
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022 Exercise 23
In the country of Ruritania there are two regions, A and B. Two goods (X and Y) are produced in both regions. Production functions for region A are given by 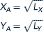
LX and LY are the quantity of labor devoted to X and Y production, respectively. Total labor available in region A is 100 units. That is,
Lx + Ly = 100
Using a similar notation for region B, production functions are given by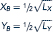
There are also 100 units of labor available in region B: Lx + Ly = 100
a. Calculate the production possibility curves for regions A and B.
b. What condition must hold if production in Ruritania is to be allocated efficiently between regions A and B (assuming that labor cannot move from one region to the other)?
c. Calculate the production possibility curve for Ruritania (again assuming that labor is immobile between regions). How much total Y can Ruritania produce if total X output is 12? (Hint: A graphic analysis may be of some help here.)d. Without making any explicit calculations, explain how you might develop a production possibility frontier for this whole country.
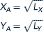
LX and LY are the quantity of labor devoted to X and Y production, respectively. Total labor available in region A is 100 units. That is,
Lx + Ly = 100
Using a similar notation for region B, production functions are given by
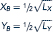
There are also 100 units of labor available in region B: Lx + Ly = 100
a. Calculate the production possibility curves for regions A and B.
b. What condition must hold if production in Ruritania is to be allocated efficiently between regions A and B (assuming that labor cannot move from one region to the other)?
c. Calculate the production possibility curve for Ruritania (again assuming that labor is immobile between regions). How much total Y can Ruritania produce if total X output is 12? (Hint: A graphic analysis may be of some help here.)d. Without making any explicit calculations, explain how you might develop a production possibility frontier for this whole country.
Explanation
The production possibility frontier (PPF...
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



