
Biomedical Informatics 4th Edition by Edward Shortliffe, James Cimino
Edition 4ISBN: 9781447144748
Biomedical Informatics 4th Edition by Edward Shortliffe, James Cimino
Edition 4ISBN: 9781447144748 Exercise 1
Associate each of the following hypo thetical evaluation scenarios with one or more of the nine types of studies listed in Table 11.1 . 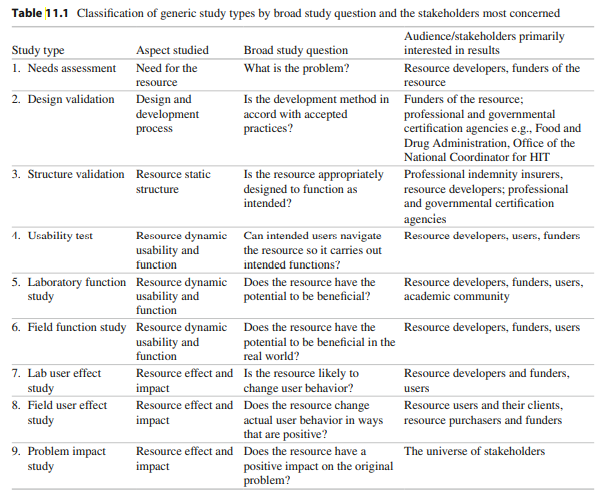 Note that some scenarios may include more than one type of study.
Note that some scenarios may include more than one type of study.
(a) An order communication system is implemented in a small hospital. Changes in laboratory workload are assessed.
(b) The developers of the order com munication system recruit fi ve potential users to help them assess how readily each of the main func tions can be accessed from the opening screen and how long it takes users to complete them.
(c) A study team performs a thorough analysis of the information required by psychiatrists to whom patients are referred by a community social worker.
(d) A biomedical informatics expert is asked for her opinion about a PhD project on a new bioinformatics algorithm. She requests copies of the student's code and documenta tion for review.
(e) A new intensive care unit system is implemented alongside manual paper charting for a month. At the end of this time, the quality of the computer-derived data and data recorded on the paper charts is com pared. A panel of intensive care experts is asked to identify, inde pendently, episodes of hypotension from each data set.
(f) A biomedical informatics professor is invited to join the steering group for a series of apps to support people living with diabetes. The only documentation available to critique at the first meeting is a statement of the project goal, description of the planned development method, and the advertisements and job descrip tions for team members.
(g) Developers invite educationalists to test a prototype of a computer-aided learning system as part of a user centered design workshop
(h) A program is devised that generates a predicted 24-h blood glucose pro fi le using seven clinical parameters. Another program uses this profi le and other patient data to advise on insulin dosages. Diabetologists are asked to prescribe insulin for a series of "paper patients" given the 24-h profi le alone, and then again after seeing the computer-generated advice. They are also asked their opinion of the advice.
(i) A program to generate alerts to pre vent drug interactions is installed in a geriatric clinic that already has a computer-based medical record system. Rates of clinically signifi-cant drug interactions are compared before and after installation of the alerting program.
 Note that some scenarios may include more than one type of study.
Note that some scenarios may include more than one type of study.(a) An order communication system is implemented in a small hospital. Changes in laboratory workload are assessed.
(b) The developers of the order com munication system recruit fi ve potential users to help them assess how readily each of the main func tions can be accessed from the opening screen and how long it takes users to complete them.
(c) A study team performs a thorough analysis of the information required by psychiatrists to whom patients are referred by a community social worker.
(d) A biomedical informatics expert is asked for her opinion about a PhD project on a new bioinformatics algorithm. She requests copies of the student's code and documenta tion for review.
(e) A new intensive care unit system is implemented alongside manual paper charting for a month. At the end of this time, the quality of the computer-derived data and data recorded on the paper charts is com pared. A panel of intensive care experts is asked to identify, inde pendently, episodes of hypotension from each data set.
(f) A biomedical informatics professor is invited to join the steering group for a series of apps to support people living with diabetes. The only documentation available to critique at the first meeting is a statement of the project goal, description of the planned development method, and the advertisements and job descrip tions for team members.
(g) Developers invite educationalists to test a prototype of a computer-aided learning system as part of a user centered design workshop
(h) A program is devised that generates a predicted 24-h blood glucose pro fi le using seven clinical parameters. Another program uses this profi le and other patient data to advise on insulin dosages. Diabetologists are asked to prescribe insulin for a series of "paper patients" given the 24-h profi le alone, and then again after seeing the computer-generated advice. They are also asked their opinion of the advice.
(i) A program to generate alerts to pre vent drug interactions is installed in a geriatric clinic that already has a computer-based medical record system. Rates of clinically signifi-cant drug interactions are compared before and after installation of the alerting program.
Explanation
Every evaluation scenario demands a spec...
Biomedical Informatics 4th Edition by Edward Shortliffe, James Cimino
Why don’t you like this exercise?
Other Minimum 8 character and maximum 255 character
Character 255



