
The Essentials Of Computer Organization And Architecture 4th Edition by Linda Null,Julia Lobur
Edition 4ISBN: 978-1284074482
The Essentials Of Computer Organization And Architecture 4th Edition by Linda Null,Julia Lobur
Edition 4ISBN: 978-1284074482 Exercise 25
Consider a 32-bit hexadecimal number stored in memory as follows: 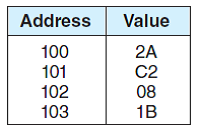
a) If the machine is big endian and uses two's complement representation for integers, write the 32-bit integer number stored at address 100 (you may write the number in hex).
b) If the machine is big endian and the number is an IEEE single-precision floating point value, is the number positive or negative?
c) If the machine is big endian and the number is an IEEE single-precision floating-point value, determine the decimal equivalent of the number stored at address 100 (you may leave your answer in scientific notation form, as a number times a power of two).
d) If the machine is little endian and uses two's complement representation for integers, write the 32-bit integer number stored at address 100 (you may write the number in hex).
e) If the machine is little endian and the number is an IEEE single-precision floating point value, is the number positive or negative?
f) If the machine is little endian and the number is an IEEE single-precision floating point value, determine the decimal equivalent of the number stored at address 100 (you may leave your answer in scientific notation form, as a number times a power of two).

a) If the machine is big endian and uses two's complement representation for integers, write the 32-bit integer number stored at address 100 (you may write the number in hex).
b) If the machine is big endian and the number is an IEEE single-precision floating point value, is the number positive or negative?
c) If the machine is big endian and the number is an IEEE single-precision floating-point value, determine the decimal equivalent of the number stored at address 100 (you may leave your answer in scientific notation form, as a number times a power of two).
d) If the machine is little endian and uses two's complement representation for integers, write the 32-bit integer number stored at address 100 (you may write the number in hex).
e) If the machine is little endian and the number is an IEEE single-precision floating point value, is the number positive or negative?
f) If the machine is little endian and the number is an IEEE single-precision floating point value, determine the decimal equivalent of the number stored at address 100 (you may leave your answer in scientific notation form, as a number times a power of two).
Explanation
Problem to transfer data from big endian...
The Essentials Of Computer Organization And Architecture 4th Edition by Linda Null,Julia Lobur
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



