
Introductory Econometrics 4th Edition by Jeffrey Wooldridge
Edition 4ISBN: 978-0324660609
Introductory Econometrics 4th Edition by Jeffrey Wooldridge
Edition 4ISBN: 978-0324660609 Exercise 14
Use the data in OKUN.RAW to answer this question; see also Computer Exercise.
(i) Estimate the equation pcrgdp t = 0 + 1 unem t + u t and test the errors for AR(1) serial correlation, without assuming { unemt: t = 1, 2,...} is strictly exogenous. What do you conclude
(ii) Regress the squared residuals, û 2 t , on Aunemt (this is the Breusch-Pagan test for heteroskedasticity in the simple regression case). What do you conclude
(iii) Obtain the heteroskedasticity-robust standard error for the OLS estimate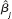 . Is it substantially different from the usual OLS standard error
. Is it substantially different from the usual OLS standard error
Exercise Okun's Law-for example, Mankiw (1994, Chapter 2)-implies the following relationship between the annual percentage change in real GDP, pcrgdp, and the change in the annual unemployment rate, unem:
pcrgdp = 3 - 2 unem.
If the unemployment rate is stable, real GDP grows at 3% annually. For each percentage point increase in the unemployment rate, real GDP grows by two percentage points less. (This should not be interpreted in any causal sense; it is more like a statistical description.)
To see if the data on the U.S. economy support Okun's Law, we specify a model that allows deviations via an error term, pcrgdp t = 0 + 1 unem t + u t.
(i) Use the data in OKUN.RAW to estimate the equation. Do you get exactly 3 for the intercept and 2 for the slope Did you expect to
(ii) Find the t statistic for testing H0: 1 = 2. Do you reject H0 against the two-sided alternative at any reasonable significance level
(iii) Find the t statistic for testing H0: 0 = 3. Do you reject H 0 at the 5% level against he two-sided alternative Is it a "strong" rejection
(iv) Find the F statistic and p-value for testing H 0 : 0 = 3, 1 = 2 against the alternative that H 0 is false. Overall, would you say the data reject or tend to support Okun's law
(i) Estimate the equation pcrgdp t = 0 + 1 unem t + u t and test the errors for AR(1) serial correlation, without assuming { unemt: t = 1, 2,...} is strictly exogenous. What do you conclude
(ii) Regress the squared residuals, û 2 t , on Aunemt (this is the Breusch-Pagan test for heteroskedasticity in the simple regression case). What do you conclude
(iii) Obtain the heteroskedasticity-robust standard error for the OLS estimate
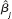 . Is it substantially different from the usual OLS standard error
. Is it substantially different from the usual OLS standard error Exercise Okun's Law-for example, Mankiw (1994, Chapter 2)-implies the following relationship between the annual percentage change in real GDP, pcrgdp, and the change in the annual unemployment rate, unem:
pcrgdp = 3 - 2 unem.
If the unemployment rate is stable, real GDP grows at 3% annually. For each percentage point increase in the unemployment rate, real GDP grows by two percentage points less. (This should not be interpreted in any causal sense; it is more like a statistical description.)
To see if the data on the U.S. economy support Okun's Law, we specify a model that allows deviations via an error term, pcrgdp t = 0 + 1 unem t + u t.
(i) Use the data in OKUN.RAW to estimate the equation. Do you get exactly 3 for the intercept and 2 for the slope Did you expect to
(ii) Find the t statistic for testing H0: 1 = 2. Do you reject H0 against the two-sided alternative at any reasonable significance level
(iii) Find the t statistic for testing H0: 0 = 3. Do you reject H 0 at the 5% level against he two-sided alternative Is it a "strong" rejection
(iv) Find the F statistic and p-value for testing H 0 : 0 = 3, 1 = 2 against the alternative that H 0 is false. Overall, would you say the data reject or tend to support Okun's law
Explanation
(i)
Estimating the equation given by: T...
Introductory Econometrics 4th Edition by Jeffrey Wooldridge
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



