
International Economics 8th Edition by Dennis Appleyard, Alfred Field
Edition 8ISBN: 9780078021671
International Economics 8th Edition by Dennis Appleyard, Alfred Field
Edition 8ISBN: 9780078021671 Exercise 3
Suppose that in Figure a terms-of-trade line TOT 2 appears that is steeper than TOT E. In terms of excess supply and excess demand, explain why the terms of trade will fall from TOT 2 to TOT E.
FIGURE Trading Equilibrium
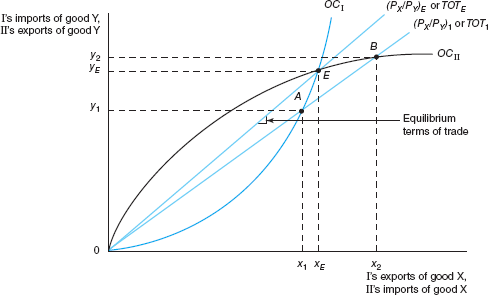
Relative prices ( P X / P Y ) E (or terms of trade TOT E ) are market-clearing prices since the quantity of good X (0 x E ) that country I wishes to export equals the quantity of good X that country II wishes to import and the quantity of good Y that country I wishes to import (0 y E ) equals the quantity of good Y that country II wishes to export. Thus, point E is the trading equilibrium position, and the equilibrium terms of trade are equal to the slope of the ray from the origin through point E. If relative prices ( P X / P Y ) 1 or TOT 1 prevailed in the market instead of ( P X / P Y ) E or TOT E , there would be excess demand for good X of amount x 1 x 2 and excess supply of good Y of amount y 1 y 2. Therefore, ( P X / P Y ) 1 or TOT 1 would rise until the excess demand and excess supply were eliminated at ( P X / P Y ) E or TOT E.
FIGURE Trading Equilibrium

Relative prices ( P X / P Y ) E (or terms of trade TOT E ) are market-clearing prices since the quantity of good X (0 x E ) that country I wishes to export equals the quantity of good X that country II wishes to import and the quantity of good Y that country I wishes to import (0 y E ) equals the quantity of good Y that country II wishes to export. Thus, point E is the trading equilibrium position, and the equilibrium terms of trade are equal to the slope of the ray from the origin through point E. If relative prices ( P X / P Y ) 1 or TOT 1 prevailed in the market instead of ( P X / P Y ) E or TOT E , there would be excess demand for good X of amount x 1 x 2 and excess supply of good Y of amount y 1 y 2. Therefore, ( P X / P Y ) 1 or TOT 1 would rise until the excess demand and excess supply were eliminated at ( P X / P Y ) E or TOT E.
Explanation
Terms of trade shows a ratio in between ...
International Economics 8th Edition by Dennis Appleyard, Alfred Field
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



