
Advanced Accounting 11th Edition by Paul Fischer,William Tayler, Rita Cheng
Edition 11ISBN: 978-0538480284
Advanced Accounting 11th Edition by Paul Fischer,William Tayler, Rita Cheng
Edition 11ISBN: 978-0538480284 Exercise 18
Worksheet, separate tax, simple equity, inventory, fixed asset sale, analyze price. Refer to the preceding facts for Penske's acquisition of Stock common stock. Penske uses the simple equity method to account for its investment in Stock. During 2012, Stock sells $30,000 worth of merchandise to Penske. As a result of these intercompany sales, Penske holds beginning inventory of $12,000 and ending inventory of $16,000 of merchandise acquired from Stock. At December 31, 2012, Penske owes Stock $6,000 from merchandise sales. Stock has a gross profit rate of 30%.
On January 1, 2011, Penske sells equipment having a net book value of $50,000 to Stock for $90,000. The equipment has a 5-year useful life and is depreciated using the straight-line method.
Penske and Stock do not qualify as an affiliated group for tax purposes and, thus, will file separate tax returns. Assume a 40% corporate tax rate and an 80% dividends received exclusion.
On December 31, 2012, Penske and Stock have the following trial balances: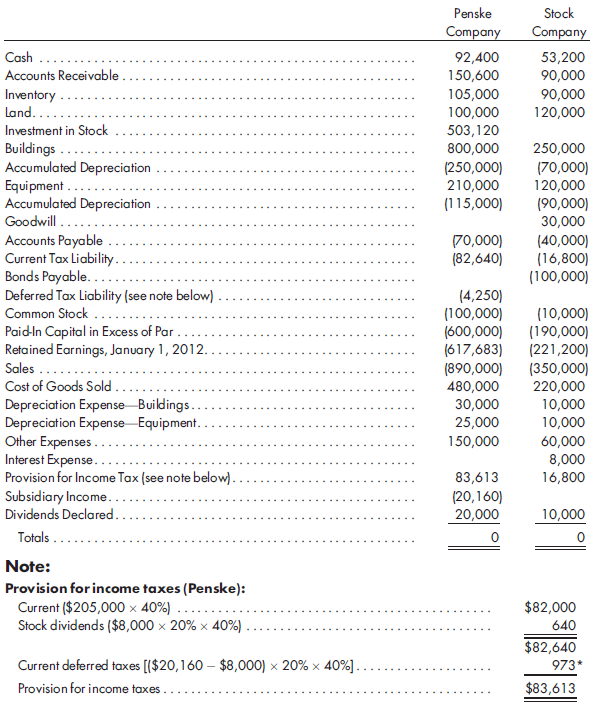
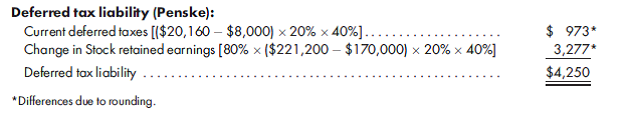
1. Prepare a value analysis and a determination and distribution of excess schedule.
2. Prepare a consolidated worksheet for the year ended December 31, 2012. Include a provision for income tax and income distribution schedules.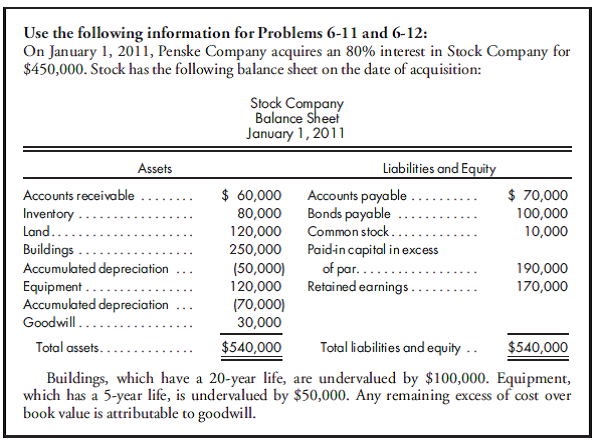
On January 1, 2011, Penske sells equipment having a net book value of $50,000 to Stock for $90,000. The equipment has a 5-year useful life and is depreciated using the straight-line method.
Penske and Stock do not qualify as an affiliated group for tax purposes and, thus, will file separate tax returns. Assume a 40% corporate tax rate and an 80% dividends received exclusion.
On December 31, 2012, Penske and Stock have the following trial balances:

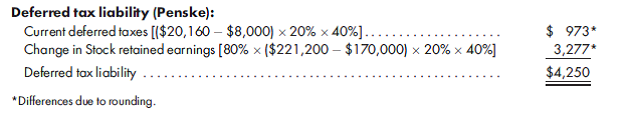
1. Prepare a value analysis and a determination and distribution of excess schedule.
2. Prepare a consolidated worksheet for the year ended December 31, 2012. Include a provision for income tax and income distribution schedules.

Explanation
Intercompany Inventory Profit Deferral ...
Advanced Accounting 11th Edition by Paul Fischer,William Tayler, Rita Cheng
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



