Field
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



