
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022 Exercise 9
Suppose A can somehow change the game in problem to a new one in which his payoff from Up is reduced by 2, producing the following payoff matrix. 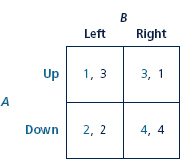
a. Find the Nash equilibrium or equilibria.
b. Which player, if any, has a dominant strategy?
c. Does A benefit from changing the game by reducing his or her payoff in this way?
Consider a simultaneous game in which player A chooses one of two actions (Up or Down), and B chooses one of two actions (Left or Right). The game has the following payoff matrix, where the first payoff in each entry is for A and the second for B.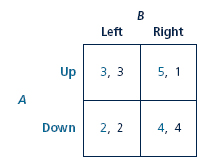
a. Find the Nash equilibrium or equilibria.
b. Which player, if any, has a dominant strategy?

a. Find the Nash equilibrium or equilibria.
b. Which player, if any, has a dominant strategy?
c. Does A benefit from changing the game by reducing his or her payoff in this way?
Consider a simultaneous game in which player A chooses one of two actions (Up or Down), and B chooses one of two actions (Left or Right). The game has the following payoff matrix, where the first payoff in each entry is for A and the second for B.

a. Find the Nash equilibrium or equilibria.
b. Which player, if any, has a dominant strategy?
Explanation
The payoff matrix is a table that shows ...
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



