
Human Heredity 11th Edition by Michael Cummings
Edition 11ISBN: 978-1305251052
Human Heredity 11th Edition by Michael Cummings
Edition 11ISBN: 978-1305251052 Exercise 14
Using Figures 1 and 2 as a guide, draw a dinucleotide composed of C and A. Next to this, draw the complementary dinucleotide in an antiparallel fashion. Connect the dinucleotides with the appropriate hydrogen bonds.
FIGURE 1 Nucleotides can be joined together to form chains called polynucleotides. Polynucleotides are polar molecules with a 59 end (at the phosphate group) and a 39 end (at the sugar group). An RNA polynucleotide is shown at the left , and a DNA polynucleotide is shown at the right.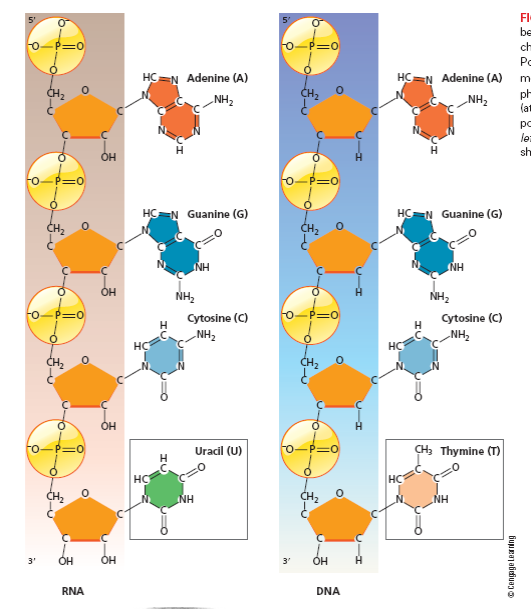
FIGURE 2 The two polynucleotide chains in DNA run in opposite directions. The left strand runs 59 to 39, and the right strand runs 39 to 59. The base sequences in each strand are complementary. An A in one strand pairs with a T in the other strand, and a C in one strand is paired with a G in the opposite strand.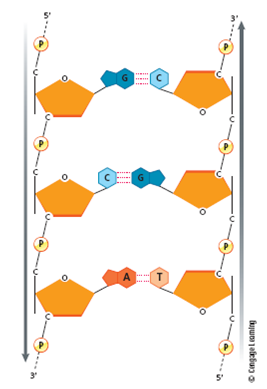
FIGURE 1 Nucleotides can be joined together to form chains called polynucleotides. Polynucleotides are polar molecules with a 59 end (at the phosphate group) and a 39 end (at the sugar group). An RNA polynucleotide is shown at the left , and a DNA polynucleotide is shown at the right.

FIGURE 2 The two polynucleotide chains in DNA run in opposite directions. The left strand runs 59 to 39, and the right strand runs 39 to 59. The base sequences in each strand are complementary. An A in one strand pairs with a T in the other strand, and a C in one strand is paired with a G in the opposite strand.

Explanation
The following structure shows dinucleoti...
Human Heredity 11th Edition by Michael Cummings
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



