
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341 Exercise 33
The technique of Western blotting can be used to detect proteins that are translated from a particular mRNA. This method is described in Chapter 20 and also in experimental question E5.Let's suppose a researcher was interested in the effects of mutations on the expression of a protein-encoding gene that encodes a protein we will call protein X. This protein is expressed in skin cells and contains 572 amino acids. Its molecular mass is approximately 68,600 Da, or 68.6 kDa. Make a drawing that shows the expected results of a Western blot using proteins isolated from the skin cells obtained from the following individuals:
Lane 1: A normal individual
Lane 2: An individual who is homozygous for a deletion, which removes the promoter for this gene
Lane 3: An individual who is heterozygous in which one gene is normal and the other gene has a mutation that introduces an early stop codon at codon 421
Lane 4: An individual who is homozygous for a mutation that introduces an early stop codon at codon 421
Lane 5: An individual who is homozygous for a mutation that changes codon 198 from a valine codon into a leucine codon
Question E5
Chapter 20 describes a blotting method known as Western blotting that can be used to detect the production of a polypeptide that is translated from a particular mRNA. In this method, a protein is detected with an antibody that specifically recognizes and binds to its amino acid sequence. The antibody acts as a probe to detect the presence of the protein. In a Western blotting experiment, a mixture of cellular proteins is separated using gel electrophoresis according to their molecular masses. After the antibody has bound to the protein of interest within a blot of a gel, the protein is visualized as a dark band. For example, an antibody that recognizes the -globin polypeptide could be used to specifically detect the -globin polypeptide in a blot. As shown here, the method of Western blotting can be used to determine the amount and relative size of a particular protein that is produced in a given cell type.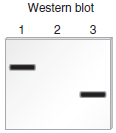
a.
Lane 1 is a sample of proteins isolated from normal red blood cells.Lane 2 is a sample of proteins isolated from kidney cells. Kidney cells do not produce globin.Lane 3 is a sample of proteins isolated from red blood cells from a patient with -thalassemia. This patient is homozygous for a mutation that results in the shortening of the -globin polypeptide.Now here is the question. A protein called troponin contains 334 amino acids. Because each amino acid weighs 120 daltons (Da) (on average), the molecular mass of this protein is about 40,000 Da, or 40 kDa. Troponin functions in muscle cells, and it is not expressed in nerve cells. Draw the expected results of a Western blot for the following samples:
Lane 1: Proteins isolated from muscle cells
Lane 2: Proteins isolated from nerve cells
Lane 3: Proteins isolated from the muscle cells of an individual who is homozygous for a mutation that introduces a stop codon at codon 177
Lane 1: A normal individual
Lane 2: An individual who is homozygous for a deletion, which removes the promoter for this gene
Lane 3: An individual who is heterozygous in which one gene is normal and the other gene has a mutation that introduces an early stop codon at codon 421
Lane 4: An individual who is homozygous for a mutation that introduces an early stop codon at codon 421
Lane 5: An individual who is homozygous for a mutation that changes codon 198 from a valine codon into a leucine codon
Question E5
Chapter 20 describes a blotting method known as Western blotting that can be used to detect the production of a polypeptide that is translated from a particular mRNA. In this method, a protein is detected with an antibody that specifically recognizes and binds to its amino acid sequence. The antibody acts as a probe to detect the presence of the protein. In a Western blotting experiment, a mixture of cellular proteins is separated using gel electrophoresis according to their molecular masses. After the antibody has bound to the protein of interest within a blot of a gel, the protein is visualized as a dark band. For example, an antibody that recognizes the -globin polypeptide could be used to specifically detect the -globin polypeptide in a blot. As shown here, the method of Western blotting can be used to determine the amount and relative size of a particular protein that is produced in a given cell type.

a.
Lane 1 is a sample of proteins isolated from normal red blood cells.Lane 2 is a sample of proteins isolated from kidney cells. Kidney cells do not produce globin.Lane 3 is a sample of proteins isolated from red blood cells from a patient with -thalassemia. This patient is homozygous for a mutation that results in the shortening of the -globin polypeptide.Now here is the question. A protein called troponin contains 334 amino acids. Because each amino acid weighs 120 daltons (Da) (on average), the molecular mass of this protein is about 40,000 Da, or 40 kDa. Troponin functions in muscle cells, and it is not expressed in nerve cells. Draw the expected results of a Western blot for the following samples:
Lane 1: Proteins isolated from muscle cells
Lane 2: Proteins isolated from nerve cells
Lane 3: Proteins isolated from the muscle cells of an individual who is homozygous for a mutation that introduces a stop codon at codon 177
Explanation
(a)
Lane 1 protein X is expressed in nor...
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



