
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341 Exercise 5
The experiment of Figure 6.7 is not like a standard testcross, because neither parent is homozygous recessive for both genes. If you were going to carry out this same kind of experiment to verify that crossing over can explain the recombination of alleles of different genes, how would you modify this experiment to make it a standard testcross For both parents, you should designate which alleles are found on an abnormal chromosome (i.e., knobbed, translocation chromosome 9) and which alleles are found on normal chromosomes.FIGURE 6.7 Experimental correlation between genetic recombination and crossing over.
Starting materials: Two different strains of corn. One strain (referred to as parent A) had an abnormal chromosome 9 (knobbed/ translocation) with a dominant C allele and a recessive wx allele. It also had a cytologically normal copy of chromosome 9 that carried the recessive c allele and the dominant Wx allele. Its genotype was Cc Wxwx. The other strain (referred to as parent B) had two normal versions of chromosome 9. The genotype of this strain was cc Wxwx.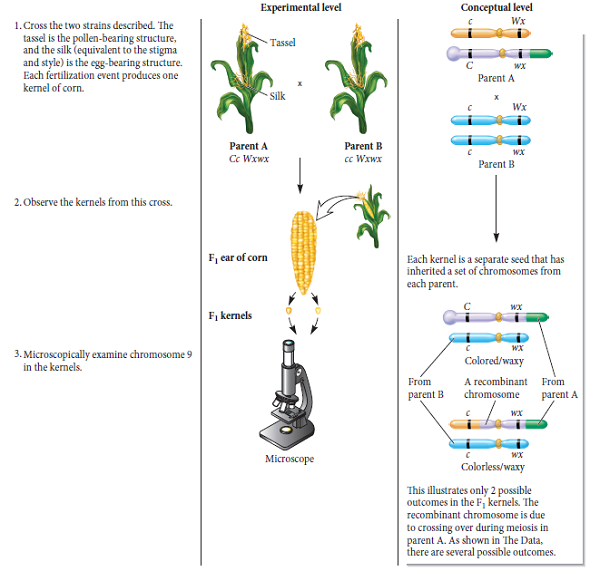
Starting materials: Two different strains of corn. One strain (referred to as parent A) had an abnormal chromosome 9 (knobbed/ translocation) with a dominant C allele and a recessive wx allele. It also had a cytologically normal copy of chromosome 9 that carried the recessive c allele and the dominant Wx allele. Its genotype was Cc Wxwx. The other strain (referred to as parent B) had two normal versions of chromosome 9. The genotype of this strain was cc Wxwx.

Explanation
McClintock and Creighton conducted an ex...
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



