
Business Law with UCC Applications 13th Edition by Gordon Brown,Paul Sukys
Edition 13ISBN: 978-0073524955
Business Law with UCC Applications 13th Edition by Gordon Brown,Paul Sukys
Edition 13ISBN: 978-0073524955 Exercise 2
What are the differences among positive law, natural law, and negative rights?
Explanation
Positive Law:
Positive Law is one which believes that the emergence of law is a result of the social institutions which took birth from the society. For example, Positive Law argues that people living communally in society need a set of rules to govern themselves so that all the people's rights are protected equally. They create a set of rules documented in a way to protect their rights equally.
Natural Law :
Natural Law argues that there exists a strong connection between law and that of morality. Natural law theories argue that a law without any morality cannot be termed as a law. For example, if a law is made saying that every driver should also own a car is morally incorrect. Thus, it cannot be made into a law, according to Natural law.
Negative Rights:
The Negative rights theory argues against people having rights. It argues that rights are used by people to defend themselves against the law. For example, the theory argues that the right of freedom to speak will provide people the opportunity to lie and help them in proving the lies as right.
Differences between Natural law, Positive Law and negative rights:
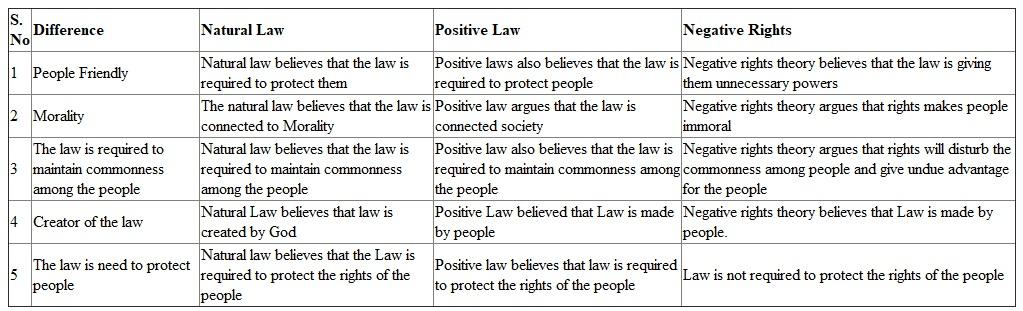 These are the various differences between Natural Law, Positive Law and Negative rights.
These are the various differences between Natural Law, Positive Law and Negative rights.
Positive Law is one which believes that the emergence of law is a result of the social institutions which took birth from the society. For example, Positive Law argues that people living communally in society need a set of rules to govern themselves so that all the people's rights are protected equally. They create a set of rules documented in a way to protect their rights equally.
Natural Law :
Natural Law argues that there exists a strong connection between law and that of morality. Natural law theories argue that a law without any morality cannot be termed as a law. For example, if a law is made saying that every driver should also own a car is morally incorrect. Thus, it cannot be made into a law, according to Natural law.
Negative Rights:
The Negative rights theory argues against people having rights. It argues that rights are used by people to defend themselves against the law. For example, the theory argues that the right of freedom to speak will provide people the opportunity to lie and help them in proving the lies as right.
Differences between Natural law, Positive Law and negative rights:
 These are the various differences between Natural Law, Positive Law and Negative rights.
These are the various differences between Natural Law, Positive Law and Negative rights.Business Law with UCC Applications 13th Edition by Gordon Brown,Paul Sukys
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



