
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022 Exercise 26
In Figure, the demand curve facing a firm in a monopolistically competitive industry is shown as being tangent to its average cost curve at q'. Explain why this is a long-run equilibrium position for this firm. That is, why does marginal revenue equal marginal cost, and why are longrun profits zero? 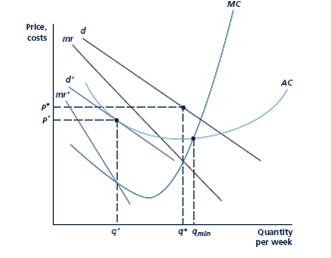
Initially the demand curve facing the firm is d. Marginal revenue is given by mr, and q* is the profit-maximizing output level. If entry is costless, new firms ttracted by the possibility for profits may shift the firm's demand curve inward to d0, where profits are zero. Output level q0 is below the level qmin, where average costs reach a minimum. The firm xhibits excess capacity, given by qmin _ q0.

Initially the demand curve facing the firm is d. Marginal revenue is given by mr, and q* is the profit-maximizing output level. If entry is costless, new firms ttracted by the possibility for profits may shift the firm's demand curve inward to d0, where profits are zero. Output level q0 is below the level qmin, where average costs reach a minimum. The firm xhibits excess capacity, given by qmin _ q0.
Explanation
In this case, the given point is the poi...
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



