
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Edition 12ISBN: 978-1133189022 Exercise 18
Ben assembles units of the iSpy, a surveillance device remotely controlled from an app on customers' mobile phones. By exerting effort E, he produces 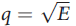 devices, implying that the marginal product of his effort is
devices, implying that the marginal product of his effort is 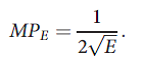
The iSpy sells for $100 each. Ben's marginal cost of a unit of effort is $1. His manager, Sarah, considers three different incentive schemes she might offer him:
• Scheme 1 pays him a constant $750.
• Scheme 2 pays him $500 plus a 40% share of the revenue from sales of the iSpys he assembles that week.
• Scheme 3 gives him a 60% share of the revenue from sales of the iSpys he assembles but no fixed compensation.
Complete the following tasks for each incentive scheme.
a. Represent each incentive contract on the same graph, with quantity (non-defective units per week) on the horizontal axis and pay (dollars per week) on the vertical axis as in Figure 15.2.
b. Determine how many iSpys Ben assembles under each scheme.
c. Determine which scheme Sarah should offer him.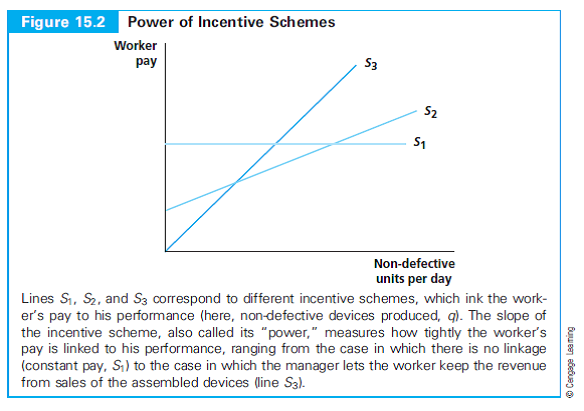
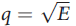 devices, implying that the marginal product of his effort is
devices, implying that the marginal product of his effort is 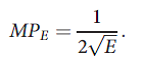
The iSpy sells for $100 each. Ben's marginal cost of a unit of effort is $1. His manager, Sarah, considers three different incentive schemes she might offer him:
• Scheme 1 pays him a constant $750.
• Scheme 2 pays him $500 plus a 40% share of the revenue from sales of the iSpys he assembles that week.
• Scheme 3 gives him a 60% share of the revenue from sales of the iSpys he assembles but no fixed compensation.
Complete the following tasks for each incentive scheme.
a. Represent each incentive contract on the same graph, with quantity (non-defective units per week) on the horizontal axis and pay (dollars per week) on the vertical axis as in Figure 15.2.
b. Determine how many iSpys Ben assembles under each scheme.
c. Determine which scheme Sarah should offer him.

Explanation
a)The three incentive schemes can be gra...
Intermediate Microeconomics and Its Application 12th Edition by Walter Nicholson,Christopher Snyder
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



