
Cornerstones of Cost Accounting 1st Edition by Don Hansen,Maryanne Mowen
Edition 1ISBN: 978-0538736787
Cornerstones of Cost Accounting 1st Edition by Don Hansen,Maryanne Mowen
Edition 1ISBN: 978-0538736787 Exercise 23
JOB COSTS USING ACTIVITY-BASED COSTING
Prentice Company is a job-order costing firm that uses activity-based costing to apply overhead to jobs. Prentice identified three overhead activities and related drivers. Budgeted information for the year is as follows:

Prentice worked on four jobs in July. Data are as follows:
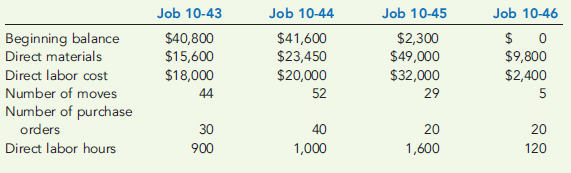
By July 31, Jobs 10-43 and 10-44 were completed and sold. Job 10-45 was completed but not sold. The remaining job was in process.
Required:
1. Calculate the activity rates for each of the three overhead activities.
2. Prepare job-order cost sheets for each job showing all costs through July 31.
3. Calculate the balance in Work in Process on July 31.
4. Calculate cost of goods sold for July.
5. What if Job 10-46 required no moves? What is the new cost of Job 10-46? How would the cost of the other jobs be affected?
Prentice Company is a job-order costing firm that uses activity-based costing to apply overhead to jobs. Prentice identified three overhead activities and related drivers. Budgeted information for the year is as follows:

Prentice worked on four jobs in July. Data are as follows:

By July 31, Jobs 10-43 and 10-44 were completed and sold. Job 10-45 was completed but not sold. The remaining job was in process.
Required:
1. Calculate the activity rates for each of the three overhead activities.
2. Prepare job-order cost sheets for each job showing all costs through July 31.
3. Calculate the balance in Work in Process on July 31.
4. Calculate cost of goods sold for July.
5. What if Job 10-46 required no moves? What is the new cost of Job 10-46? How would the cost of the other jobs be affected?
Explanation
We are given the overhead activities and...
Cornerstones of Cost Accounting 1st Edition by Don Hansen,Maryanne Mowen
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



