
Advanced Accounting 11th Edition by Paul Fischer,William Tayler, Rita Cheng
Edition 11ISBN: 978-0538480284
Advanced Accounting 11th Edition by Paul Fischer,William Tayler, Rita Cheng
Edition 11ISBN: 978-0538480284 Exercise 29
80%, equity, several excess distributions, inventory, fixed assets, parent and subsidiary sales. Refer to the preceding facts for Purple's acquisition of Salmon common stock. On January 1, 2013, Salmon held merchandise sold to it from Purple for $12,000. This beginning inventory had an applicable gross profit of 35%. During 2013, Purple sold merchandise to Salmon for $55,000. On December 31, 2013, Salmon held $10,000 of this merchandise in its inventory. This ending inventory had an applicable gross profit of 40%. Salmon owed Purple $7,500 on December 31 as a result of this intercompany sale.
Purple held $16,000 worth of merchandise in its January 1, 2013, inventory from sales from Salmon. This beginning inventory had an applicable gross profit of 30%. During 2013, Salmon sold merchandise to Purple for $35,000. Purple held $20,000 of this inventory at the end of the year. This ending inventory had an applicable gross profit of 35%. Purple owed Salmon $5,000 on December 31 as a result of this intercompany sale.
On January 1, 2011, Purple sold equipment to Salmon at a profit of $40,000. Depreciation on this equipment is computed over an 8-year life using the straight-line method.
On January 1, 2012, Salmon sold equipment with a book value of $30,000 to Purple for $54,000. This equipment has a 6-year life and is depreciated using the straight-line method.
Purple and Salmon had the following trial balances on December 31, 2013: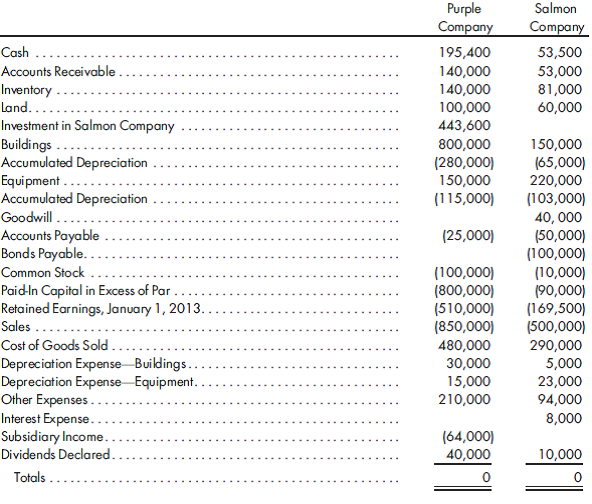
1. Prepare a value analysis and a determination and distribution of excess schedule for the investment in Salmon.
2. Complete a consolidated worksheet for Purple Company and its subsidiary Salmon Company as of December 31, 2013. Prepare supporting amortization and income distribution schedules.
Purple held $16,000 worth of merchandise in its January 1, 2013, inventory from sales from Salmon. This beginning inventory had an applicable gross profit of 30%. During 2013, Salmon sold merchandise to Purple for $35,000. Purple held $20,000 of this inventory at the end of the year. This ending inventory had an applicable gross profit of 35%. Purple owed Salmon $5,000 on December 31 as a result of this intercompany sale.
On January 1, 2011, Purple sold equipment to Salmon at a profit of $40,000. Depreciation on this equipment is computed over an 8-year life using the straight-line method.
On January 1, 2012, Salmon sold equipment with a book value of $30,000 to Purple for $54,000. This equipment has a 6-year life and is depreciated using the straight-line method.
Purple and Salmon had the following trial balances on December 31, 2013:

1. Prepare a value analysis and a determination and distribution of excess schedule for the investment in Salmon.
2. Complete a consolidated worksheet for Purple Company and its subsidiary Salmon Company as of December 31, 2013. Prepare supporting amortization and income distribution schedules.

Explanation
Calculate non-controlling interest value...
Advanced Accounting 11th Edition by Paul Fischer,William Tayler, Rita Cheng
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



