
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022 Exercise 2
Consider the example of the Stackelberg model discussed in the text. Firms choose quantities, with firm A moving first, and then firm B. As in the text, market demand is given by
Q = 120 - P
and production is costless.
a. Recall that firm B's best-response function is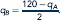
Substitute this best-response function into the equation for A's profit, (Equation), to express A's profit as a function of qA, labeled pA. Next, substitute this best-response function into the analogous equation for B's profit to compute B's profit as a function of qA, labeled pB. Finally, write the expression for A's profit if B produces zero as a function of qA, labeled pM (where the M subscript stands for the fact that A is a monopoly if B produces zero).
b. Use the formulae from part a to fill in the following table. c. Does your table from part b confirm the result from the text that firm A would choose qA = 60 in the Stackelberg game? How much would A have to produce to deter B's entry if B had a fixed cost of entry equal to a bit more than 400? If B had a fixed cost of entry a bit more than 100? Would it be worthwhile for A to deter B's entry in these cases?
c. Does your table from part b confirm the result from the text that firm A would choose qA = 60 in the Stackelberg game? How much would A have to produce to deter B's entry if B had a fixed cost of entry equal to a bit more than 400? If B had a fixed cost of entry a bit more than 100? Would it be worthwhile for A to deter B's entry in these cases? 
Q = 120 - P
and production is costless.
a. Recall that firm B's best-response function is
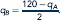
Substitute this best-response function into the equation for A's profit, (Equation), to express A's profit as a function of qA, labeled pA. Next, substitute this best-response function into the analogous equation for B's profit to compute B's profit as a function of qA, labeled pB. Finally, write the expression for A's profit if B produces zero as a function of qA, labeled pM (where the M subscript stands for the fact that A is a monopoly if B produces zero).
b. Use the formulae from part a to fill in the following table.
 c. Does your table from part b confirm the result from the text that firm A would choose qA = 60 in the Stackelberg game? How much would A have to produce to deter B's entry if B had a fixed cost of entry equal to a bit more than 400? If B had a fixed cost of entry a bit more than 100? Would it be worthwhile for A to deter B's entry in these cases?
c. Does your table from part b confirm the result from the text that firm A would choose qA = 60 in the Stackelberg game? How much would A have to produce to deter B's entry if B had a fixed cost of entry equal to a bit more than 400? If B had a fixed cost of entry a bit more than 100? Would it be worthwhile for A to deter B's entry in these cases? 
Explanation
a) The market demand is or
…… (1)where...
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



