
Introductory Econometrics 4th Edition by Jeffrey Wooldridge
Edition 4ISBN: 978-0324660609
Introductory Econometrics 4th Edition by Jeffrey Wooldridge
Edition 4ISBN: 978-0324660609 Exercise 3
Let 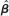 be the OLS estimate from the regression of y on X. Let A be a (k + 1) × (k + 1) nonsingular matrix and define zt = xtA, t = 1,….,n. Therefore, zt is 1 × (k + 1) and is a nonsingular linear combination of xt. Let Z be the n × (k + 1) matrix with rows zt. Let
be the OLS estimate from the regression of y on X. Let A be a (k + 1) × (k + 1) nonsingular matrix and define zt = xtA, t = 1,….,n. Therefore, zt is 1 × (k + 1) and is a nonsingular linear combination of xt. Let Z be the n × (k + 1) matrix with rows zt. Let 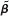 denote the OLS estimate from a regression of y on Z.
denote the OLS estimate from a regression of y on Z.
(i) Show that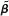 =A-1
=A-1 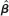 .
.
(ii) L et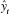 be the fitted values from the original regression and let. y t be the fitted values from regressing y on Z. Show that
be the fitted values from the original regression and let. y t be the fitted values from regressing y on Z. Show that 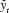 =
= 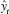 , for all t =- 1, 2,…., n. How do the residuals from the two regressions compare
, for all t =- 1, 2,…., n. How do the residuals from the two regressions compare
(iii) Show that the estimated variance matrix for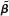 is
is 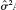 A1(X X)1A1 , where
A1(X X)1A1 , where 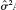 is the usual variance estimate from regressing y on X.
is the usual variance estimate from regressing y on X.
(iv) L et the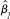 be the OLS estimates from regressing yt on 1, xt1,...,xtk, and let the
be the OLS estimates from regressing yt on 1, xt1,...,xtk, and let the 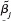 be the OLS estimates from the regression of yt on 1, a1xt1,…,ak xtk, where aj 0, j =1,…,k. Use the results from part (i) to find the relationship between the
be the OLS estimates from the regression of yt on 1, a1xt1,…,ak xtk, where aj 0, j =1,…,k. Use the results from part (i) to find the relationship between the 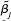 and the
and the 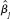
(v) Assuming the setup of part (iv), use part (iii) to show that se(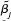 ) = se(
) = se( 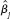 )/aj.
)/aj.
(vi) Assuming the setup of part (iv), show that the absolute values of the t statistics for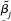 and
and 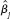 are identical.
are identical.
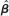 be the OLS estimate from the regression of y on X. Let A be a (k + 1) × (k + 1) nonsingular matrix and define zt = xtA, t = 1,….,n. Therefore, zt is 1 × (k + 1) and is a nonsingular linear combination of xt. Let Z be the n × (k + 1) matrix with rows zt. Let
be the OLS estimate from the regression of y on X. Let A be a (k + 1) × (k + 1) nonsingular matrix and define zt = xtA, t = 1,….,n. Therefore, zt is 1 × (k + 1) and is a nonsingular linear combination of xt. Let Z be the n × (k + 1) matrix with rows zt. Let 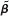 denote the OLS estimate from a regression of y on Z.
denote the OLS estimate from a regression of y on Z.(i) Show that
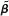 =A-1
=A-1 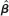 .
.(ii) L et
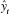 be the fitted values from the original regression and let. y t be the fitted values from regressing y on Z. Show that
be the fitted values from the original regression and let. y t be the fitted values from regressing y on Z. Show that 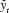 =
= 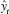 , for all t =- 1, 2,…., n. How do the residuals from the two regressions compare
, for all t =- 1, 2,…., n. How do the residuals from the two regressions compare (iii) Show that the estimated variance matrix for
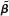 is
is 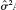 A1(X X)1A1 , where
A1(X X)1A1 , where 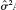 is the usual variance estimate from regressing y on X.
is the usual variance estimate from regressing y on X.(iv) L et the
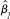 be the OLS estimates from regressing yt on 1, xt1,...,xtk, and let the
be the OLS estimates from regressing yt on 1, xt1,...,xtk, and let the 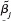 be the OLS estimates from the regression of yt on 1, a1xt1,…,ak xtk, where aj 0, j =1,…,k. Use the results from part (i) to find the relationship between the
be the OLS estimates from the regression of yt on 1, a1xt1,…,ak xtk, where aj 0, j =1,…,k. Use the results from part (i) to find the relationship between the 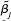 and the
and the 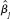
(v) Assuming the setup of part (iv), use part (iii) to show that se(
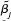 ) = se(
) = se( 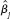 )/aj.
)/aj.(vi) Assuming the setup of part (iv), show that the absolute values of the t statistics for
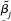 and
and 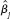 are identical.
are identical.Explanation
Given:
1) is the OLS estimate of regres...
Introductory Econometrics 4th Edition by Jeffrey Wooldridge
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



