
Introduction to Flight 7th Edition by John Anderson
Edition 7ISBN: 978-0073380247
Introduction to Flight 7th Edition by John Anderson
Edition 7ISBN: 978-0073380247 Exercise 2
Consider 1 kg of helium at 500 K. Assuming that the total internal energy of helium is due to the mean kinetic energy of each atom summed over all the atoms, calculate the internal energy of this gas. Note: The molecular weight of helium is 4. Recall from chemistry that the molecular weight is the mass per mole of gas; that is, 1 mol of helium contains 4 kg of mass. Also. 1 mol of any gas contains 6.02 × 10 23 molecules or atoms (Avogadro's number).
Explanation
The mean kinetic energy of each atom is,
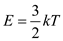 Here, k is the bellman constant and T is the temperature.
Here, k is the bellman constant and T is the temperature.
Substitute
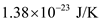 for k and 500 K for T in
for k and 500 K for T in
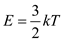 .
.
 Given that,
Given that,
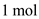 of helium contains 4 kg of mass and
of helium contains 4 kg of mass and
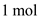 of helium gas contains
of helium gas contains
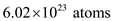 . So, 1 kg of helium gas contains one fourth of atoms. So, the number of atoms in 1 kg of helium gas is,
. So, 1 kg of helium gas contains one fourth of atoms. So, the number of atoms in 1 kg of helium gas is,
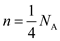 Here,
Here,
 is the Avogadro's number.
is the Avogadro's number.
Substitute
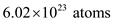 for
for
 .
.
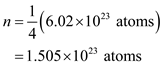 Total internal emery is,
Total internal emery is,
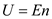 Substitute
Substitute
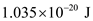 for E and
for E and
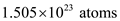 for n.
for n.
 Hence, the internal energy is
Hence, the internal energy is
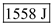 .
.
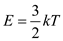 Here, k is the bellman constant and T is the temperature.
Here, k is the bellman constant and T is the temperature.Substitute
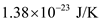 for k and 500 K for T in
for k and 500 K for T in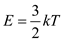 .
.  Given that,
Given that, 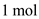 of helium contains 4 kg of mass and
of helium contains 4 kg of mass and 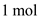 of helium gas contains
of helium gas contains 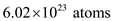 . So, 1 kg of helium gas contains one fourth of atoms. So, the number of atoms in 1 kg of helium gas is,
. So, 1 kg of helium gas contains one fourth of atoms. So, the number of atoms in 1 kg of helium gas is,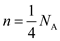 Here,
Here,  is the Avogadro's number.
is the Avogadro's number.Substitute
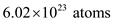 for
for  .
. 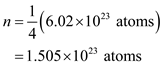 Total internal emery is,
Total internal emery is,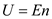 Substitute
Substitute 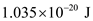 for E and
for E and 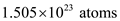 for n.
for n.  Hence, the internal energy is
Hence, the internal energy is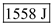 .
.Introduction to Flight 7th Edition by John Anderson
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



