
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022 Exercise 20
The text mentioned a model of predatory pricing in which an incumbent tries to ''beat up'' a rival, exhausting the resources the rival needs to continue operating in the market, causing it to exit. Consider a specific example of this sort of model given by the extensive form in Figure. As the figure shows, there are three possible outcomes. If the entrant E does not enter, leaving the incumbent I to operate alone, the incumbent earns 3,600. If the entrant spends fixed entry cost K 1,600 and is not preyed upon, each firm earns 1,600 (not including the entry cost). If the entrant comes in and the incumbent preys upon the entrant, it can exhaust the entrant's resources and force it to exit the industry. The period of predation costs the 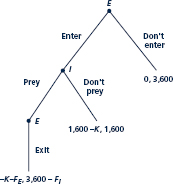
entrant FE and the incumbent F/ (where F stands for ''fighting''). Compute the subgame-perfect equilibrium for F/ 2,000 and for F/ 2,000. Is predation ever observed in equilibrium? Would a law prohibiting predation affect the equilibrium?

entrant FE and the incumbent F/ (where F stands for ''fighting''). Compute the subgame-perfect equilibrium for F/ 2,000 and for F/ 2,000. Is predation ever observed in equilibrium? Would a law prohibiting predation affect the equilibrium?
Explanation
Predatory pricing includes the process i...
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



