
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022 Exercise 13
Robinson Crusoe obtains utility from the quantity of fish he consumes in one day (F), the quantity of coconuts he consumes that day (C), and the hours of leisure time he has during the day (H) according to the utility function:
Utility = F 1/4 C 1/4 H 1/2
Robinson's production of fish is given by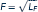
(where LF is the hours he spends fishing), and his production of coconuts is determined by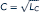
(where LC is the time he spends picking coconuts). Assuming that Robinson decides to work an eight-hour day (that is, H = 16), graph his production possibility curve for fish and coconuts. Show his optimal choices of those goods.
Utility = F 1/4 C 1/4 H 1/2
Robinson's production of fish is given by
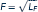
(where LF is the hours he spends fishing), and his production of coconuts is determined by
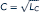
(where LC is the time he spends picking coconuts). Assuming that Robinson decides to work an eight-hour day (that is, H = 16), graph his production possibility curve for fish and coconuts. Show his optimal choices of those goods.
Explanation
Robinson's production function is given ...
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



