
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341 Exercise 26
As shown in Figure 7.16, phages with rII mutations cannot produce plaques in E. coli K12( ), but wild-type phages can. From an experimental point of view, explain why this observation is so significant.Figure 7.16 A comparison of noncomplementation and complementation. Four different T4 phage strains (designated 1 through 4) carry rII mutations in gene A or gene B. (a) If the rII mutations are in different genes, a coinfected cell can produce new phages and plaques will form. This result is called complementation because the defective genes in each rII strain are complemented by the corresponding wild-type genes. (b) If E. coli K12( ) is coinfected with two rII phage strains with mutations in the same gene, noncomplementation will occur. 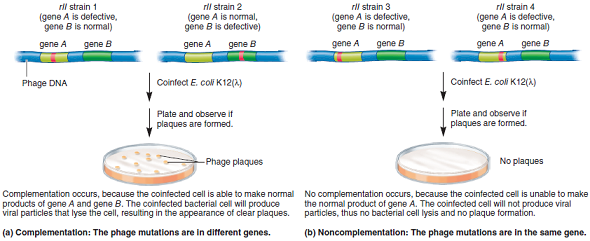

Explanation
In an experiment, two mutant phages are ...
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



