
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341 Exercise 27
According to Figure 13.17, explain why the ribosome translocates along the mRNA in a 5 to 3 direction rather than a 3 to 5 direction.FIGURE 13.17 The elongation stage of translation in bacteria. This process begins with the binding of an incoming charged tRNA. The hydrolysis of GTP by EF-Tu provides the energy for the binding of the tRNA to the A site. A peptide bond is then formed between the amino acid at the A site and the last amino acid in the growing polypeptide. This moves the polypeptide to the A site. The ribosome then translocates in the 3. direction so the two tRNAs are moved to the E and P sites. The tRNA carrying the polypeptide is now back in the P site. This translocation requires the hydrolysis of GTP via EF-G. The uncharged tRNA in the E site is released from the ribosome. Now the process is ready to begin again. Each cycle of elongation causes the polypeptide to grow by one amino acid. 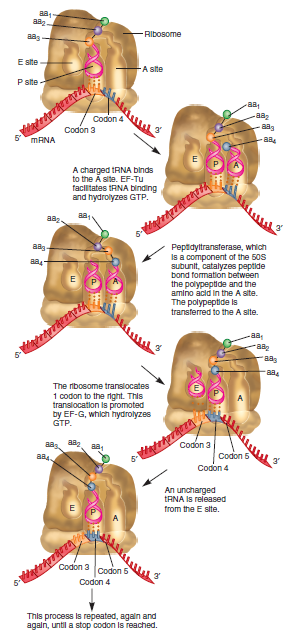

Explanation
The tRNAs anticodon binds to codon regio...
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



