
Accounting for Decision Making and Control 6th Edition by Jerold Zimmerman
Edition 6ISBN: 9780071283700
Accounting for Decision Making and Control 6th Edition by Jerold Zimmerman
Edition 6ISBN: 9780071283700 Exercise 27
Carlos Sanguine Winery
Carlos Sanguine, Inc., makes premium wines and table wines. Grapes are crushed and the freeflowing juice and the first-processing juice are made into premium wines (bottles with corks). The second- and third-processing juices are made into table wines (bottles with screw tops).
Table 1 summarizes operations for the year, and Table 2 breaks down manufacturing overhead expenses into general winery costs and production facilities costs.
T ABLE 1 Summary of Operations for the Year
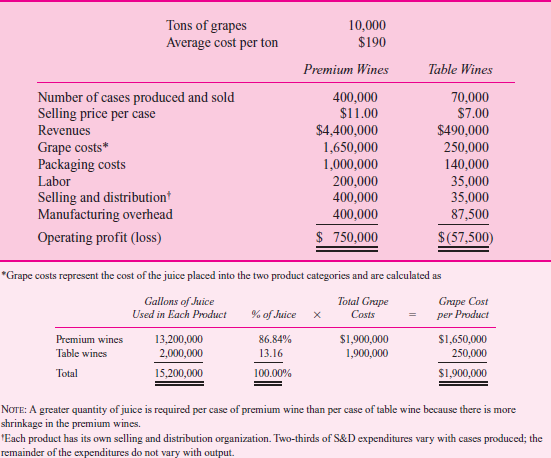
T ABLE 2 Manufacturing Overhead by Products
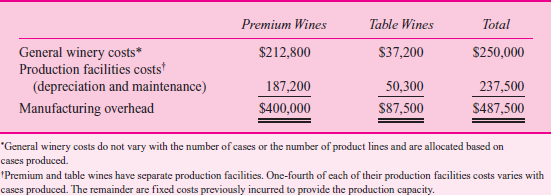
T ABLE 3 Product Line Cost Structure per Case
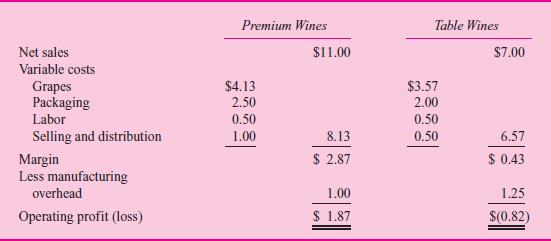
Based on Tables 1 and 2, the accounting department prepared the report in Table 3. Management is concerned that the table wines have such a low margin. Some of the managers urge that these lines be dropped. Competition keeps the price down to $7 per case, which causes some managers to question how the competition could afford to sell the wine at this price.
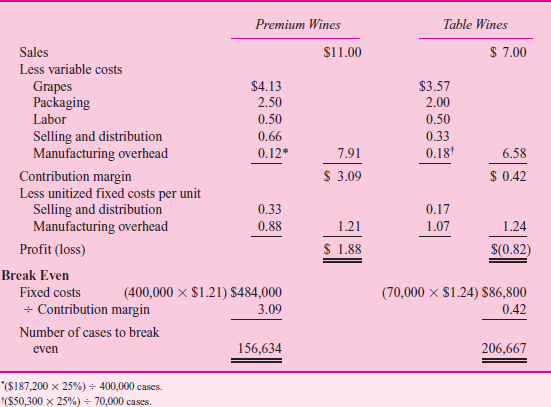
Before making a final decision, top management asked for an analysis of the fixed and variable costs by product line and their break-even points. When management saw Table 4, the president remarked, "Well, this is the final nail in the coffin. We'd have to almost triple our sales of table wines just to break even. But we don't have that kind of capacity. We'd have to buy new tanks, thereby driving up our fixed costs and break-even points. This looks like a vicious circle. By next month, I want a detailed set of plans on what it'll cost us to shut down our table wines." Table 5 summarizes the shutdown effects.
Based on the facts presented in the case, what should management do
T ABLE 4 Fixed and Variable Costs per Product and Product Break-Even Points
T ABLE 5 Effects of Discontinuing Table Wines

Carlos Sanguine, Inc., makes premium wines and table wines. Grapes are crushed and the freeflowing juice and the first-processing juice are made into premium wines (bottles with corks). The second- and third-processing juices are made into table wines (bottles with screw tops).
Table 1 summarizes operations for the year, and Table 2 breaks down manufacturing overhead expenses into general winery costs and production facilities costs.
T ABLE 1 Summary of Operations for the Year

T ABLE 2 Manufacturing Overhead by Products

T ABLE 3 Product Line Cost Structure per Case

Based on Tables 1 and 2, the accounting department prepared the report in Table 3. Management is concerned that the table wines have such a low margin. Some of the managers urge that these lines be dropped. Competition keeps the price down to $7 per case, which causes some managers to question how the competition could afford to sell the wine at this price.
Before making a final decision, top management asked for an analysis of the fixed and variable costs by product line and their break-even points. When management saw Table 4, the president remarked, "Well, this is the final nail in the coffin. We'd have to almost triple our sales of table wines just to break even. But we don't have that kind of capacity. We'd have to buy new tanks, thereby driving up our fixed costs and break-even points. This looks like a vicious circle. By next month, I want a detailed set of plans on what it'll cost us to shut down our table wines." Table 5 summarizes the shutdown effects.
Based on the facts presented in the case, what should management do
T ABLE 4 Fixed and Variable Costs per Product and Product Break-Even Points

T ABLE 5 Effects of Discontinuing Table Wines

Explanation
The company in question is producing two...
Accounting for Decision Making and Control 6th Edition by Jerold Zimmerman
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



