
Clinical Laboratory Hematology 3rd Edition by Shirlyn McKenzie, Lynne Williams
Edition 3ISBN: 978-0133076011
Clinical Laboratory Hematology 3rd Edition by Shirlyn McKenzie, Lynne Williams
Edition 3ISBN: 978-0133076011 Exercise 39
Hancock, a 65-year-old white male, was seen in triage with complaints of fatigue, malaise, anorexia, and hemoptysis of recent onset. A complete blood count (CBC) was ordered and revealed anemia and a shift to the left in granulocytes. Hematopoietic cells showed dysplastic features.
Consider diagnostic probabilities and reflex testing that could provide differential diagnostic information.
The results of the CBC on Hancock were: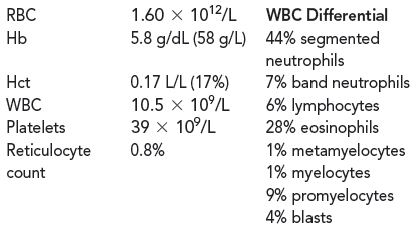
The neutrophilic cells show marked hyposegmentation and hypogranulation. Red blood cell (RBC) morphology includes anisocytosis and poikilocytosis, teardrop cells, ovalocytes, and schistocytes.
A bone marrow was performed on Hancock. The marrow showed a cellularity of about 75%. There was myeloid hyperplasia with 9% blasts, 26% promyelocytes, 18% myelocytes, 6% metamyelocytes, 4% bands, and 37% eosinophils. The ratio of myeloid-to-erythroid precursors (M:E) was 12:1. The myelocytes were hypogranular, and some had two nuclei. The erythroid precursors showed megaloblastoid changes. Megakaryocytes were adequate in number but showed abnormal forms with nuclear separation and single nucleated forms.
Identify at least two features of the bone marrow that are compatible with a diagnosis of MDS.
Consider diagnostic probabilities and reflex testing that could provide differential diagnostic information.
The results of the CBC on Hancock were:

The neutrophilic cells show marked hyposegmentation and hypogranulation. Red blood cell (RBC) morphology includes anisocytosis and poikilocytosis, teardrop cells, ovalocytes, and schistocytes.
A bone marrow was performed on Hancock. The marrow showed a cellularity of about 75%. There was myeloid hyperplasia with 9% blasts, 26% promyelocytes, 18% myelocytes, 6% metamyelocytes, 4% bands, and 37% eosinophils. The ratio of myeloid-to-erythroid precursors (M:E) was 12:1. The myelocytes were hypogranular, and some had two nuclei. The erythroid precursors showed megaloblastoid changes. Megakaryocytes were adequate in number but showed abnormal forms with nuclear separation and single nucleated forms.
Identify at least two features of the bone marrow that are compatible with a diagnosis of MDS.
Explanation
The MDS (myelodysplastic syndromes) are ...
Clinical Laboratory Hematology 3rd Edition by Shirlyn McKenzie, Lynne Williams
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



