
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022 Exercise 31
A salesperson has a utility function for earnings of the form 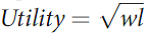 where w is the hourly wage received and l is the number of hours worked in a typical day. This person is choosing between two jobs. The first promises a constant workday of 8 hours per day and an hourly wage of $50 per hour. The second offers a random workday in which he or she sometimes gets only 4 hours of work, whereas other times he or she gets 12 hours of work.
where w is the hourly wage received and l is the number of hours worked in a typical day. This person is choosing between two jobs. The first promises a constant workday of 8 hours per day and an hourly wage of $50 per hour. The second offers a random workday in which he or she sometimes gets only 4 hours of work, whereas other times he or she gets 12 hours of work.
a. If the probability of 4 hour days is 0.5 (and the probability of 12 hour days is also 0:5), how high must the hourly wage rate be on the risky job to get this person to take it?
b. Assuming that the wage for the risky job is that described in part a, will a proportional tax on daily earnings affect this person's choice of job?
c. How would your answer to part b change if daily earnings were subject to a progressive tax rate in which the first $300 of daily earnings is not taxed and daily earnings over $300 are taxed at a rate of 50 percent?
d. What proportional tax rate would yield the same tax revenue as the progressive tax, but not affect this person's choices among jobs?
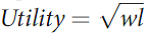 where w is the hourly wage received and l is the number of hours worked in a typical day. This person is choosing between two jobs. The first promises a constant workday of 8 hours per day and an hourly wage of $50 per hour. The second offers a random workday in which he or she sometimes gets only 4 hours of work, whereas other times he or she gets 12 hours of work.
where w is the hourly wage received and l is the number of hours worked in a typical day. This person is choosing between two jobs. The first promises a constant workday of 8 hours per day and an hourly wage of $50 per hour. The second offers a random workday in which he or she sometimes gets only 4 hours of work, whereas other times he or she gets 12 hours of work. a. If the probability of 4 hour days is 0.5 (and the probability of 12 hour days is also 0:5), how high must the hourly wage rate be on the risky job to get this person to take it?
b. Assuming that the wage for the risky job is that described in part a, will a proportional tax on daily earnings affect this person's choice of job?
c. How would your answer to part b change if daily earnings were subject to a progressive tax rate in which the first $300 of daily earnings is not taxed and daily earnings over $300 are taxed at a rate of 50 percent?
d. What proportional tax rate would yield the same tax revenue as the progressive tax, but not affect this person's choices among jobs?
Explanation

This question doesn’t have an expert verified answer yet, let Quizplus AI Copilot help.
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



