
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022 Exercise 24
In our numerical example, Hamburger Heaven s expansion path requires K = L because w (the wage) and v (the rental rate of grills) are equal. More generally, for this type of production function, it can be shown that
K /L = w/v
for cost minimization. Hence, relative input usage is determined by relative input prices.
a. Suppose both wages and grill rents rise to $10 per hour. How would this affect the firm s expansion path? How would long-run average and marginal cost be affected? What can you conclude about the effect of uniform inflation of input costs on the costs of hamburger pro-duction?
b. Suppose wages rise to $20 but grill rents stay fixed at $5. How would this affect the firm s expansion path? How would this affect the long-run average and marginal cost of hamburger production? Why does a multiplication of the wage by four result in a much smaller increase in average costs?
c. In the numerical example in Chapter 6, we explored the consequences of technical progress in hamburger flipping. Specifically, we assumed that the hamburger production function shifted for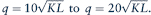 How would this shift offset the cost increases in part a? That is, what cost curves are implied by this new production function with v = w = 10? How do these compare with the original curves shown in Figure?
How would this shift offset the cost increases in part a? That is, what cost curves are implied by this new production function with v = w = 10? How do these compare with the original curves shown in Figure?
d. Answer part c with the input costs in part b of this problem (v = 5, w = 20). What do you conclude about the ability of technical progress to offset rising input costs?
Figure Total, Average, and Marginal Cost Curves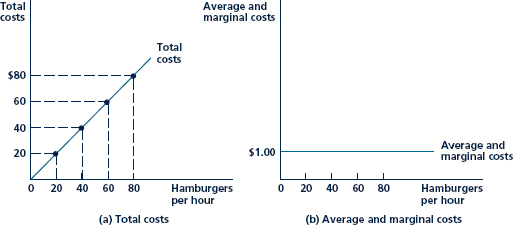
The total cost curve is simply a straight line through the origin reflecting constant returns to scale. Long-run average and marginal costs are constant at $1 per hamburger.
K /L = w/v
for cost minimization. Hence, relative input usage is determined by relative input prices.
a. Suppose both wages and grill rents rise to $10 per hour. How would this affect the firm s expansion path? How would long-run average and marginal cost be affected? What can you conclude about the effect of uniform inflation of input costs on the costs of hamburger pro-duction?
b. Suppose wages rise to $20 but grill rents stay fixed at $5. How would this affect the firm s expansion path? How would this affect the long-run average and marginal cost of hamburger production? Why does a multiplication of the wage by four result in a much smaller increase in average costs?
c. In the numerical example in Chapter 6, we explored the consequences of technical progress in hamburger flipping. Specifically, we assumed that the hamburger production function shifted for
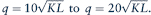 How would this shift offset the cost increases in part a? That is, what cost curves are implied by this new production function with v = w = 10? How do these compare with the original curves shown in Figure?
How would this shift offset the cost increases in part a? That is, what cost curves are implied by this new production function with v = w = 10? How do these compare with the original curves shown in Figure?d. Answer part c with the input costs in part b of this problem (v = 5, w = 20). What do you conclude about the ability of technical progress to offset rising input costs?
Figure Total, Average, and Marginal Cost Curves

The total cost curve is simply a straight line through the origin reflecting constant returns to scale. Long-run average and marginal costs are constant at $1 per hamburger.
Explanation
In this problem, the expansion path is g...
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



