
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022 Exercise 11
Sometimes it is convenient to think about the consumer s problem in its ''dual form. This alternative approach asks how a person could achieve a given target level of utility at minimal cost.
a. Develop a graphical argument to show that this approach will yield the same choices for this consumer as would the utility maximization approach.
b. Returning to problem, assume that Paul's target level of utility is U = 10. Calculate the costs of attaining this utility target for the following bundles of goods:
i. C = 100, D = 1
ii. C = 50, D = 2
iii. C = 25, D = 4
iv. C = 20, D = 5
v. C = 10, D = 10
vi. C = 5, D = 20.
c. Which of the bundles in part b provides the least costly way of reaching the U = 10 target? How does this compare to the utility-maximizing solution found in problem?
Problem Paul derives utility only from CDs and DVDs. His utility function is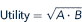
a. Sketch Paul's indifference curves for U = 5, U = 10, and U = 20.
b. Suppose Paul has $200 to spend and that CDs cost $5 and DVDs cost $20. Draw Paul s budget constraint on the same graph as his indifference curves.
c. Suppose Paul spends all of his income on DVDs. How many can he buy and what is his utility?
d. Show that Paul's income will not permit him to reach the U = 20 indifference curve.
e. If Paul buys 5 DVDs, how many CDs can he buy? What is his utility?
f. Use a carefully drawn graph to show that the utility calculated in part e is the highest Paul can achieve with his $200.
a. Develop a graphical argument to show that this approach will yield the same choices for this consumer as would the utility maximization approach.
b. Returning to problem, assume that Paul's target level of utility is U = 10. Calculate the costs of attaining this utility target for the following bundles of goods:
i. C = 100, D = 1
ii. C = 50, D = 2
iii. C = 25, D = 4
iv. C = 20, D = 5
v. C = 10, D = 10
vi. C = 5, D = 20.
c. Which of the bundles in part b provides the least costly way of reaching the U = 10 target? How does this compare to the utility-maximizing solution found in problem?
Problem Paul derives utility only from CDs and DVDs. His utility function is
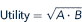
a. Sketch Paul's indifference curves for U = 5, U = 10, and U = 20.
b. Suppose Paul has $200 to spend and that CDs cost $5 and DVDs cost $20. Draw Paul s budget constraint on the same graph as his indifference curves.
c. Suppose Paul spends all of his income on DVDs. How many can he buy and what is his utility?
d. Show that Paul's income will not permit him to reach the U = 20 indifference curve.
e. If Paul buys 5 DVDs, how many CDs can he buy? What is his utility?
f. Use a carefully drawn graph to show that the utility calculated in part e is the highest Paul can achieve with his $200.
Explanation
Point A in the graph below shows solutio...
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



