
Human Heredity 11th Edition by Michael Cummings
Edition 11ISBN: 978-1305251052
Human Heredity 11th Edition by Michael Cummings
Edition 11ISBN: 978-1305251052 Exercise 30
How does DNA replication occur in a precise manner to ensure that identical genetic information is put into the new chromatid? See Figures 3 and 4.
FIGURE 3 In DNA replication, the two polynucleotide strands uncoil, and each is a template for synthesizing a new strand. A replicated DNA molecule contains one new strand and one old strand. This mechanism is called semiconservative replication.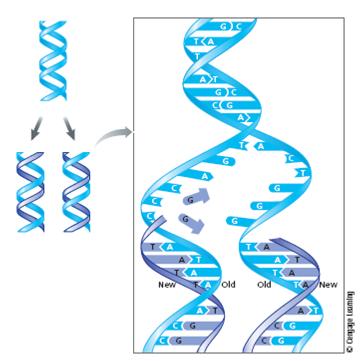
FIGURE 4 A close-up look at the process of DNA replication. (a) As the strands uncoil, bases are added to the newly synthesized strand by complementary base pairing with bases in the template strand. The new bases are linked together by DNA polymerase. (b) DNA synthesis can proceed only in the 5' ? 3' direction; newly synthesized DNA on one template strand is made in short segments and linked together by the enzyme DNA ligase.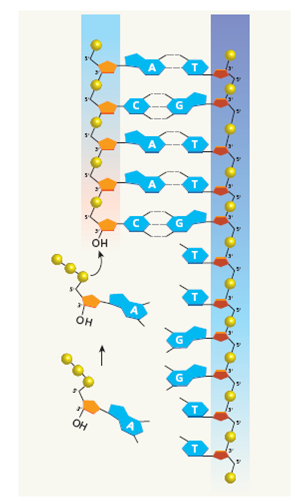
a) Each DNA strand has two ends: one with a 59 carbon, and one with a 39 carbon. DNA polymerase can add nucleotides only at the 39 carbon. In other words, DNA synthesis proceeds only in the 59 to 39 direction.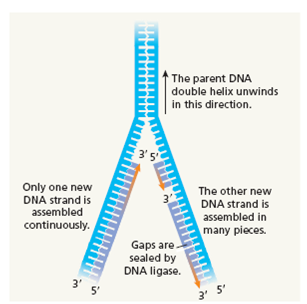
b) Because DNA synthesis proceeds only in the 5' to 3' direction, only one of the DNA strands can be assembled in a single piece. The other new DNA strand forms in short segments, which are called Okazaki fragments after the two scientists who discovered them. DNA ligase joins the fragments into a continuous strand of DNA.
FIGURE 3 In DNA replication, the two polynucleotide strands uncoil, and each is a template for synthesizing a new strand. A replicated DNA molecule contains one new strand and one old strand. This mechanism is called semiconservative replication.

FIGURE 4 A close-up look at the process of DNA replication. (a) As the strands uncoil, bases are added to the newly synthesized strand by complementary base pairing with bases in the template strand. The new bases are linked together by DNA polymerase. (b) DNA synthesis can proceed only in the 5' ? 3' direction; newly synthesized DNA on one template strand is made in short segments and linked together by the enzyme DNA ligase.

a) Each DNA strand has two ends: one with a 59 carbon, and one with a 39 carbon. DNA polymerase can add nucleotides only at the 39 carbon. In other words, DNA synthesis proceeds only in the 59 to 39 direction.

b) Because DNA synthesis proceeds only in the 5' to 3' direction, only one of the DNA strands can be assembled in a single piece. The other new DNA strand forms in short segments, which are called Okazaki fragments after the two scientists who discovered them. DNA ligase joins the fragments into a continuous strand of DNA.
Explanation
DNA replication ensures identical geneti...
Human Heredity 11th Edition by Michael Cummings
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



