
Introduction to Flight 7th Edition by John Anderson
Edition 7ISBN: 978-0073380247
Introduction to Flight 7th Edition by John Anderson
Edition 7ISBN: 978-0073380247 Exercise 1
Consider the low-speed flight of the Space Shuttle as it is nearing a landing. If the air pressure and temperature at the nose of the shuttle are 1.2 atm and 300 K, respectively, what are the density and specific volume?
Explanation
Air is an ideal gas and for an ideal gas, the characteristic equation is given by the expression:
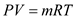 Here, P is the pressure, V is the volume, m is the mass, R is the characteristic gas constant and T is the absolute temperature.
Here, P is the pressure, V is the volume, m is the mass, R is the characteristic gas constant and T is the absolute temperature.
The density,
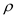 , of any fluid is given by the equation:
, of any fluid is given by the equation:
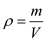 Rearrange the characteristic equation:
Rearrange the characteristic equation:
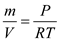 Therefore, the density of the air is:
Therefore, the density of the air is:
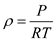 Convert the units of pressure into MKS system:
Convert the units of pressure into MKS system:
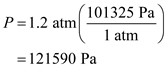 Substitute,
Substitute,
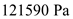 for P ,
for P ,
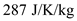 for R and
for R and
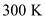 for T ,
for T ,
 Hence, the density of air is
Hence, the density of air is
 .
.
The specific volume, v, of the air is given as:
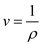 Substitute
Substitute
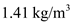 for
for
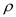 .
.
 Hence, the specific volume of air is
Hence, the specific volume of air is
 .
.
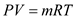 Here, P is the pressure, V is the volume, m is the mass, R is the characteristic gas constant and T is the absolute temperature.
Here, P is the pressure, V is the volume, m is the mass, R is the characteristic gas constant and T is the absolute temperature.The density,
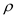 , of any fluid is given by the equation:
, of any fluid is given by the equation: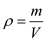 Rearrange the characteristic equation:
Rearrange the characteristic equation: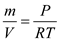 Therefore, the density of the air is:
Therefore, the density of the air is: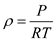 Convert the units of pressure into MKS system:
Convert the units of pressure into MKS system: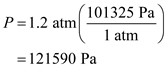 Substitute,
Substitute, 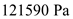 for P ,
for P , 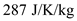 for R and
for R and 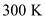 for T ,
for T , Hence, the density of air is
Hence, the density of air is  .
.The specific volume, v, of the air is given as:
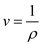 Substitute
Substitute 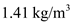 for
for 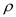 .
. Hence, the specific volume of air is
Hence, the specific volume of air is  .
.Introduction to Flight 7th Edition by John Anderson
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



