
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341 Exercise 37
Let's suppose that a gene affecting pigmentation is found on the X chromosome (in mammals or insects) or the Z chromosome (in birds) but not on the Y or W chromosome. It is found on an autosome in bees. This gene exists in two alleles; D (dark), is dominant to d (light). What would be the phenotypic results of crosses between a true-breeding dark female and true-breeding light male, and the reciprocal crosses involving a true-breeding light female and true-breeding dark male, in the following species Refer back to Figure 3.17 for the mechanism of sex determination in these species
a. Birds
B. Drosophila
C. Bees
D. Humans
FIGURE 3.17 Different mechanisms of sex determination in animals. See text for a description.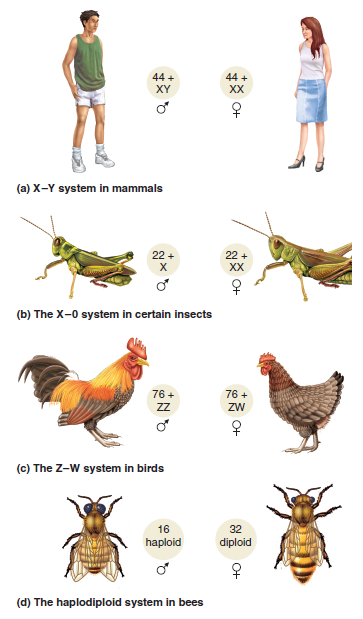
a. Birds
B. Drosophila
C. Bees
D. Humans
FIGURE 3.17 Different mechanisms of sex determination in animals. See text for a description.

Explanation
If we suppose the gene responsible for p...
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



