
Introduction to Econometrics 3rd Edition by James Stock, Mark Watson
Edition 3ISBN: 978-9352863501
Introduction to Econometrics 3rd Edition by James Stock, Mark Watson
Edition 3ISBN: 978-9352863501 Exercise 3
Using the data in Exercise:
a. Construct a 95 % confidence interval for p.
b. Construct a 99% confidence interval for p.
c. Why is the interval in (b) wider than the interval in (a)
d. Without doing any additional calculations, test the hypothesis H 0 : p = 0.50 vs. H 1 : p 0.50 at the 5% significance level.
Exercise
In a survey of 400 likely voters, 215 responded that they would vote for the incumbent and 185 responded that they would vote for the challenger. Let p denote the fraction of all likely voters who preferred the incumbent at the time of the survey, and let
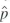 be the fraction of survey respondents who preferred the incumbent.
be the fraction of survey respondents who preferred the incumbent.
a. Use the survey results to estimate p.
b. Use the estimator of the variance of
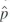 ,
,
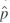 ( 1 -
( 1 -
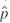 )/n, to calculate the standard error of your estimator.
)/n, to calculate the standard error of your estimator.
c. What is the p-value for the test H 0 : p = 0.5 vs. H 1. p 0.5
d. What is the p-value for the test H 0 : p = 0.5 vs. H 1. p 0.5
e. Why do the results from (c) and (d) differ
f. Did the survey contain statistically significant evidence that the incumbent was ahead of the challenger at the time of the survey Explain.
a. Construct a 95 % confidence interval for p.
b. Construct a 99% confidence interval for p.
c. Why is the interval in (b) wider than the interval in (a)
d. Without doing any additional calculations, test the hypothesis H 0 : p = 0.50 vs. H 1 : p 0.50 at the 5% significance level.
Exercise
In a survey of 400 likely voters, 215 responded that they would vote for the incumbent and 185 responded that they would vote for the challenger. Let p denote the fraction of all likely voters who preferred the incumbent at the time of the survey, and let
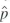 be the fraction of survey respondents who preferred the incumbent.
be the fraction of survey respondents who preferred the incumbent.a. Use the survey results to estimate p.
b. Use the estimator of the variance of
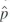 ,
,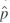 ( 1 -
( 1 - 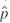 )/n, to calculate the standard error of your estimator.
)/n, to calculate the standard error of your estimator.c. What is the p-value for the test H 0 : p = 0.5 vs. H 1. p 0.5
d. What is the p-value for the test H 0 : p = 0.5 vs. H 1. p 0.5
e. Why do the results from (c) and (d) differ
f. Did the survey contain statistically significant evidence that the incumbent was ahead of the challenger at the time of the survey Explain.
Explanation
Based on the following information, we a...
Introduction to Econometrics 3rd Edition by James Stock, Mark Watson
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



