
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Edition 5ISBN: 978-0073525341 Exercise 32
Two techniques commonly used to study the expression patterns of genes that play a role in development are Northern blotting and in situ hybridization. As described in Chapter 20, Northern blotting is used to detect RNA that is transcribed from a particular gene. In this method, a specific RNA is detected by using a short segment of cloned DNA as a probe. The DNA probe, which is labeled, is complementary to the RNA that the researcher wishes to detect. After the probe DNA binds to the RNA within a blot of a gel, the RNA is visualized as a labeled band on a nylon membrane. For example, a DNA probe that is complementary to the bicoid mRNA could be used to specifically detect the amount and size of the mRNA in a blot.A second technique, termed fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), is used to identify the locations of genes on chromosomes. This technique is also used to locate gene products within oocytes, embryos, and larvae. For this reason, it has been commonly used by developmental geneticists to understand the expression patterns of genes during development. The micrograph in Figure 25.8b is derived from the application of the FISH technique. In this case, the probe was complementary to bicoid mRNA.Now here is the question. Suppose a researcher has three different Drosophila strains that have loss-of-function mutations in the bicoid gene. We will call them bicoid-A, bicoid-B, and bicoid-C; the wild type is designated bicoid +. To study these mutations, phenotypically normal female flies that are homozygous for the bicoid mutation were obtained, and their oocytes were analyzed using these two techniques. A wild-type strain was also analyzed as a control. In other words, RNA was isolated from some oocytes and analyzed by Northern blotting, and some oocytes were subjected to in situ hybridization. In both cases, the probe was complementary to the bicoid mRNA. The results are shown next. 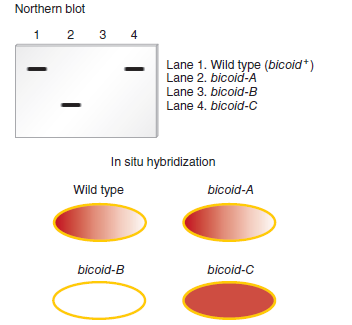
a. How can phenotypically normal female flies be homozygous for a loss-of-function allele in the bicoid gene
B. Explain the type of mutation (e.g., deletion, point mutation, etc.) in each of the three strains. Explain how the mutation may cause a loss of normal function for the bicoid gene product
c. Discuss how the use of both techniques provides more definitive information than the application of just one of the two techniques.FIGURE 25.8 Asymmetrical localization of gene products during oogenesis in Drosophila. ( a ) The nurse cells transport gene products into the anterior (left) end of the developing oocyte. ( b ) An in situ hybridization experiment showing that the bicoid mRNA is trapped near the anterior end of the oocyte. ( c ) The bicoid mRNA is translated into protein soon after fertilization. The location of the Bicoid protein is revealed by immunostaining using an antibody that specifically recognizes this protein.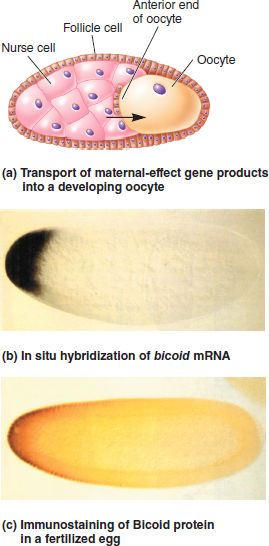

a. How can phenotypically normal female flies be homozygous for a loss-of-function allele in the bicoid gene
B. Explain the type of mutation (e.g., deletion, point mutation, etc.) in each of the three strains. Explain how the mutation may cause a loss of normal function for the bicoid gene product
c. Discuss how the use of both techniques provides more definitive information than the application of just one of the two techniques.FIGURE 25.8 Asymmetrical localization of gene products during oogenesis in Drosophila. ( a ) The nurse cells transport gene products into the anterior (left) end of the developing oocyte. ( b ) An in situ hybridization experiment showing that the bicoid mRNA is trapped near the anterior end of the oocyte. ( c ) The bicoid mRNA is translated into protein soon after fertilization. The location of the Bicoid protein is revealed by immunostaining using an antibody that specifically recognizes this protein.

Explanation
One can use two assays - Northern blot a...
Genetics: Analysis and Principles 5th Edition by Robert Brooker
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



