
Introduction to Econometrics 3rd Edition by James Stock, James Stock
Edition 3ISBN: 978-9352863501
Introduction to Econometrics 3rd Edition by James Stock, James Stock
Edition 3ISBN: 978-9352863501 Exercise 3
On the textbook Web site Mww.pearsonhighered.coni/stock_watson, you will find a data file USMacro_Quarterly that contains quarterly data on several macroeconomic series for the United States; the data are described in the file USMacro_Description. Compute Y t = ln( GDP t ; ) , the logarithm of real GDP, and Y t the quarterly growth rate of GDP. In Empirical Exercises 14.1 through 14.6, use the sample period 1955:1-2009:4 (where data before 1955 may be used, as necessary, as initial values for lags in regressions).
a. Construct pseudo out-of-sample forecasts using the AR(1) model beginning in 1989:4 and going through the end of the sample. (That is, compute 1990:1|1989:4,
1990:1|1989:4,  1990:2|1990:1) and so forth.)
1990:2|1990:1) and so forth.)
b. Construct pseudo out-of-sample forecasts using the ADL(1,4) model.
c. Construct pseudo out-of-sample using the following "naive" model: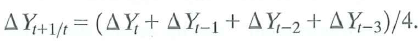
d. Compute the pseudo out-of-sample forecast errors for each model. Are any of the forecasts biased Which model has the smallest root mean squared forecast error (RMSFE) How large is the RMSFE (expressed in percentage points at an annual rate) for the best model
a. Construct pseudo out-of-sample forecasts using the AR(1) model beginning in 1989:4 and going through the end of the sample. (That is, compute
 1990:1|1989:4,
1990:1|1989:4,  1990:2|1990:1) and so forth.)
1990:2|1990:1) and so forth.)b. Construct pseudo out-of-sample forecasts using the ADL(1,4) model.
c. Construct pseudo out-of-sample using the following "naive" model:
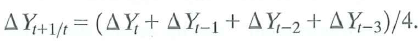
d. Compute the pseudo out-of-sample forecast errors for each model. Are any of the forecasts biased Which model has the smallest root mean squared forecast error (RMSFE) How large is the RMSFE (expressed in percentage points at an annual rate) for the best model
Explanation

This question doesn’t have an expert verified answer yet, let Quizplus AI Copilot help.
Introduction to Econometrics 3rd Edition by James Stock, James Stock
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



