
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341 Exercise 8
In the experiment of Figure 7.1, a met bio thr + leu + thi + cell could become met + bio + thr + leu + thi + by a (rare) double mutation that converts the met bio genes into met + bio +. Likewise, a met + bio + thr leu thi cell could become met + bio + thr + leu + thi + by three mutations that convert the thr leu thi genes into thr + leu + thi +. From the results of Figure 7.1, how do you know that the occurrence of 10 met + bio + thr + leu + thi + colonies is not due to these types of rare double or triple mutations
FIGURE 7.1 Experiment of Lederberg and Tatum demonstrating genetic transfer during conjugation in E. coli. When plated on a growth medium lacking amino acids, biotin, and thiamine, the met bio thr + leu + thi + or met + bio + thr leu thi strains were unable to grow. However, if they were mixed together and then plated, some colonies were observed. These colonies were due to the transfer of genetic material between these two strains by conjugation. Note: In bacteria, it is common to give genes a three-letter name (shown in italics) that is related to the function of the gene. A plus superscript ( + ) indicates a functional gene, and a minus superscript ( ) indicates a mutation that has caused the gene or gene product to be inactive. In some cases, several genes have related functions. These may have the same three-letter name followed by different capital letters. For example, different genes involved with leucine biosynthesis may be called leuA, leuB, leuC, and so on. In the experiment described in Figure 7.1, the genes involved in leucine biosynthesis had not been distinguished, so the gene involved is simply referred to as leu + (for a functional gene) and leu (for a nonfunctional gene).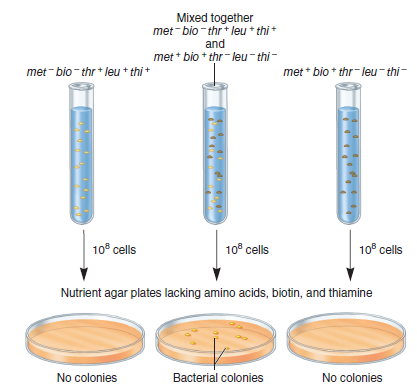
FIGURE 7.1 Experiment of Lederberg and Tatum demonstrating genetic transfer during conjugation in E. coli. When plated on a growth medium lacking amino acids, biotin, and thiamine, the met bio thr + leu + thi + or met + bio + thr leu thi strains were unable to grow. However, if they were mixed together and then plated, some colonies were observed. These colonies were due to the transfer of genetic material between these two strains by conjugation. Note: In bacteria, it is common to give genes a three-letter name (shown in italics) that is related to the function of the gene. A plus superscript ( + ) indicates a functional gene, and a minus superscript ( ) indicates a mutation that has caused the gene or gene product to be inactive. In some cases, several genes have related functions. These may have the same three-letter name followed by different capital letters. For example, different genes involved with leucine biosynthesis may be called leuA, leuB, leuC, and so on. In the experiment described in Figure 7.1, the genes involved in leucine biosynthesis had not been distinguished, so the gene involved is simply referred to as leu + (for a functional gene) and leu (for a nonfunctional gene).

Explanation
Each bacterium got different nutritional...
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



